Genital herpes: symptoms of the disease, methods of treatment and prevention
Genital herpes is classified as a viral pathology that is sexually transmitted. Statistics show that every fifth inhabitant of the planet has this infection. At the same time, symptoms appear only in 2 out of 9 patients.
Among sexually transmitted diseases, herpes ranks second after trichomoniasis. has special receptors on its surface, which determine its tropism (attachment) to nerve and skin cells.
The genital form of this disease is caused by its types I and II, the first is also known as the "cold on the lips." 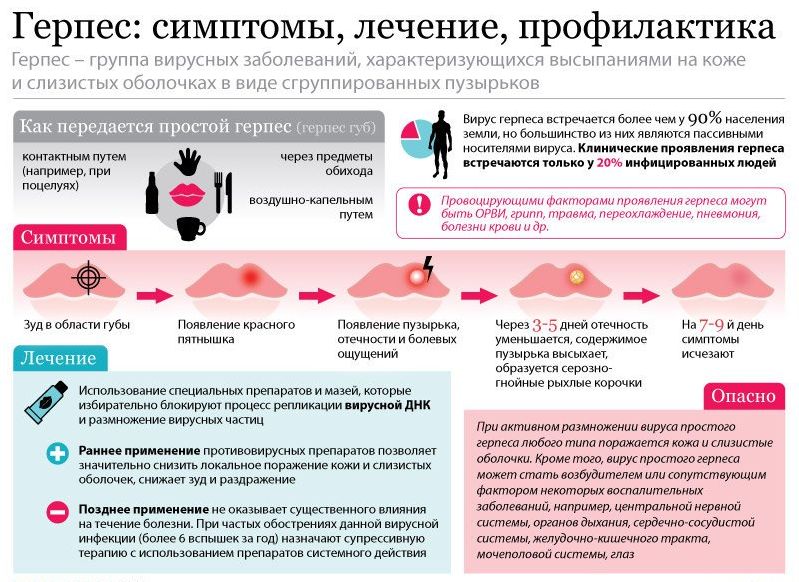
Causes and ways of transmission of genital herpes
The main cause of the genital form of the disease is infection with the Herpes simplex virus (HSV). Moreover, this disease is caused both by a type I virus (HSV-I), usually familiar to us from the “cold” rashes on the lips, and by a type II virus (HSV-II), which directly affects the genitals.
Type I virus infection can occur even in childhood. In this case, a child or adolescent becomes infected as a result of contact with a sick person or his household items through mucous membranes and lesions on the skin. The provoking factor is the lack of personal hygiene, low socio-economic standard of living, weakened immunity, etc.
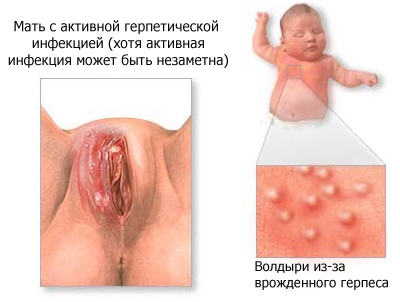
Sometimes it is possible to transmit the disease from mother to newborn child during childbirth. Such a development of events is usually possible if the woman was initially infected and the first manifestations of the disease occurred immediately before childbirth, and the child was born naturally - through the vagina.
Infection with the second type of virus (HSV-II) most often occurs already at a young or young age (20-30 years) through unprotected sexual contact.
The reasons for this situation are rather banal.:
- decrease in immune forces;
- the presence of other pathologies that are sexually transmitted;
- casual sexual relations;
- belonging to the female sex (statistics confirm that women get herpes more often than men);
- close contact with a virus carrier in everyday life;
- early sexual life;
- abortion;
- intrauterine device;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- virus carrier.
Ways of transmission of herpes are as follows:
- oral;
- domestic;
- sexual;
- anal;
- autoinfection;
- intrauterine.
