The microsoft account service is unavailable. Troubleshooting Windows error "Unable to sign in to account". Let's solve the problem "Unable to load user profile" in a simple way
User account corruption is a common Windows problem. The problem occurs when you enter a password or pin on the lock screen and when you press enter, you will get the error "User Profile Service failed to log in. Unable to load user profile" in windows 10 or User Profile Service is preventing login in Windows 7. .
Solve the problem "User Profile Service failed to log on" using Registry Editor
Option 1: Fix the user account profile
Sometimes your account can be corrupted and this prevents you from accessing files in windows 10. Let's go to the registry editor in several ways, through safe mode:
Step 1. Press keyboard shortcut " windows + R" to call the "execute" command and enter the command regedit to enter the register.

Step 2. In the window that opens, follow the path:
Step 3. In parameter you will have multiple keys s-1-5. You will need to select the longest key with a long array of numbers and your account on which the "User Profile Service failed to log on" error. Make sure that the path is correct, click on the long key and there should be a name in the right column, if not found, then scroll through all the long keys until you come across in the right column with your broken profile, in my case, the account .

Step 4. If you incorrectly renamed the user profile folder C:\User\site of the affected account, then open the explorer along the path C:\User\site and right-click on the broken profile, select rename and manually enter the correct profile name (site). After renaming, we go back to the folder in the registry and see that the name is written as in the picture (step 3) C:\User\website.

See two options step 6 and step 7 depending on how
Step 5. Now let's make two options, if we have one long key S-1-5-21-19949....-1001. bak(at the end of the .bak extension) and with the second without .bak those. just S-1-5-21-19949....-1001. Depending on who has two or one profiles lined up.
Step 6. There is only one key at the end of c.bak (S-1-5-21-19949....-1001.bak).
- A) If you only have one key at the end of c .bak(S-1-5-21-19949....-1001.bak), right-click on it and click rename. (see picture below).

- B) Delete the word itself with a dot .bak to get just numbers. Continue with step 8. (See the picture below)

Step 7. If you have two identical keys, one without .bak, the other with .bak. (S-1-5-21-19949....-1001 and S-1-5-21-19949....-1001.bak) .

- A) In the left pane of the registry, right-click on the key without .bak and add a dot, two letters .bk(see picture below).

- B) Now right-click on the key with .bak, select rename and delete .bak with a dot. (see picture below).

- C) Now go back and rename the first key with .bk in .bak. Press enter and follow step 8.

Step 8. Highlight the key that was renamed without .bak and with the right in the column, double-click to open the parameter settings, and assign a value of 0. If you do not have such a parameter, then right-click on an empty field with the right mouse button and create a DWORD (32-bit) value, rename it to RefCount and set the value to 0.

Step 9. In the right field, select the key without .bak and in the parameter State set the value to 0. If there is no such parameter, then click on the empty field on the right and click create DWORD (32-bit), rename it to State and set the value to 0.

Step 10. Restart your computer and the error "user profile service failed to log in" and "unable to load user profile" in windows 10 should be gone.
Option 2: Delete and create a new user profile for the account
This option will delete the user profile and you will lose all your account settings and personalization.
Step 1. If there is another admin account that doesn't have the error, log out of the current account (for example: site) and log in to the admin account.
If you don't have another admin account to sign in, you can do one of the following options below to enable the built-in admin account to sign in and skip to step 2 below.
- BUT). Boot into safe mode, enable the built-in Administrator, log out and log in to Administrator.
- B). Open a command prompt window at boot, enable the built-in administrator, restart your computer, and log in to Administrator.
Step 2. Back up anything you don't want to lose in the C:\Users\(username) profile folder (ex: site) of the respective user account to another location. When finished, delete the C:\Users\(username) folder.
Step 3. Press the windows + R buttons to open the Run dialog box, type regedit and click OK.
Step 4. In Registry Editor, navigate to the location below.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
Step 5. In the left pane, in the ProfileList, click on the long key on which the account failed. The profile is visible on the right.
Step 6. Delete profiles with .bak and without .bak errors. For example ( S-1-5-21-19949....-1001 and S-1-5-21-19949....-1001.bak)-delete.
Step 7. Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer, after which it will automatically recreate the new user.
Let's solve the problem "Unable to load user profile" in a simple way
Method 1. This method does not work for everyone, but it helped many. Try to copy your documents in the folder (C:\Users\) to another location to create a backup just in case. The problem usually occurs due to a corruption in the "NTUSER.DAT" file located in the "C:\Users\Default" folder. To solve this problem you need to replace the "NTUSER.DAT" file with another profile. .

