Increased platelet count in a child. Platelets in a child. Causes of elevated platelets
The lifespan of these cells is only 10 days. Renewal occurs continuously, and new ones are formed instead of destroyed ones.
Platelet rate
The child’s immune system, especially in the first year of life, is not fully formed. Therefore, it is important to monitor his health and conduct regular medical examinations. You should not refuse to conduct a general clinical blood test if your local pediatrician recommends taking it. Among other indicators, it will show the level of platelets, which will allow you to assess blood clotting and diagnose a number of diseases.
For analysis, you need to donate blood from your finger. Blood sampling from babies is done in the morning on an empty stomach.
Taking blood from a finger
For breastfed infants, it is recommended to get tested between feedings, but not earlier than two hours after eating. The fingers of newborns are too small for this procedure, so blood is taken from thumb on the foot or from the heel.
Attention! If a child asks to drink before the test, you can give him regular water without carbon. It is not allowed to drink teas, juices, compotes and other sweet drinks.
A number of factors can affect the veracity of the result of the general analysis, so before the procedure it is important to avoid:
- morning meal;
- physical stress;
- stressful situations;
- freezing;
- taking certain medications (antibiotics, corticosteroids).
Platelet histogram
During the day, the number of platelets in a child’s blood often changes. A deviation of up to 10% is considered normal. In general, the number of blood platelets is determined by the age of the child. In a healthy baby, the normal cell content (per 1 microliter of blood) is considered to be in the range:
- only births – thousand. units;
- 2 weeks – 1 year – thousand. units;
- 1-5 years – thousand units;
- 5-7 years – thousand units;
In girls during menstruation, the figure ranges from 75 to 220 thousand units. It is advisable to take general analysis blood once a year, and, if indicated, more often.
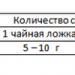
Important! To increase the accuracy of the result, it is better to take the test three times every 3-5 days.
In what cases is it necessary to get tested?
Rarely do childhood diseases go unnoticed by parents. It is enough to pay attention to the general condition of the baby or listen to his complaints. A signal for testing is the appearance of the following symptoms:
- frequent nosebleeds;
- bleeding gums;
- swelling of the legs, arms;
- pain in the limbs;
- itching, tingling in the fingertips;
- causeless appearance of bruises;
- fast fatiguability;
- visual impairment.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia often develops, which is characterized by changes in blood pressure, high pulse, headache.
If the child is outwardly healthy, then deviations from the normal level of platelet levels in the blood of children are not easy to identify. This will require clinical studies. It is important to regularly monitor the cell count if the child is sick:
High platelet count
In medicine, elevated platelets in a child’s blood are called thrombocytosis (or thrombocythemia). This pathology is diagnosed when the number of blood cells deviates from the established norm by more than 20 thousand units. As this indicator increases, blood clotting increases and there is a risk of blockage. blood vessels, as well as the formation of blood clots. Such pathologies have negative consequences for the baby, including death.
Adults are more susceptible to the disease, but there are many known cases of thrombocytosis in the younger generation.
The danger is that the disease does not manifest itself in any way. As a rule, the baby becomes lethargic, weak, and may complain of a headache, but such signs are characteristic of many diseases.
Thrombocytosis occurs for many reasons:
- Clonal - occurs due to a defect in stem cells that begin to uncontrollably synthesize blood platelets. Most often this occurs due to the appearance of a tumor.
- Primary (essential) - manifests itself against the background of disruption and growth in the number of stem cells. The emergence of additional sources of production leads to an increase in platelets. This pathology can be inherited or acquired as a result of blood pathologies (myeloid leukemia, erythremia).
- Secondary – is not associated with a violation of the process of blood formation, and is the body’s response to:
- infectious disease (toxoplasmosis, meningitis, pneumonia, hepatitis);
- trauma (fracture, wound);
- surgery (in particular, removal of the spleen);
- chemotherapy;
- acute blood loss;
- inflammatory processes in the children's body;
- lack of iron;
- oncology;
- fungus;
- virus;
- severe stress.
Dangerous! Analysis during primary and clonal thrombocytosis often reveals lamina sticking together (aggregation), which increases the risk of blood clots.
How to treat pathology
If the platelets in a child's blood are elevated, this leads to a thickening of his blood. It should be understood that thrombocytosis is not a separate disease. Therefore, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the root cause of the increase in blood platelets. Thinning the blood will not solve the problem as a whole.
The choice of therapy depends on how much the indicator is overestimated. When the norm is exceeded slightly, the baby’s nutrition should be adjusted.
- lemons;
- fish fat;
- berries with high acidity (viburnum, lingonberries, cranberries);
- olive oil;
- sugar beets;
- pomegranate;
- linseed oil;
- ginger;
- garlic.
The diet includes iodine-containing seafood, red meats rich in iron and calcium, milk and its processed products. Freshly prepared, natural juices (lemon, tomato, orange) help. Do not eat blood thickening products:
Remove unhealthy, smoked, fried, fatty, spicy, salty foods.
Products for thrombocytosis
It is better for food to dominate the diet plant origin, containing B vitamins. The child should drink plenty of fluids. It should be still water, green tea, vegetable broth, compote. Be careful with herbal decoctions, because many of them are medicinal and can aggravate the disease.
In more severe cases without drug treatment not enough. If the culprit of thrombocytosis is an infectious, viral or other disease, then it must be eliminated first. At the same time, drugs are prescribed to prevent thrombosis and improve microcirculation.
After eliminating the pathology that caused the increase in blood platelets in the child, their level gradually normalizes. Timely diagnosis will simplify treatment and avoid serious consequences.
How to get rid of varicose veins
The World Health Organization has officially declared varicose veins one of the most dangerous mass diseases of our time. According to statistics for the last 20 years, 57% of patients with varicose veins die in the first 7 years after the disease, of which 29% die in the first 3.5 years. The causes of death vary - from thrombophlebitis to trophic ulcers and the cancerous tumors caused by them.
The head of the Phlebology Research Institute and academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences spoke in an interview about how to save your life if you have been diagnosed with varicose veins. Watch the full interview here.
Increased platelets in a child’s blood: what does this mean?
Platelets are the smallest blood cells that look like platelets and are responsible for the process of blood clotting. In fact, it is platelets that ensure the liquid state of the blood and participate in the formation of clots (thrombi).
Platelets are produced by special cells of the red bone marrow and are short-lived - their “life” is only 10 days, and then the platelets are destroyed in the spleen and liver. Instead of already destroyed blood platelets, new ones are formed, and this process is continuous. In some cases, platelet counts in the blood can be elevated in childhood, and parents should know not only why this happens, but also how to solve the problem.
Normal platelet counts in children
The number of platelets can be determined by performing a general clinical blood test - they are recalculated per 1 cubic milliliter. This indicator is considered one of the most important, since it characterizes the child’s body’s ability to cope with bleeding and assess the level of blood clotting. The normal number of platelets in the blood of children depends on their age:
- in newborns, the norm is considered to be the number of platelets in the thousands per 1 cubic milliliter of blood;
- for children aged 10 days to 12 months – thousands;
- over the age of 12 months – thousands.
Note: in teenage girls, the first days of menstrual bleeding may be characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets, so the norm will be in the thousands.
A high number of platelets in the peripheral blood is classified as thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia, but a decrease in their number is thrombocytopenia. An increase in the norm may indicate the possibility of increased thrombus formation, but a reduced platelet count may indicate bleeding.
To determine the number of platelets, blood is taken from a finger or vein; in newborns, blood is taken from a toe or heel. The study requires some specific preparation - the patient must donate blood on an empty stomach, but the child can be given something to drink. If we're talking about about taking blood from a baby, the manipulation is carried out 2 hours after feeding.
Doctors warn that emotional or physical exercise, because even ordinary hypothermia will show distorted analysis results. In addition, the results of the study may be affected by the use of certain medications - antibacterials, corticosteroids. If the doctor has doubts about the accuracy of the results obtained, then you can donate blood for platelet count 3-5 times. The results of the study will be ready on the day of blood donation.