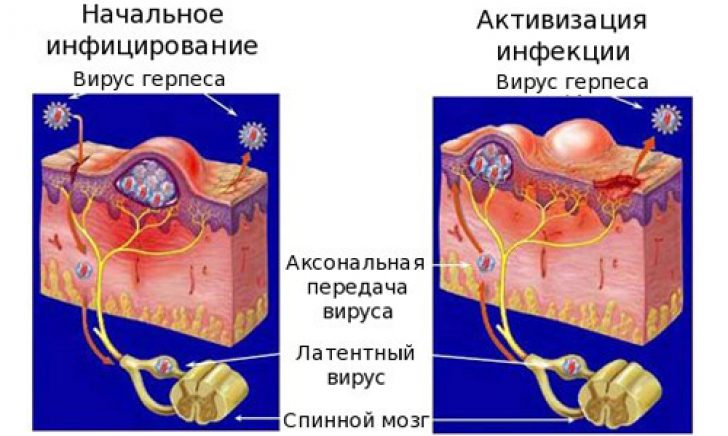
Getting on the genitals, this virus penetrates the mucous layer of the internal genital organs and urinary tract. The purpose of the virus is to enter the nucleus of cells and make changes to their DNA. This provides the virus with life in the human body, since the infected cell begins to actively synthesize the proteins of the virus, as if it were its own. New virions are created from them, and when their number reaches a certain level, the patient begins to show typical symptoms of herpes.
Symptoms of genital herpes
The clinical picture of herpes depends on the type of pathological process.
At the same time, it affects certain parts of the body:
- CNS - (encephalitis, meningitis);
- skin, mucous membranes (face, genitals);
- eyes (keratitis, conjunctivitis).
Clinical types of symptoms of herpes
During the course of the disease:
- Primary infection(usually occurs sexually) from a sick person to a healthy person. It is manifested by the following symptom complex: rash (vesicles) on the genitals - purulent pustules - purulent sores - scabs. The duration of the disease is 30 days. There is also discharge, urinary problems, and swollen or swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
- Secondary infection- occurs when HSV-II is present in the body, which is in a latent state. It is activated after weakening of the immune system or re-infection. Symptoms are the same as with the initial infection.
- Recurrent herpes- This is a virus carrier, in which there are stages of exacerbation and remission, depending on the state of the body's immune forces.
- Atypical course of herpes characterized by manifestations of other pathologies. It is usually detected in a laboratory study.
- Asymptomatic form occurs quite often (in 6 people out of 10 patients with herpes) and is considered the most dangerous in terms of the epidemic spread of this disease.
Given gender, herpes has some differences in symptoms.
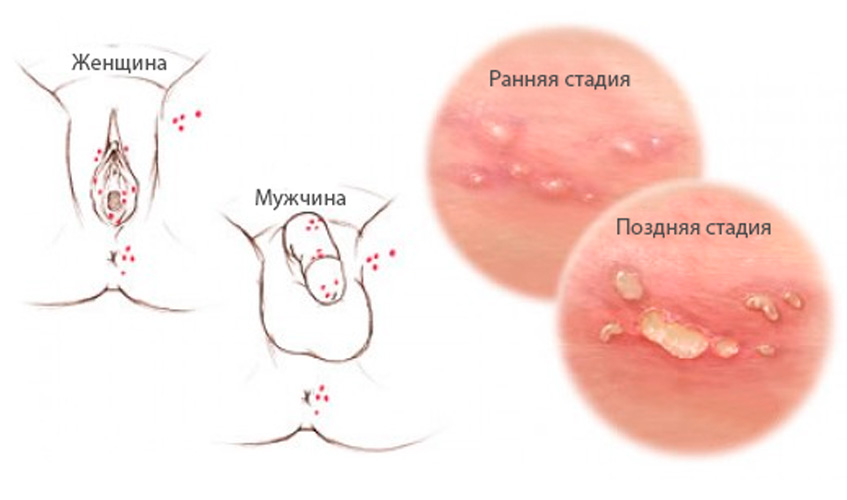
Symptoms of genital herpes in men
The following signs may indicate the presence of genital herpes in men:
- rashes on the penis itself and the foreskin;
- local temperature rise
- compacted lymph nodes are palpated in the groin;
- rash on the scrotum and perineum;
- genital itching in the places of rashes - at first mild, with a feeling of tingling and burning, and then turns into constant pain;
- rash in the urethra.