- Log in to the system in safe mode with a profile account that works.
- Locate the file (C:\Users\Default) "NTUSER.DAT" and rename the .DAT extension to .OLD. Should be (NTUSER.OLD).
- Locate the "NTUSER.DAT" file in the work profile such as "Guest", "General". Example (C:\Users\Guest\NTUSER.DAT).
- Copy it and paste it in the default folder C:\Users\Default.
- To restart a computer.
You can copy this file from another computer with the same version of windows and paste it into your C:\Users\Default path.
Method 2. You can try replacing the entire "C:\Users\" folder from another computer.
- Take a flash drive in FAT32 format and write down the C:\Users\ folder from another computer and upload it to your computer.
If anyone knows how else to fix the error, "User Profile Service Prevents Login" by some other method, then write in the "report a bug" form.
User profile corruption issues are among the most common, usually accompanied by "Unable to sign in" and "You are signed in with a temporary profile" messages. Therefore, today we decided to tell you how the user profile is arranged, what can lead to its damage, and what methods can be used to restore the normal operation of the system.
Let's start with the symptoms, the first sign that something went wrong is the inscription Preparing Windows on the welcome screen instead of Welcome.
 You will then be "pleased" with a message "Unable to sign in" with options to re-enter and continue working.
You will then be "pleased" with a message "Unable to sign in" with options to re-enter and continue working.
 If we close this window, we will see another message that sheds some light on what is happening. "You are logged in with a temporary profile".
If we close this window, we will see another message that sheds some light on what is happening. "You are logged in with a temporary profile".
 If the profile is temporary, then it turns out that for some reason the permanent user profile could not be loaded. Therefore, we will not flog the fever, but will try to figure out what a user profile is, what data it contains, and what may be the reason for the impossibility of loading it.
If the profile is temporary, then it turns out that for some reason the permanent user profile could not be loaded. Therefore, we will not flog the fever, but will try to figure out what a user profile is, what data it contains, and what may be the reason for the impossibility of loading it.
In the very first approximation, the user profile is the contents of the directory C:\Users\Name, where Name- username, there we will see the folders familiar to everyone Desktop, Documents, Downloads, Music etc., as well as a hidden folder AppData.