Platelet counting in a blood test is done quite often in childhood. This can be caused by frequent nosebleeds, or parents have noticed that the baby often has hematomas on the body and bleeding gums. The reason for taking blood tests to determine the platelet count may be a child’s dizziness, coupled with fatigue and periodic numbness in the upper/lower extremities.
An absolute indication for conducting this type of study is the presence of certain diseases in the anamnesis:
Causes of thrombocytosis in children
- erythremia – increased formation of blood platelets by red bone marrow;
- too slow “utilization” of platelets – this usually occurs when the spleen is removed;
- impaired distribution of platelets in the bloodstream - most often observed against the background of mental or physical fatigue.
If a high platelet level is detected in blood tests, the doctor will need to determine the real reason development of such a pathological condition, for which additional examinations of the patient will be prescribed. In children, thrombocytosis can develop at any age, but parents should be aware that such a diagnosis is made by doctors even with a minimal increase in the number of platelets in the blood.
Thrombocytosis in medicine is divided into three main types:
- Clonal thrombocythemia. In this case, there is a defect in stem cells in the bone marrow, which may also be due to their damage by the tumor process. Stem cells do not respond to ongoing endocrine processes, and therefore the formation of the blood component in question becomes uncontrollable.
- Primary thrombocythemia. This condition is always associated with the proliferation of several areas of red bone marrow, and the result is an incredible amount of newly formed platelets. Some hereditary/congenital diseases, as well as erythremia or myeloid leukemia, can lead to such a pathology. Primary thrombocythemia is characterized not only by an increase in the number of platelets, but these blood components are enormous in size and have an altered shape.
- Secondary thrombocytosis. The mechanism of its development is quite variable:
- against the background of removal of the spleen, when old platelets have not yet been destroyed, and new ones are already actively being formed;
- during the inflammatory process, the body intensively produces a hormone that promotes the maturation of blood platelets;
- in case of malignant neoplasms, they produce biologically active substances that have a stimulating effect on bone marrow megakaryocytes, which increases the number of newly formed platelets.
Secondary thrombocythemia can develop in the presence of a number of pathologies in a person:
- any malignant neoplasms;
- tuberculosis;
- amyloidosis;
- anemia of iron deficiency or hemolytic type;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- rheumatism occurring in the active stage;
- fractures of tubular bones;
- ulcerative colitis;
- acute blood loss;
- osteomyelitis;
- splenectomy;
- acute and/or chronic infectious diseases;
- any major surgical interventions.
With secondary thrombocytosis, a less pronounced increase in the number of platelets in the blood will be characteristic, while their morphology and functions are absolutely not impaired.
If the pathology in question was diagnosed for the first time, the doctor will definitely refer the patient to undergo the following tests:
- definition C-reactive protein;
- determination of serum ferritin and iron;
- ultrasound examination of organs abdominal cavity and small pelvis;
- bone marrow examination.
Symptoms of thrombocytosis in children
Primary thrombocytosis will be characterized by the following symptoms:
- enlarged spleen;
- formation of blood clots of different localization;
- possible bleeding in the digestive organs;
- pain in the fingertips;
- unbearable itching of the skin;
- disorders of the central nervous system appear;
- The process of urination is disrupted, and pain may occur in the area of the anatomical location of the kidneys.
Specifically in childhood, the pathological condition in question may be accompanied by frequent nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and the appearance of bruises on the body even with a light touch. In addition, the child has cold extremities, periodic headaches, variability in blood pressure, and increased heart rate.
General principles of treatment
When diagnosing primary type thrombocytosis, doctors use the cytostatics Myelobromol and Myelosan. The treatment will be long-term until the result is obtained, namely the normalization of the number of platelets in the blood.
If the pathology in question is severe, then in addition to medication, plateletpheresis is used as treatment, when platelets are removed from the bloodstream using special equipment.
An integral part of therapy for thrombocytosis is the prescription of medications that improve microcirculation and prevent the adhesion of blood platelets - for example, Aspirin, Trental. But it is worth knowing that Aspirin is used only if, against the background of the pathology in question, there are no erosive changes in the digestive tract.
When clonal thrombocytosis is diagnosed, patients are prescribed Ticlopidine or Clobidogrel in an individual dosage - these are antiplatelet drugs.
Often, against the background of the pathology under consideration, thrombosis and ischemic manifestations occur - with this development of events, anticoagulants Heparin, Livarudin, Argotoban are used. Such treatment should be carried out under strict laboratory monitoring of platelet counts.
Secondary thrombocytosis is a reason for carrying out not only general therapy, but also preventive measures to prevent the development of thrombosis. In any case, there is no need to worry, because doctors, even with secondary thrombocytosis, give quite favorable prognoses.
Nutrition of a child with thrombocytosis
Drug treatment of the pathology in question is important, but doctors say that in order to obtain the expected result, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s diet. Naturally, babies the best option will become breast-feeding, but for older children it is extremely important to include the following products in the menu:
Ginger, olive oil, beets, tomato juice, fish oil, cranberries, lemons, viburnum and sea buckthorn have an excellent blood thinning effect. It is important that the child consumes the required amount of liquid per day - at least 30 ml per kilogram of weight; it is imperative to give the child tea, compotes and vegetable decoctions.
During the treatment of thrombocytosis, it is strictly forbidden to consume walnuts, rose hips, bananas and mangoes - these products actively thicken the blood, which can lead to the development of complications.
An increased number of platelets in a child’s blood is a pathology that needs to be investigated. Carry out competent examinations, identify the true cause of the pathology and prescribe effective treatment Only a doctor can - independent decisions lead to a deterioration in the child’s condition.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
3 month old baby blood test platelets 600
Help me. please decipher UAC
The child is 1 year and 3 months old, male, 11.6 kg. -weight.
Why might platelets be elevated?
The test was taken yesterday, two days before the child was stung by a bee, could this have affected it?
Thanks in advance for your answer
What was the purpose of the blood test?
According to various sources, in children under 5 years of age, the upper limit of normal for platelets is 550x10*3\L, i.e. in your case, the platelet count is not increased.
The fact is that the baby, having slept all night, woke up crying and could not calm down. We thought that the teeth were given 4 ml. Nurofen, but it seemed to me that there was a hard tummy, they called the doctor back, she advised me to take a blood test and come for a consultation. She didn’t make an exact diagnosis - she said either teeth or mild poisoning. The child had no vomiting or distress. The baby did not come off my hands, and only in the evening I noticed that it was painful for him to turn his head in left side, we turned to a neurologist and he said that there was indeed myositis. (by the evening of the same day the baby was already a completely different person - he was running and crawling as usual) Now we apply Traumeel on the neck, it is easier to turn the head.
But the first doctor was alarmed by the high platelets in the blood and he said to take the baby off water, although I didn’t notice any signs of dehydration - he pees normally.
Tell me please. Are other indicators normal?
Apparently, the analysis was done manually (not on an analyzer); I am confused by the number of red blood cells, slightly below normal, but a laboratory error cannot be ruled out.
Thank you very much for your prompt response, but what should we do next - retake it, if so, after how long and in the same laboratory, or maybe in a private one (on an analyzer)? The analysis was actually done manually in the children's clinic.
I don’t recommend retaking it, because... there is no reason to repeat a manipulation that is quite painful for the child. Let's be sorry. You write yourself that there are no complaints.
Love, feed, walk, play, etc.
You don't have to apply Traumeel.
Doctor, maybe I seem very persistent, could you provide links to the UAC standards. Thank you very much.