Symptoms of genital herpes in women
The female has the following manifestations of this virus, which are usually observed 3-15 days after infection:
- pain;
- local irritation in the genital area;
- pathological discharge;
- typical rash in the labia, perineum and vagina;
- rashes also appear on the eve of the vagina, urethra, near the anus, on the thighs;
- the cervix is also affected, on which there may be rashes, cervicitis, erosion, pus.
Diagnosis of genital herpes
 The doctor confirms the diagnosis based on the data of an objective examination and results.
The doctor confirms the diagnosis based on the data of an objective examination and results.
To detect the herpes virus in the body, the following studies are used:
- Serological analysis of serum, which determines the presence and level of specific antibodies in the blood to the herpes virus.
- DNA diagnostics implies the isolation of the pathogen from the biological material of the patient, taken in the lesion. To do this, take a scraping from the urethra, cervix, rashes on the mucous membranes and skin.
- Analyzes for comorbidities sexually transmitted (at the discretion of the attending physician).
The specialist tells about the features of the diagnosis and treatment of genital herpes:
Features of the course of genital herpes during pregnancy
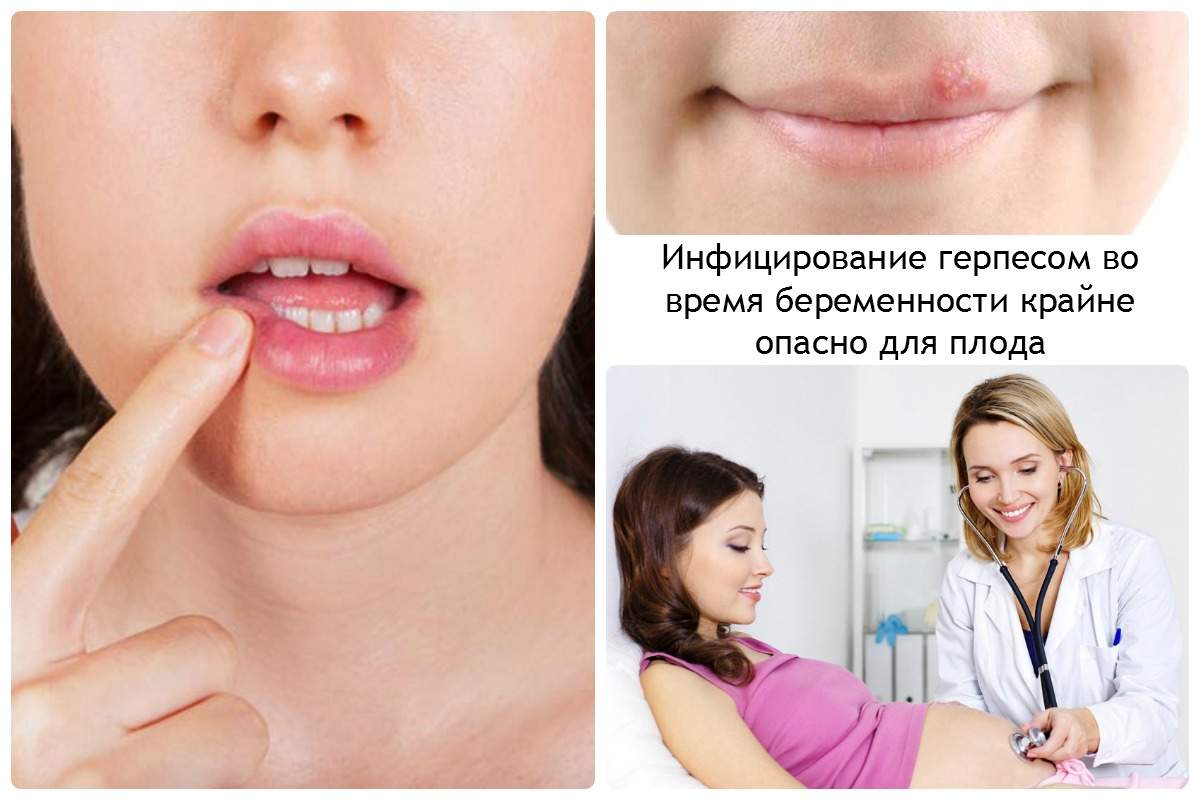
In women who are carrying a child, the herpes virus in most cases is in a relapsing form. Very often the patient does not make any complaints, but at the same time she releases the virus into the environment and thus infects her sexual partner. Their children are born already sick with neonatal herpes, but 9 out of 10 women in labor have absolutely no symptoms of this disease.