Thrombocythemia
Essential thrombocythemia is a chronic megakaryocytic leukemia related to myeloproliferative diseases. The process involves stem cells in the bone marrow. The disease is by its nature hemoblastosis, that is, tumor. The number of megakaryocytes and then platelets increases uncontrollably. Essential thrombocythemia is quite rare. The prevalence is 3-4 cases per 100 thousand adults. Older people are more susceptible to this disease. Women get sick somewhat more often than men. As with any cancer, the exact causes of essential thrombocythemia are unknown. There is a connection with radiation damage to the environment. The role of other factors cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms of thrombocythemia
The disease is characterized by a long course without visible manifestations. The progression of the disease is slow. Often, months and even years pass from the first recorded changes in blood tests to the appearance of the first complaints. Symptoms of thrombocythemia consist of a simultaneous tendency to form blood clots and bleed. The mechanism of occurrence of these phenomena includes disturbances in platelet aggregation (both upward and downward). Cerebral, coronary and peripheral arterial thrombosis are characteristic. With essential thrombocythemia, pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis of the legs are possible. The most common types of bleeding are gastrointestinal, pulmonary, renal, and skin hemorrhages. In addition, thrombocythemia may cause enlargement of the spleen and liver. These symptoms occur in 50 and 20 percent of patients, respectively. There is numbness and decreased sensitivity in the fingers and toes, earlobes, and tip of the nose, associated with impaired blood circulation in small vessels. Some patients may experience pain in the hypochondrium and along the intestines. Many patients lose weight. Sometimes enlarged groups of lymph nodes appear. There are many nonspecific symptoms of thrombocythemia: general weakness, headache, decreased ability to work, fatigue, itchy skin, frequent mood swings, increased body temperature.
Diagnosis of thrombocythemia
Diagnosis of the disease begins with recording a large number of platelets in a general blood test. The diagnosis is made when thrombocytosis exceeds 600 thousand per microliter after excluding reactive thrombosis. Platelets have varying degrees functional inferiority. Prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, bleeding time, life time of blood platelets were within normal limits. In the bone marrow, puncture results reveal increased cellularity and megakaryocytosis. Platelet precursor cells are gigantic in size and dysplastic. Not strictly specific genetic abnormalities in essential thrombocythemia are JAK2V617F and MPLW515L/K mutations.
Differential diagnosis of thrombocythemia and secondary thrombosis
It is difficult to distinguish essential thrombocythemia from secondary thrombosis caused by amyloidosis, infection, cancer, or other factors. The American College of Hematology has developed the following criteria for differential diagnosis:
The platelet count is more than µl in two consecutive blood tests performed at an interval of 1 month;
No known cause of reactive thrombocytosis;
Normal red blood cell count;
No significant fibrosis in the bone marrow;
Absence of the Philadelphia chromosome;
Bone marrow hypercellularity with megakaryocyte hyperplasia;
The presence of pathological cells in the form of colonies in the bone marrow;
Normal levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6;
Absence of iron deficiency anemia;
In women, there is polymorphism of X chromosome genes.
The more matches found, the more evidence supports essential thrombocythemia.
Treatment of thrombocythemia
If a patient is diagnosed with essential thrombocythemia, then individual treatment should be selected for him in accordance with the existing regimen. Therapy is especially intensive for those who are at risk of thrombosis. Such patients include elderly patients, patients diabetes mellitus, hypertension, having dyslipidemia. Such patients are most often indicated for treatment of thrombocythemia with cytostatics. These are chemotherapy drugs that reduce the activity of cell division. Hydroxyurea (0.5-4 g orally daily) has been used for the treatment of thrombocythemia for a long time and with success. Because of its potential to cause leukemia (eg, acute myeloblastic leukemia), this drug is not prescribed to children.
Thrombocythemia can be treated with interferon-alpha. It is used especially widely in pregnant women, as it does not have a damaging effect on the fetus. In general, the limitation of prescribing interferon-alpha is its high cost and poor tolerability. The initial dose of the drug is 1 million IU three times a week, then the dose is increased to 3-6 million IU three times a week. About 20% of patients are forced to stop treatment because they are very worried about increased body temperature, pain in joints and muscles, nausea, loss of appetite, and flu-like symptoms.
Anagrelide is also used to treat thrombocythemia. This drug selectively inhibits the maturation of megakaryocytes, with little effect on other hematopoietic germs. The initial dose of the drug is 2 mg per day, the maximum is 10 mg. The medicine has side effects associated with cardiovascular system. Characterized by vasodilatation, increased heart rate, and swelling. If the patient already has any heart pathology, then it is not advisable to prescribe anagrelide. Under the influence of the drug, thrombocythemia may transform into myelofibrosis. Because of all these phenomena, anagrelide is used mainly for intolerance to hydroxyurea and interferon-alpha.
It is possible to successfully use thrombopheresis in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (325 mg orally per day) for the prevention of thrombosis in thrombocythemia.
Treatment of essential thrombocythemia with folk remedies
Folk remedies are sometimes used by patients to treat this disease. No research on traditional methods There are no methods that have proven their effectiveness. Any such methods are used by the patient at his own risk. Most likely, positive changes are associated with the placebo effect, that is, self-hypnosis. It is fundamentally important for the patient to inform the attending physician about what else is used independently to combat the disease. Treatment of essential thrombocythemia folk remedies includes the use of fasting and various herbal remedies. The most often recommended are infusions of blueberry fruits, mordovnik seeds and a decoction of string.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
How are platelets indicated in a blood test?
Determination of the number and structural parameters of platelets is included in the mandatory minimum of a general blood test. This simple test allows you to evaluate all key blood parameters, including its clotting ability.
Platelets are small plates that are responsible for the first stages of blood clotting. When the vascular wall is damaged, they stick together into a single conglomerate, on the basis of which, after some time, a dense thrombus is formed. It reliably closes the defect in the vessel wall and thereby protects against bleeding.
Determining platelet levels may be necessary in cases where the patient notices the appearance of bruises on the body for no reason, frequent nosebleeds, increased bleeding of the gums, as well as unusual or unusually long periods.
A blood test makes it possible to determine not only the number of platelets, but also their the most important properties, the slightest change of which can lead to pathology.
How are platelets indicated in a general blood test?
Where can I find platelets in a blood test?
The designation of platelets in a blood test varies depending on how the test was performed (manually or on an automated analyzer) and what form the results were printed on.
On the old forms that were in circulation back in the USSR, all blood parameters are written in Russian. The number of platelets can be found in the column, which is called “Platelets”. In this case, everything is quite simple.
Difficulties arise when the study was carried out on an automatic analyzer, and the results are indicated in the form of a table of numbers and Latin letters. Here, the platelet count is indicated opposite the abbreviation PLT (in English, platelets are called “platelets”).
Platelet count
In a healthy person, the absolute number of platelets in peripheral blood is thousands per 1 microliter.
During menstruation and pregnancy, the lower limit can drop to 70 thousand/µl, which is completely normal.
In children, the absolute level of platelets in the blood varies depending on the age and sex of the child:
Decreased platelet count
A decrease in platelet levels below normal levels is called thrombocytopenia. This can be observed in many diseases and pathological conditions:
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof's disease).
- Congenital thrombocytopenia.
- Pregnancy.
- Massive bleeding.
- Oncological diseases, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- Hemoblastoses, or malignant neoplasms of the hematopoietic system.
- Taking certain medications.
- Hypersplenism is a syndrome of increased spleen function.
Thrombocytopenia is manifested by increased bleeding of the mucous membranes, the formation of spontaneous bruises on the body, as well as a number of others unpleasant symptoms. For a more accurate assessment of the pathology, it is necessary to do a coagulogram - an analysis for the content of the most important blood clotting factors.
Increased platelet count
An increase in platelet levels above normal levels is called thrombocytosis. This condition is much less common than thrombocytopenia and may be due to the following reasons:
- Idiopathic myelofibrosis.
- Polycythemia vera (Vaquez-Osler disease).
- Serious inflammatory diseases.
- Condition after massive blood loss.
- Essential thrombocythemia.
Severe thrombocytosis is clinically manifested by systemic thrombosis and embolism, which can pose an immediate threat to life (acute cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, mesenteric thrombosis). A slight increase in platelet count is usually asymptomatic.
Other platelet indicators
IN modern analyzes blood, in addition to determining the number of platelets, other parameters that are of particular clinical importance are also assessed.
MPV is a measure of mean platelet volume. Normally, it is 7.5-10.5 fl (femtoliters), and these values increase with age. The “younger” the platelet, the greater its volume.
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
- Splenectomy (removal of the spleen).
A change in MPV has any important diagnostic value only with a concomitant change in the platelet content in the blood.
PDW is a parameter of the width of platelet distribution over their volume. This is an additional indicator that shows how much the platelets in a blood sample vary in size. Normal PDW is 10-20%.
PDW is closely related to MPV, and these indicators usually change together. In particular, a significant change in PDW, up or down, is observed in hemoblastoses - malignant neoplasms of the hematopoietic system.
An increase in PDW may indicate the presence of microthrombi in the blood.
PCT is thrombocrit. or the specific gravity of platelets in a blood sample. Calculated as the total platelet count divided by the volume of the entire blood sample. Normally, this figure is 0.15-0.40%.
An increase in thrombocrit is observed in infectious and inflammatory diseases, after massive blood loss, as well as in other conditions accompanied by thrombocytosis, or an increase in the absolute number of platelets.
In clinical practice, assessment of secondary platelet parameters is carried out only when there is a significant change in the number of platelets in the blood. as well as in difficult clinical cases accompanied by bleeding of unknown origin.
Increased level of platelets in the blood of a child
Blood test indicators are important for assessing the health of children, so their changes always alarm adults - both mothers and doctors. If parents see an increased level of platelets in their child’s blood in the results, they are always interested in whether this is dangerous for their daughter or son. To get timely help for your baby, you need to find out why platelets may be higher than normal and what to do if the level is elevated.
What platelet count is considered elevated?
Platelets are small blood cells without nuclei, the second name of which is “blood plates”. They are important for blood clotting, in particular for the formation of blood clots to close a damaged vessel and stop bleeding. Such cells are formed in the red bone marrow, live up to ten days, after which they are destroyed in the spleen.
The upper limit of the norm for a newborn is considered to be 490 x 10 9 / l of platelets, but by the fifth day of life their number begins to decrease, amounting to no more than 400 x 10 9 / l at the age of 5 days to a month, and in a one-year-old child and older - a maximum 390 x 10 9 /l.
A slight excess is not considered dangerous by doctors, but if the number of platelets exceeds the norm by 10 9 / l or more, this condition is called thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia.
Causes of thrombocytosis
Depending on the provoking factor, thrombocytosis is divided into:
- Primary. Its appearance is due to a disruption in the formation of blood platelets in the bone marrow, for example, due to a tumor process.
- Secondary. This increase in platelets develops due to a disease that does not affect the bone marrow. However, it is only one of the symptoms of the disease.
Causes of secondary thrombocytosis include:
- Surgery to remove the spleen. The increase in blood platelets after such an intervention is associated with a slowdown in their decay. In addition, the spleen normally produces compounds that inhibit platelet synthesis, and after removal they no longer inhibit their production.
- Acute inflammation, for example due to bacterial or viral infections, rheumatism, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis and other pathologies. As a result of the inflammatory process, the production of the hormone thrombopoietin begins, which stimulates platelet maturation.
- Cancerous tumors, such as lymphogranulomatosis or lung sarcoma. Due to the growth of a malignant neoplasm, the bone marrow is activated, as a result of which blood platelets are produced in increased quantities.
- Blood loss caused by injuries, liver cirrhosis, anemia (both iron deficiency and hemolytic), gastrointestinal ulcers and other factors. In such situations, thrombocythemia acts as a compensatory response.
A slight increase in platelet count can be observed during mental or physical stress. Sometimes platelets increase as a result of side effects of certain medications.
Symptoms of increased platelets
If a child develops thrombocytosis, this may include:
- Swelling and a feeling of heaviness in the limbs.
- Soreness in the fingertips.
- Skin itching.
- Weakness.
- Blueness of the skin of the extremities and lips.
- Cool to the touch hands and feet.
- Dizziness.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
Why is thrombocytosis dangerous in children?
Due to too many platelets, the blood clotting process accelerates. Platelets begin to stick together and clog blood vessels, resulting in the formation of blood clots. Their appearance disrupts the functions of internal organs, which is especially dangerous if the vessels of the heart or brain are blocked.
Diagnostics
Changes in platelet count are determined during a clinical blood test. If thrombocytosis is detected, the child should be carefully examined, since the cause of the disease is a fundamental factor in prescribing treatment. If the indicator is significantly elevated, the child should:
- Determine the amount of iron in the blood, as well as the level of ferritin, to rule out anemia.
- Determine seromucoids and C-reactive protein in the blood to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Do a blood clotting test.
- Conduct an ultrasound examination of internal organs.
- Do a urine test.
If indicated, the child is referred to a hematologist, and after his consultation, a bone marrow test may be prescribed.
Treatment
In the treatment of primary thrombocytosis, cytostatic agents, drugs to improve blood circulation, and drugs that prevent blood platelets from sticking together are used. In some cases, anticoagulants and other drugs are prescribed.
In case of severe thrombocythemia, the child is referred for a thrombocytopheresis procedure, when blood platelets are removed from the blood with a special device. If thrombocytosis is secondary, attention is paid to treating the underlying disease, and also protecting the child from increased thrombosis.
What to do if there is a slight increase
If platelets are only slightly elevated, no medications are prescribed. In such situations, the doctor will advise you to pay attention balanced diet child. The children's diet should include:
- Products that contain a lot of iodine. These include fish and seafood.
- Calcium-rich foods. First of all, these are dairy products.
- Products from which the child will receive iron. This could be meat, liver, cereals, fruits, etc.
- Products that help thin the blood. Lemon, ginger, cranberries, viburnum, lingonberries, garlic, beets, tomato juice, fish oil and some other products have this effect.
It is advisable to avoid foods that increase clotting, such as bananas, lentils, walnuts, rosehip, pomegranate. In addition, the child should be given a sufficient amount of fluid, and any folk remedies in children with thrombocytosis can be used only after consultation with the doctor.
You can learn more about platelets, their role and normal levels in the blood by watching the following video.
Increased platelets in a child’s blood – why and what to do?
Platelets are the smallest blood cells that do not contain nuclei in the form of blood platelets, which are responsible for the process of blood clotting, i.e., for stopping bleeding that occurs. These plates essentially provide the liquid state of the blood and participate in the formation of clots called thrombi.
Platelets are produced by special cells in the red bone marrow (megakaryocytes). Platelets are short-lived cells: they live only up to 10 days, and then are destroyed in the spleen and liver. Instead of the “old” destroyed blood platelets (also called platelets), new ones are formed. This process is continuous. Why platelet counts in a child’s blood may be elevated and what to do in this case, we will discuss in this article.
Normal platelet counts in children
The number of platelets is determined in a general clinical blood test in terms of 1 cubic millimeter. The number of blood platelets is an important indicator of health, since it characterizes the child’s body’s ability to cope with bleeding and assess blood clotting.
Depending on the age of the child, the number of platelets varies:
- for a newborn, their normal content is from 100 thousand to 420 thousand;
- at the age of 10 days to a year, the norm is already 150–350 thousand;
- in children after a year, platelets are normally 180–320 thousand;
- in adolescence, in girls in the first days of menstrual bleeding, the number of platelets is 75–220 thousand.
An increased number of platelets in the peripheral blood is called thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia, and a decrease in their number is called thrombocytopenia. In the first case, a deviation from the norm may indicate the possibility of increased thrombus formation, and in the second, it may indicate bleeding. In both cases, the relationship between the formation of new platelets and their destruction is disrupted.