The method for diagnosing genital herpes during pregnancy or at the stage of pregnancy planning is described in detail in the article.
Genital herpes during pregnancyprimary sexual infection is manifested by the following clinic:
- duration of the incubation period - up to 5 days;
- after its expiration, papules can be seen on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, which turn into a vesicular form;
- after a few days, the bubbles burst and turn into erosion, which bring pain;
- erosions are covered with crusts;
- a woman is constantly worried about genital itching;
- urination disorders;
- purulent discharge;
- general poor health;
- subfebrile condition;
- muscle pain;
- swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
Every fourth patient has an increased risk of developing aseptic meningitis, fungal and bacterial superinfection,
After 7-14 days, the disease ends on its own, but relapses occur much more often than in non-pregnant women.
After the pathological elements on the skin have disappeared, the virus is released for at least a week, a maximum of 3 months.
Herpes can provoke premature birth, spontaneous abortion, chorioretinitis, neonatal infection. Infection of a child with a virus occurs during childbirth, that is, through direct contact with infected mother's secretions, transplacental, through breast milk, kisses, antenatally.
The virus enters the child's body through the mucous membrane of the mouth and nasopharynx. The highest risk of infection of the child in the case of primary herpes mother in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Important: During pregnancy, the appointment of antiretroviral therapy is allowed only in the case of a severe form of the virus. At the same time, prevention of antenatal infection of the fetus and relapse must be carried out.
Prevention includes some immunostimulating agents, immunoglobulin (normal human IV), homeopathic medicines. The issue of delivery should be decided taking into account the results of tests for the presence of the herpes virus in the cervical canal and the study of the titer of antiherpetic antibodies. Diagnosis is carried out 2-3 weeks before delivery.
The direct treatment of herpes in pregnant women consists of the following items:
- acyclovir (drip);
- immunoglobulin;
- local treatment of rashes with aniline dyes;
- suppositories Viferon;
- acyclovir cream.
The appointment of Acyclovir just before childbirth avoids cesarean section for pregnant women with genital herpes. Such patients must treat the birth canal with an antiviral solution of Poludan.
note: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with fresh rashes, then this is an indication for a mandatory caesarean section.
Women in labor after childbirth immediately begin to conduct active antiviral therapy. The child is isolated from the sick mother to make sure he has not been infected by her. This becomes clear 10-14 days after his birth. At the same time, it is important that the child receives mother's milk, regardless of what type of herpes she is sick with.
Breast milk in this case is a source of anti-herpetic antibodies for the newborn, even if it contains the herpes antigen.
With symptoms of herpes, only every second child is born whose mother was initially infected. In the case of the relapsing form, signs of the disease are observed in only 1 out of 20 children born to infected mothers. Symptoms of herpes in these children are of varying severity: from skin lesions to encephalitis.
The most favorable prognosis is for babies who suffer from herpes in a localized form. With a disseminated type of herpes, it affects the internal organs, affects the brain, many glands and proceeds according to the type of neonatal sepsis. Mortality in this case is 90%.