The platelet count is determined by testing blood from a finger or a vein. In newborns, blood is usually taken from a toe or heel. This study does not require special preparation. Blood should be donated on an empty stomach (you can give the child something to drink). In young children, the sample is taken before the next feeding or 2 hours after the previous feeding.
Before taking the test, physical and emotional stress is undesirable for the child. Even hypothermia can show distorted analysis results. The use of certain medications (corticosteroids, antibiotics) can also change the number of blood platelets. To ensure the authenticity of the detected increase in platelet count, it is recommended to take a blood test three times with intervals of 3-5 days.
The result of the blood test is ready on the same day (in some cases, the analysis is performed urgently in a shorter period of time). Platelet counting in a blood test is done quite often for children, especially for those who often have nosebleeds, often have hematomas (bruises) on the body, and bleeding gums. Parents may be alerted to the child’s complaints of weakness and dizziness, and frequent numbness in the limbs.
Indications for platelet counting are the following diseases:
Causes of thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis can be caused by:
- increased production of blood platelets by megakaryocytes of the red bone marrow (with erythremia);
- slow platelet utilization (when the spleen is removed);
- disturbance of the distribution of platelets in the bloodstream (due to physical or mental stress).
When an elevated platelet count is detected, it is very important to determine the cause of this condition. Only a pediatrician or hematologist (a specialist in blood diseases) can identify this cause.
Thrombocytosis as a disease can develop in children at any age. But such a diagnosis is made with a significant increase in the number of platelets - more than 800 thousand/l. More often, a mild increase in the number of blood platelets occurs due to a number of reasons or in a number of diseases.
With clonal thrombocythemia, there is a defect in the stem cells themselves in the bone marrow (they are damaged by the tumor process). They do not respond to stimulation of the process by the endocrine system, and the process of platelet formation becomes uncontrollable.
A similar mechanism is observed in primary thrombocythemia. It is associated with the proliferation of several areas of the red bone marrow and, as a consequence, with an increase in the number of newly formed blood platelets. The causes of this condition can be hereditary (congenital) diseases or acquired (myeloid leukemia, erythremia).
In primary thrombocytosis, the number of blood platelets can vary: from a slight increase to several million in 1 μl, but high levels are more typical. In addition, their morphology also changes: platelets of enormous size and altered shape are found in the blood smear.
The mechanism of development of secondary thrombocytosis can be different:
- when the spleen is removed, old or obsolete platelets do not have time to destroy, and new ones continue to form; in addition, the spleen produces antiplatelet antibodies and a humoral factor that inhibits platelet production;
- During the inflammatory process, the body intensively produces a hormone (thrombopoietin), which promotes the maturation of blood platelets, which help cope with inflammation; biologically active substances (for example, interleukin-6) are anti-inflammatory cytokines that stimulate platelet synthesis;
- in malignant diseases, the tumor produces biologically active substances that have a stimulating effect on bone marrow megakaryocytes and the production of blood platelets; this is more often observed in lung sarcoma, kidney hypernephroma, lymphogranulomatosis;
- thrombocytosis also develops as a response of the body to repeated blood loss (with ulcerative lesions of the intestine, with cirrhosis of the liver),
Secondary thrombocytosis is characterized by a less pronounced increase in the number of platelets: in very rare cases, their number exceeds a million in 1 μl. The morphology and function of blood platelets are not impaired.
In any case, detected thrombocytosis requires a full examination and clarification of the cause of its occurrence.
In addition to diseases, it can also be caused by side effects of medications (Vincristine, epinephrine, adrenaline, corticosteroids, etc.). There are no specific symptoms of thrombocytosis.
When an increased platelet count is initially detected, the following studies must be performed:
- determination of serum iron and serum ferritin;
- determination of C-reactive protein and seromucoids;
- blood coagulation analysis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- if necessary, consult a hematologist;
- bone marrow examination (only as prescribed by a hematologist).
Symptoms of thrombocytosis
With primary thrombocytosis, the size of the spleen is enlarged, blood clots of different locations can form, but bleeding in the digestive organs can also occur. Blood clots can also form in large vessels (veins and arteries). These changes contribute to the development of prolonged hypoxia or ischemia, which is manifested by severe itching and pain in the fingertips, and gangrene of the fingers may even develop. Hypoxia of tissues and organs leads to disruption of their function: disorders of the central nervous system and kidneys may be observed.
Clinical manifestations are caused by the underlying disease, the symptom of which is thrombocytosis.
Children, as noted above, may experience frequent nose and gum bleeding, bruises on the body with the slightest injury or even for no apparent reason. Vegetative-vascular dystonia (fluctuations in blood pressure, headaches, cold extremities, increased heart rate), and iron deficiency anemia may develop.
Reactive thrombocytosis is clinically mild and may be asymptomatic.
Treatment
To treat primary thrombocytosis, the cytostatics Myelobromol, Myelosan and others are used for a long time until results are obtained.
In severe cases, in addition to cytostatics, thrombocytopheresis is used (removal of platelets from the bloodstream using special equipment).
Drugs that improve microcirculation and prevent the adhesion of blood platelets (Trental, aspirin, etc.) are also used. Aspirin can be used only if erosive changes in the digestive tract are excluded.
For clonal thrombocytosis, antiplatelet agents (Ticlopidine or Clobidogrel) are used in individual dosages.
In case of thrombosis or ischemic manifestations, anticoagulants (Heparin, Argotoban, Livarudin, Bivalirudin) are used under daily laboratory monitoring of platelet counts.
For secondary thrombocytosis, treatment includes therapy of the underlying disease and prevention of thrombosis associated with an increased platelet count. As a rule, reactive thrombocytosis does not lead to thrombohemorrhagic complications and therefore does not require special therapy. The prognosis is usually favorable.
In addition to drug treatment for thrombocytosis, it is important to provide the child with a balanced, balanced diet, rich in vitamins (especially group B). Breastfeeding is the most beneficial for infants.
- rich in iodine (seafood, nuts);
- rich in calcium (dairy products);
- iron-rich (offal and red meat);
- freshly squeezed juices (pomegranate, lemon, lingonberry, orange), diluted with water 1:1.
The following have a thinning effect on the blood: berries (cranberries, sea buckthorn, viburnum), lemons, ginger, beets, fish oil, flaxseed and olive oil, tomato juice and a number of other products.
It is very important to drink enough fluid (at the rate of 30 ml/kg). In addition to water, you should drink green tea, compotes and vegetable decoctions.
Bananas, mangoes, rose hips, and walnuts contribute to blood thickening.
Without the consent of a hematologist, you should not use herbal medicine - after all, medicinal herbs are quite serious medicines and if chosen incorrectly, they can significantly aggravate the child’s condition.
Summary for parents
Careful monitoring of the child’s health and timely examination will help diagnose any disease in the early stages, including thrombocytosis. When the number of platelets in the baby’s blood increases, it is important to determine the cause of its appearance. An updated diagnosis will help the doctor decide on the need for treatment and prescribe the necessary medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a child has an increased level of platelets in the blood, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician, and after the initial examination, a hematologist. If thrombocytosis is secondary, it is necessary to treat the disease that caused this syndrome with the help of an appropriate specialized specialist - oncologist, infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, traumatologist, nephrologist. It will also be useful to consult a nutritionist to select proper nutrition with thrombocytosis.
An increased level of platelets in the blood in children can often indicate the development of a disease, so the doctor will always pay attention to their number in the analysis.
It is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis based only on blood cell counts. However, the pediatrician will already know which direction to move.
What are they responsible for?
Platelets – These are small colorless blood cells, which originate in bone marrow cells and are then sent into the blood, where their total amount is 65%. The remaining 35% remains in the spleen.
The cells do not have a nucleus, are disc-shaped, and their size is 2-4 microns.
The formation process takes from 8 to 10 days. Analysis of the number of these cells in children is included in the mandatory list of studies.
What are the functions of colorless blood cells?
- Responsible for blood clotting (hemostasis).
- Participate in the dissolution of blood clots and thrombi (fibrinolysis).
- Are suppliers nutrients(growth factors) for the cells of the vascular wall for the normal functioning of the immune system.
- They have the ability to release many useful substances into the blood - fibrinogen, serotonin, etc.
These colorless bodies can accumulate and stick together (adhere), forming a plug in places where the vessel wall is damaged. Due to this, blood loss is eliminated.
However, an increased platelet count can contribute to the formation of dangerous clots. This is why it is so important to have a general blood test regularly.
In our material you will learn about... Let's talk about the most effective drugs and methods of treating the disease.
Also find out what are the causes of bronchial asthma in children, what preventive measures are necessary - we suggest you read about it.
Normal for up to one year and older
A newly born baby already has a certain number of platelets in its blood, which constantly changes depending on age.

The norm for children per 1 liter of blood is:
- in newborns – 100-420×1000000000;
- in children whose birth has been 10 days – 150-400×1000000000;
- in one month old babies – 160-100×1000000000;
- for six-month-olds – 180-400×1000000000;
- for a one-year-old baby – 160-380×1000000000;
- in children aged 1-4 years – 160-400×1000000000;
- from 5 to 7 years – 180-450×1000000000.
Platelet levels may vary depending on the physiological state or the presence of any disease. But what to do if the test shows that your child has a lot of platelets in his blood?
Reasons for the increase
Elevated platelets may indicate the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream, due to which vascular blockage occurs.

Active formation of blood cells is directly related to the excessive concentration of megakaryocytes (huge bone marrow cells).
According to the results of recent studies, in patients with thrombocytosis, an increase in the concentration of these elements is constantly observed.
This manifests itself in polycythemia, a benign tumor process of the blood system. With this disease, particles of decayed megakaryocytes are found in the blood.
Elevated platelet levels can also occur with the formation of myelogenous leukemia (a malignant blood disease).
An increase in the number of platelets may precede thrombus formation in the peripheral circulatory system, which causes the development of the following diseases:
- vasoconstriction;
- swelling of the legs and arms;
- erythema;
- venous blockade of internal organs.
Why can blood platelet counts be elevated in children (including newborns)? Main reasons:

Vomiting, diarrhea and other intoxication manifestations can also affect changes in the quantitative indicator of colorless bodies.
When to see a doctor
As soon as the analysis reveals that the child’s platelet count is elevated, you should immediately consult a doctor.

A hematologist is dealing with the problem, but You can also show the child to your local pediatrician. The doctor will prescribe everything necessary tests and based on their results, establish a diagnosis.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- blood test for platelets every 4 days (3 times);
- general blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs;
- bone marrow biopsy;
- analysis to detect iron and ferritin levels;
- coagulogram (a set of blood indicators indicating the coagulation process);
- C-reactive protein test (for signs of an infectious disease).
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a consultation with a gynecologist and urologist. As soon as the results of these studies become known, the doctor will draw conclusions and prescribe effective treatment.
Do you know how to identify gastritis in a child? Find out about the first signs of the disease in the following material:.
How to reduce high content
Basics condition of therapy - diet. At high level platelets, regardless of the cause, you should eat enough foods that can thin the blood. Among them:
- olive oil;
- fish fat;
- berries;
- tomato juice (natural);
- onion;
- garlic;
- lemon;
- linseed oil.

The diet also includes foods fortified with magnesium. This:
- buckwheat;
- seaweed;
- barley grits;
- nuts (cashews, peanuts, pistachios, almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts);
- oatmeal;
- peas, beans;
- millet.
Increased attention is paid to the drinking regime. Still mineral water, green tea, fruit and vegetable juices are suitable.
If the level of platelets in a child’s blood is slightly increased, it is not recommended to eat bananas, lentils, pomegranates, and mangoes. You should also stop taking diuretics.
If the number of platelets in the analysis is exceeded Blood thinning medications are also effective, which are prescribed only by a doctor.
How to correctly decipher a blood test? Let's discuss this issue with the famous doctor Komarovsky in the following video:
Exceeding the norm of platelets often indicates that pathological changes are occurring in the body. Which ones - only a doctor can determine. With a timely diagnosis and compliance with the prescribed treatment, the cell level will return to normal.
In contact with
Parents may be faced with a test result that shows that the baby has elevated platelets. A person without any experience in this area may panic. However, at the first stage it is necessary to establish the causes of the process and become familiar with all treatment options for the pathology. The number of these blood cells is associated with the health status of the small patient. Elements are also necessary for the process of restoration of the walls of the vascular system. Thanks to them, blood can quickly clot. A normal life for children occurs only if there is a sufficient amount of them in the body. Platelets help the child grow and develop properly.
What is considered normal?
The platelet rate is determined by performing a general clinical analysis. Only a doctor can decipher it correctly. Additionally, it should be noted that the result is indicated per 1 cubic meter. mm.
An infant is characterized by a rapid growth process. Against this background, the blood vessels also enlarge. When analyzing the results obtained, the number of platelets in newborns should be taken into account depending on their age:
- The situation is considered normal when the number of these blood cells in an infant is in the range from 100 to 420 thousand.
- If the child is already 10 days old, then this indicator is fixed at a level from 150 to 350 thousand.
- The platelet count becomes constant when the child reaches two years of age. Their number is individual for each person, but should not exceed the limits of 180 to 320 thousand.
Parents should be aware that for infants the number of platelets in the blood should be less than 100-180 thousand. otherwise The baby may suffer from any sudden bleeding.
Additionally, it should be noted that during the analysis, the laboratory assistant also pays attention to the number of monocytes. These bodies develop in the presence of infection, inflammation or any other chronic disease.
Why might the platelet count be increased?
Elevated platelets in an infant are detected if the analysis shows their deviation from the norm by at least 20 units. Parents should not try to eliminate this negative manifestation on their own. Only a doctor can solve the problem. He will prescribe all the necessary diagnostic procedures. They are necessary to identify diseases in the baby’s body.
Pediatricians claim that platelets in the blood are elevated most often due to the negative impact of the following reasons:
- Hematological disease, which is congenital or acquired.
- The baby had previously been diagnosed with meningitis, pneumonia or hepatitis. The manifestation also accompanies cancer.
- The baby had a history of serious spinal injuries.
- The symptom develops during surgery.
- The baby was in a state of stress or excessive nervous tension.
The reasons directly influence the choice of further course of treatment. The platelet count should be determined for the first time when the child reaches three months of age. However, it is advisable to carry out the study much earlier if the child has pathological conditions.
You can find out your platelet count at any time. This factor directly affects the health and development of the infant. If you identify the ailment in time, you will be able to quickly and effectively get rid of serious consequences and the transition of the disease to chronic form.
The necessary indicators are determined based on a blood test
Thanks to timely diagnosis, colitis can be detected in a newborn in time. The disease causes a lot of trouble for the baby, so he is constantly capricious and crying.
Features of the manifestation of the pathological condition
High platelet counts disrupt the functioning of the child’s body.
In this case, parents may recognize the following symptoms:
- Periodic occurrence of bleeding from the nasal cavity.
- Parents will be able to see blood streaks in the child's stool.
- Systematic tingling or pain appears at the fingertips.
- Bruises appear on the skin. In this case, the obvious reasons for the process are completely absent.
- The baby's vision is deteriorating.
- The baby is constantly in a lethargic and apathetic state.
Increased platelets are very dangerous. If these negative manifestations occur, it is recommended to immediately seek advice from your doctor. The situation requires immediate diagnosis and treatment, otherwise the risk of serious complications increases.
Thrombocytosis in medical practice is divided into three types:
- In the clonal form, the child experiences damage to stem cells. The situation is also typical for oncology. The child has disorders in the body that lead to the spontaneous formation of red blood cells.