Treatment of genital herpes
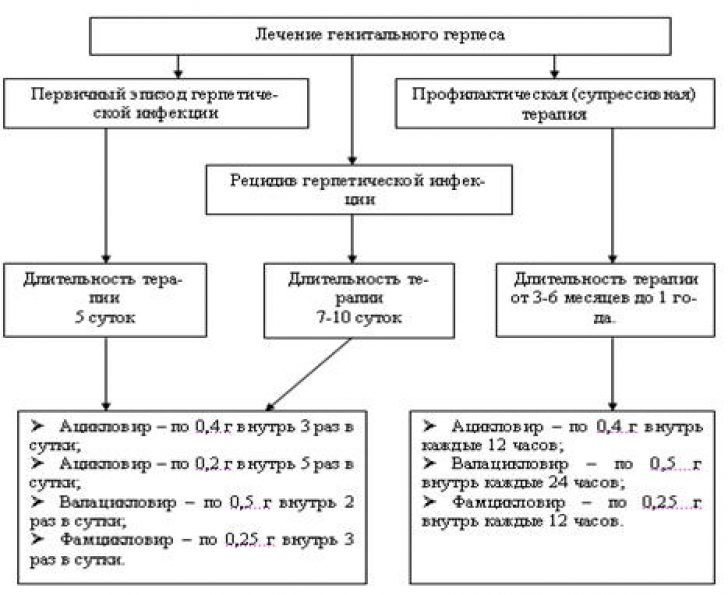
It should be borne in mind that this disease requires long-term treatment. Its task is to stop the process of reproduction of virions in the body and strengthen its immune response. The therapeutic regimen is always compiled individually, taking into account the type of herpes infection, stage, and the presence of concomitant infections.
The treatment plan usually includes the following drugs:
- antiviral (courses);
- specific antiherpetic immunoglobulin;
- ointments (topically);
- immunostimulants;
- restorative.
When undergoing treatment for herpes, it should be borne in mind that modern antiviral agents cannot completely cure this virus and protect against relapses.
In practice, the classical treatment regimen for patients with genital herpes is used:
- Pathogenetic treatment (immunomodulators, synthetic stimulants of immunogenesis).
- Prevention (specific) is vaccination.
- Etiotropic treatment (antiviral to eliminate virus replication).
- Symptomatic therapy (means are prescribed to eliminate itching, pain, fever).
- Physiotherapy (in some cases).
The base drug for herpes is Acyclovir. It belongs to the group of synthetic analogues of acyclic purine nucleosides, which have a direct effect on the virus.
In more detail about the methods of treating genital herpes, see the video review:
Treatment of genital herpes at home
Treatment of genital herpes at home allows the use of some harmless methods, but only in combination with a developed medical scheme.
In particular, you can use the following:

- Tea tree. The essential oil of this plant has a very strong antiviral effect. In the case of herpes, it is very effective in dealing with it even at the beginning of the development of symptoms. The oil can be applied directly to the rashes. If there is a burning sensation, then the drug should be diluted with water.
- Intercostal neuralgia - what is it and how to treat
- How to quickly get rid of dry corns on the legs
- How to treat left ventricular hypertrophy
- Rating of the best drugs for rotavirus for children
- Making tea from currant leaves, the benefits and harms of the drink
- How to drink hydrogen peroxide according to Neumyvakin - an oral regimen
- Features of the treatment of plantar fasciitis with folk remedies
- The composition and beneficial properties of parsley root
- How to get pregnant quickly? Folk remedies
- Herbs-ants in the "pot-bellied" period or the use of herbal medicine during pregnancy
- Why does a sore throat and dry cough occur, and what treatment is required?
- Guy's Room Design: Ideas and Examples
- General rules for drawing up a foundation plan House foundation drawings
- modern art deco bedroom small art deco bedroom
- Pansies: characteristics and photos of flowers
- Making an art deco bedroom: the choice of materials Beige art deco bedroom
- Bedroom interiors in art deco style Bedroom art deco style beige
- Young: planting and care in the open field Young planting and care in the open
- Varieties for open ground
- Pansies: cultivation and care in the open field