- The primary form of the disease is diagnosed when blood cells are formed spontaneously due to the rapid growth and development of red bone marrow. During the diagnostic process, doctors are able to identify a large number of these cells that have significant mutations in terms of shape and size. The disease is most often congenital.
- The secondary form of the disease occurs against the background of the presence of crumbs of various diseases in the body. During the analysis, only minor deviations from the normal value will be detected. Most often, the situation develops against the background of inflammation or active manifestations of oncology, tuberculosis or cirrhosis.
Thrombocytopenia can be correctly diagnosed only if diagnosed in a timely manner. A hematologist can determine the exact cause of the disease based on test results.
Features of treatment
High or low platelets are not considered normal. The doctor is required to promptly determine the cause of this negative condition. Otherwise, the therapy will not give results, and the child’s blood will continue to thin out.
The most difficult thing to normalize the situation is if the child has few platelets. The opposite clinical picture is much easier to regulate. At the first stage of treatment, it is important for the doctor to determine what type of thrombocytosis is: primary or secondary.
To eliminate the symptoms and manifestations of primary thrombocytosis, Myelosan, Myelobromol and others are used medications, which have a cytostatic effect on the body. Their composition normalizes the platelet count within a short time. Additionally, it is possible to restore general blood microcirculation.

Bananas make blood thicker
Medicines containing acetylsalicylic acid help get rid of secondary thrombocytosis. With its help, it is possible to thin the blood within a short time. Thanks to properly selected drugs, it is possible to bring the platelet count back to normal. It is advisable to use thrombocytapheresis only if this indicator in the child has already reached a critical level. The procedure involves the use of a special device that removes the necessary components from the blood.
Diet is important. If you are diagnosed with an increased number of platelets in the blood, you should not only take medications, but also start eating right.
Parents must strictly adhere to the following rules: simple rules:
- The baby should drink as much water as possible during the day. However, it cannot be replaced with carbonated drinks. The diet should contain natural fruit drinks and juices in sufficient quantities. Positive Impact A composition of sea buckthorn, cranberry and viburnum has a beneficial effect on the body. For improvement healing properties The drink contains lemon, fish oil and olive oil. Thanks to this combination, it is possible to obtain the maximum therapeutic effect.
- Your baby's diet should not include fatty or fried foods. Spicy and smoked foods also have a negative effect on the body.
- Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables has a positive and health-improving effect. It is best to buy red fruits. The total amount planned to be eaten during the day should be distributed evenly.
- If platelets deviate from the norm, you should eat as much celery and figs as possible.
- Regular consumption of plant foods in sufficient quantities helps to normalize a slight imbalance in food.
If the disease was detected in an infant, then the mother will need to eat a special diet. In this case, you need to exclude all red fruits from your diet. They are dangerous for a newborn, because they can lead to the development of allergies or diathesis. A negative picture in the baby’s body can also be due to mother’s milk. She must feed him only with her breast. Negative effects are recorded in the case of feeding on cow's milk.

A drug to normalize the number of platelets in the blood
Prevention of disease development
All doctors are confident that it is much easier to prevent a disease than to deal with its consequences later. General state The baby's health directly depends on sleep, rest, and nutrition. Parents should make sure to provide him with all the necessary resources.
You can prevent an increase in platelets in the blood by following the following recommendations from your pediatrician:
- Fruits and vegetables should be present in the baby's diet every day. Mommy is obliged to buy only those of which she is completely confident in the quality.
- Bananas, nuts and pomegranates significantly increase blood viscosity. That is why they should be completely excluded from the diet for a while.
- The child should receive enough fluid every day. It is allowed to give him only clean water.
- Parents should establish a rest routine for their child. He must sleep at least 8 hours. It is best if he also rests for several hours during the day.
- Walking on fresh air must be daily.
- Regular ventilation of the room is important. The procedure should be performed at any time of the year.
- Regular exercise helps improve your health.
An increased platelet count indicates a serious disorder in the child’s body. This symptom cannot be ignored. Only a qualified doctor can correctly determine the cause of the deviations. Parents should understand that the earlier treatment begins, the greater the likelihood of achieving a positive effect within a short time. The goal of any family is to raise a healthy child. That is why it is important to strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Platelets are the smallest blood cells that do not contain nuclei in the form of blood platelets, which are responsible for the process of blood clotting, i.e., for stopping bleeding that occurs. These plates essentially provide the liquid state of the blood and participate in the formation of clots called thrombi.
Platelets are produced by special cells in the red bone marrow (megakaryocytes). Platelets are short-lived cells: they live only up to 10 days, and then are destroyed in the spleen and liver. Instead of the “old” destroyed blood platelets (also called platelets), new ones are formed. This process is continuous. Why platelet counts in a child’s blood may be elevated and what to do in this case, we will discuss in this article.
Normal platelet counts in children
Platelets are blood cells that are responsible for blood clotting.The number of platelets is determined in a general clinical blood test in terms of 1 cubic millimeter. The number of blood platelets is an important indicator of health, since it characterizes the child’s body’s ability to cope with bleeding and assess blood clotting.
Depending on the age of the child, the number of platelets varies:
- for a newborn, their normal content is from 100 thousand to 420 thousand;
- at the age of 10 days to a year, the norm is already 150–350 thousand;
- in children after a year, platelets are normally 180–320 thousand;
- in adolescence, in girls in the first days of menstrual bleeding, the number of platelets is 75–220 thousand.
An increased number of platelets in the peripheral blood is called thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia, and the decrease in their number is . In the first case, a deviation from the norm may indicate the possibility of increased thrombus formation, and in the second, it may indicate bleeding. In both cases, the relationship between the formation of new platelets and their destruction is disrupted.
The platelet count is determined by testing blood from a finger or a vein. In newborns, blood is usually taken from a toe or heel. This study does not require special preparation. Blood should be donated on an empty stomach (you can give the child something to drink). In young children, the sample is taken before the next feeding or 2 hours after the previous feeding.
Before taking the test, physical and emotional stress is undesirable for the child. Even hypothermia can show distorted analysis results. The use of certain medications (corticosteroids, antibiotics) can also change the number of blood platelets. To ensure the authenticity of the detected increase in platelet count, it is recommended to take a blood test three times with intervals of 3-5 days.
The result of the blood test is ready on the same day (in some cases, the analysis is performed urgently in a shorter period of time). Platelet counting in a blood test is done quite often for children, especially for those who often have nosebleeds and often have hematomas (bruises) on the body, it is noted. Parents may be alerted to the child’s complaints of weakness and dizziness, and frequent numbness in the limbs.
Indications for platelet counting are the following diseases:
- systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases;
- malignant blood diseases;
- viral infections.
Causes of thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis can be caused by:
- increased production of blood platelets by megakaryocytes of the red bone marrow (with erythremia);
- slow platelet utilization (when the spleen is removed);
- disturbance of the distribution of platelets in the bloodstream (due to physical or mental stress).
When an elevated platelet count is detected, it is very important to determine the cause of this condition. Only a pediatrician or hematologist (a specialist in blood diseases) can identify this cause.
Thrombocytosis as a disease can develop in children at any age. But such a diagnosis is made with a significant increase in the number of platelets - more than 800 thousand/l. More often, a mild increase in the number of blood platelets occurs due to a number of reasons or in a number of diseases.
Distinguish primary, clonal And secondary thrombocytosis.
At clonal thrombocythemia there is a defect in the stem cells themselves in the bone marrow (they are damaged by the tumor process). They do not respond to stimulation of the process by the endocrine system, and the process of platelet formation becomes uncontrollable.
A similar mechanism has also been observed with primary thrombocythemia. It is associated with the proliferation of several areas of the red bone marrow and, as a consequence, with an increase in the number of newly formed blood platelets. The causes of this condition can be hereditary (congenital) diseases or acquired (myeloid leukemia, erythremia).
In primary thrombocytosis, the number of blood platelets can vary: from a slight increase to several million in 1 μl, but high levels are more typical. In addition, their morphology also changes: platelets of enormous size and altered shape are found in the blood smear.
Development mechanism secondary thrombocytosis may be different:
- when the spleen is removed, old or obsolete platelets do not have time to destroy, and new ones continue to form; in addition, the spleen produces antiplatelet antibodies and a humoral factor that inhibits platelet production;
- During the inflammatory process, the body intensively produces a hormone (thrombopoietin), which promotes the maturation of blood platelets, which help cope with inflammation; biologically active substances (for example, interleukin-6) are anti-inflammatory cytokines that stimulate platelet synthesis;
- in malignant diseases, the tumor produces biologically active substances that have a stimulating effect on bone marrow megakaryocytes and the production of blood platelets; this is more often observed with kidney hypernephroma, lymphogranulomatosis;
- thrombocytosis also develops as a response of the body to repeated blood loss (with, with),
Secondary thrombocythemia (symptomatic or reactive) can develop in a number of diseases:
Secondary thrombocytosis is characterized by a less pronounced increase in the number of platelets: in very rare cases, their number exceeds a million in 1 μl. The morphology and function of blood platelets are not impaired.
In any case, detected thrombocytosis requires a full examination and clarification of the cause of its occurrence.
In addition to diseases, it can also be caused by side effects of medications (Vincristine, epinephrine, adrenaline, corticosteroids, etc.). There are no specific symptoms of thrombocytosis.
When an increased platelet count is initially detected, the following studies must be performed:
- determination of serum iron and serum ferritin;
- determination of C-reactive protein and seromucoids;
- blood coagulation analysis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- if necessary, consult a hematologist;
- bone marrow examination (only as prescribed by a hematologist).
Symptoms of thrombocytosis
 An increase in the level of platelets in the blood leads to the formation of blood clots in vessels of any location.
An increase in the level of platelets in the blood leads to the formation of blood clots in vessels of any location. With primary thrombocytosis, the size of the spleen is enlarged, blood clots of different locations can form, but bleeding in the digestive organs can also occur. Blood clots can also form in large vessels (veins and arteries). These changes contribute to the development of prolonged hypoxia or ischemia, which manifests itself in pain in the fingertips and gangrene of the fingers may even develop. Hypoxia of tissues and organs leads to disruption of their function: disorders of the central nervous system and kidneys may be observed.
Clinical manifestations are caused by the underlying disease, the symptom of which is thrombocytosis.
Children, as noted above, may experience frequent nose and gum bleeding, bruises on the body with the slightest injury or even for no apparent reason. May develop (fluctuations in blood pressure, headaches, cold extremities, increased heart rate), iron deficiency anemia.
Reactive thrombocytosis is clinically mild and may be asymptomatic.
Treatment
To treat primary thrombocytosis, the cytostatics Myelobromol, Myelosan and others are used for a long time until results are obtained.
In severe cases, in addition to cytostatics, thrombocytopheresis is used (removal of platelets from the bloodstream using special equipment).
Drugs that improve microcirculation and prevent the adhesion of blood platelets (Trental, aspirin, etc.) are also used. Aspirin can be used only if erosive changes in the digestive tract are excluded.
For clonal thrombocytosis, antiplatelet agents (Ticlopidine or Clobidogrel) are used in individual dosages.
In case of thrombosis or ischemic manifestations, anticoagulants (Heparin, Argotoban, Livarudin, Bivalirudin) are used under daily laboratory monitoring of platelet counts.
For secondary thrombocytosis, treatment includes therapy of the underlying disease and prevention of thrombosis associated with an increased platelet count. As a rule, reactive thrombocytosis does not lead to thrombohemorrhagic complications and therefore does not require special therapy. The prognosis is usually favorable.
In addition to drug treatment for thrombocytosis, it is important to provide the child with a balanced, rational diet. Breastfeeding is the most beneficial for infants.
- rich (seafood, nuts);
- rich (dairy products);
- rich (offal and red meat);
- freshly squeezed juices (pomegranate, lemon, lingonberry, orange), diluted with water 1:1.
The following have a thinning effect on the blood: berries (cranberries, sea buckthorn, viburnum), lemons, ginger, beets, fish oil, flaxseed and olive oil, tomato juice and a number of other products.
Platelets- these are cellular elements of the blood that play an important role in laboratory research, since the normal course of the processes of hemostasis (prevention and stopping of bleeding) and thrombosis depends on them. Those. They keeps blood fluid, dissolving the resulting blood clots, and also protect the walls of blood vessels, “sealing” the site of damage with a blood clot and releasing growth factors for tissue regeneration.
information The study of this blood element (PLT) provides an assessment of its coagulability, which plays an important role in possible blood loss. Capillary blood is taken for examination.
Visually, platelets are small colorless flat plates, the formation of which occurs in the red bone marrow on megakaryocyte cells. Approximately 2/3 of the platelets that enter the bloodstream remain circulating in it for up to 1.5 weeks (further absorbed by phagocytes), and 1/3 is deposited in the spleen.
Normal platelet count in children
| Newborns | Up to 1 year | From 1 year and older |
| 100-420 thousand | 150-350 thousand | 180-320 thousand |
The number of platelets circulating in the blood is not constant. Therefore, the results taken in the morning may differ from the evening results.
Platelets are elevated
Thrombocytosis– a condition in which the level of platelets in the blood is elevated, which leads to blockage of blood vessels blood clots Distinguish primary, provoked by functional disorders of red bone marrow stem cells, and secondary (symptomatic) which can be caused by:
- and surgical interventions;
- hematological abnormalities (anemia);
- some (diuretics, contraceptives and other hormonal drugs).
How to lower platelet levels
For minor thrombocytosis(up to 500 x 10 9 / l) the situation can be corrected by diet and drinking plenty of fluids. It is a slight increase in platelet levels that is often a clinical sign of dehydration.
Diet includes products that thin the blood: olive oil, fish oil, onions and garlic, lemons, sour berries, tomato juice, etc. Foods rich in magnesium are also useful. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids: green tea, juices from sour berries and fruits.
important Anything that increases blood viscosity is excluded: bananas, mangoes, lentils, rose hips, walnuts, chokeberries, pomegranate, alcohol and tobacco.
Treatment with folk remedies, especially in children, can be carried out only with the permission and under the supervision of the attending physician.
With a significant increase indicator, a number of additional studies and consultation with a hematologist are recommended, since primary thrombocytosis is often discovered by chance during a routine examination.
Platelets are low in a child
Thrombocytopenia– a significant decrease in PLT platelet levels, which causes clotting disorders and increased bleeding. The danger of this condition is the high risk of developing internal bleeding or stroke.
Suspicion of the presence of this pathology may arise if the child has such signs:
- bleeding gums;
- the appearance of bruises is frequent and without mechanical impact;
- repeated, as well as bleeding in the intestines;
- specific small “stars”;
- prolonged bleeding after minor cuts or tooth extraction.
Causes of decreased platelets
Causes of low platelet levels can be:
- for medications;
- immune attack;
- symptomatic reaction provoked by hyperthyroidism or intoxication;
- transimmune attack (maternal antibodies, having overcome the placental barrier, attack fetal platelets);
additionally Also, the reason for a decrease in platelet levels may be a deficiency in the body folic acid or vitamin B12.
How to raise platelet levels
After a thorough examination and clarification of the etiology of thrombocytopenia, the patient may be prescribed various treatment options:
- platelet transfusion;
- administration of anti-Rhesus D serum;
- parenteral injections of immunoglobulin;
- glucocorticosteroid hormones.
If conservative treatment does not bring results, then resort to splenectomy– surgical removal of the spleen. After such manipulation, three quarters of patients recover completely.
Patients with thrombocytopenia are under the supervision of a hematologist and are forced to adjust lifestyle.
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?