With the visible part of the profile, everything is clear - these are standard folders for placing user data, by the way, we can safely reassign them to any other location. In recent versions of Windows, you can even reassign the Desktop.
 This is quite convenient and justified, given how much users keep on their desktops, and the same SSDs are far from rubber. But this is not about that, much more interesting is what is hidden from the eyes of a simple user.
This is quite convenient and justified, given how much users keep on their desktops, and the same SSDs are far from rubber. But this is not about that, much more interesting is what is hidden from the eyes of a simple user.
Folder AppData is designed to store settings and user data of installed programs and, in turn, contains three more folders: local, local low and Roaming.
 Let's consider them in more detail:
Let's consider them in more detail:
- Roaming- this is the "light" and, as the name implies, the movable part of the profile. It contains all the basic settings for programs and the user's work environment; if roaming profiles are used on the network, then its contents are copied to a shared resource, and then loaded onto any workstation where the user has logged on.
- Local- "heavy" part of the profile, contains cache, temporary files and other settings applicable only to the current PC. It can reach a significant size, it does not move over the network.
- local low- local data with low integrity. In this case, we again have an unsuccessful translation of the term low integrity level, actually integrity levels are another security mechanism. Without going into details, we can say that data and processes of the system have high integrity, standard - user, low - potentially dangerous. If we look into this folder, we will see there data related to browsers, flash player, etc. The logic here is simple - in case of any emergency or attack, processes launched from this folder will not have access to user data.
And now is the time to think about which of the specified data corruption can lead to problems loading the profile? Probably none. Therefore, there must be something else in the profile. Of course it is, and if you look closely at the screenshot of the user profile above, we will see the file there NTUSER.DAT. If you enable display protected system files, then we will see a whole set of files with similar names.
 Here we got to the point. In file NTUSER.DAT there is a registry branch HKEY_CURRENT_USER for each user. And it is the damage to the registry branch that makes it impossible to load the user profile. But not everything is as bad as it might seem at first glance. The registry is quite well protected from possible failures.
Here we got to the point. In file NTUSER.DAT there is a registry branch HKEY_CURRENT_USER for each user. And it is the damage to the registry branch that makes it impossible to load the user profile. But not everything is as bad as it might seem at first glance. The registry is quite well protected from possible failures.
Files ntuser.dat.LOG contain a log of registry changes since the last successful boot, which makes it possible to roll back in case of any problems. Files with extension regtrans-ms are a transaction log, which allows you to keep the registry branch in a consistent form in the event of an abrupt cessation of work while making changes to the registry. In this case, all pending transactions will be automatically rolled back.
Files of least interest blf- this is a registry branch backup log, for example, with a regular tool System Restore.
Thus, having found out what the user profile consists of and damage to which part of it makes it impossible to boot, we will consider ways to restore the system.
Method 1: Fix the user profile issue
First of all, if you have problems logging into your account, you should check the system volume for errors, to do this, boot into the recovery console or Windows PE and run the command:
Chkdsk c: /f
In some cases, this may be enough, but we will consider the worst case. After checking the disk, boot into the system and open the registry editor, go to the branch
On the left we will see a number of sections with the type name S-1-5 and a long "tail" that correspond to user profiles. In order to determine which profile belongs to which user, pay attention to the key ProfileImagePath on right:
 So, the desired profile has been found, now we look again at the tree on the left, which should contain two branches, one of which ends with bak.
So, the desired profile has been found, now we look again at the tree on the left, which should contain two branches, one of which ends with bak.
 Now our task is to rename the main profile to bak, a bak in the main. To do this, add any extension to the main profile, say .ba, then rename the backup profile to the main one, removing from its name .bak, and rename again ba in bak.
Now our task is to rename the main profile to bak, a bak in the main. To do this, add any extension to the main profile, say .ba, then rename the backup profile to the main one, removing from its name .bak, and rename again ba in bak.
By the way, there may be situations where only a branch exists for your account bak, in which case just remove its extension.
Then we find two keys in the new main profile RefCount and State and set both to zero.
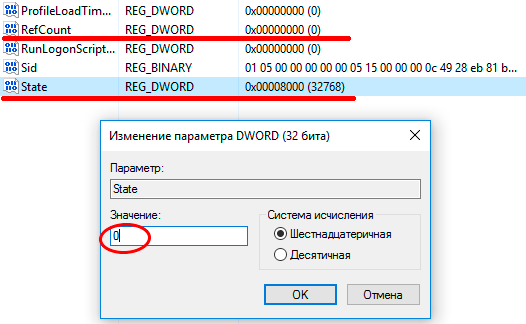 We reboot. In most cases, if the profile is not seriously damaged, these steps will succeed, otherwise go to method 2.
We reboot. In most cases, if the profile is not seriously damaged, these steps will succeed, otherwise go to method 2.
Method 2. Create a new profile and copy user data there
The official Microsoft documentation advises in this case to create a new account and copy the profile data there. But this approach gives rise to a whole range of problems, since a new user is a new security subject, and, therefore, we immediately get a problem with access rights, in addition, we will need to reconnect all network accounts, re-import personal certificates, and export-import mail (if you are using Outlook). In general, there will be enough entertainment and it’s not a fact that all problems can be successfully overcome.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
and delete all branches related to your profile. We reboot.
After that, Windows will create a new profile for your account, as if you were logging in for the first time. But your security identifier (SID) will remain unchanged, you will again be the owner of all your own objects, certificates, etc., etc.
For further actions, you will need another account with administrator rights, let's create it, in our case it is an account temp.
 After that, we exit our main account (or reboot) and enter the sub account. Our task is to copy all the contents of the old profile folder, except for the NTUSER files, to the new folder. For these purposes, it is better to use a file manager (Total Commander, Far, etc.) launched with administrator rights.
After that, we exit our main account (or reboot) and enter the sub account. Our task is to copy all the contents of the old profile folder, except for the NTUSER files, to the new folder. For these purposes, it is better to use a file manager (Total Commander, Far, etc.) launched with administrator rights.
At the end of the copying process, we log into our account again and check the operation of the account. All data and settings should be back in place. However, do not rush to delete the old folder and additional account, some data may need to be transferred again. This may be due to the fact that some programs that store settings in a damaged registry branch may decide that a new installation has been completed and overwrite the transferred files, in which case it is enough to selectively copy the necessary data.
After you work with the system for a while and make sure that everything is in place and working as it should, you can delete the old folder and additional account.
Tags:
As you know, Windows services are one of the most favorite places for attacks on the operating system. In the worst (for us, of course) case, the attacker gets the opportunity to act on the attacked computer in the context of the account under which the hacked service is running. And if this account has administrative rights, then in fact the attacker gets full control over the computer. From version to version in Windows, new mechanisms appear that provide additional isolation of services and, as a result, strengthen the security of the system as a whole. I would like to briefly consider what has fundamentally changed in this direction over the past few years.
The first significant changes in the protection mechanisms of services appeared in Windows XP Service Pack 2. It’s hard to imagine now, but before the release of SP2, all services of the operating system itself ran in the context of the built-in Local System account, which has the most complete administrative rights on the computer. SP2 added two more entries: Local Service and Network Service. The fundamental differences between the three listed records can be found in Table. one.
Table 1
Accordingly, starting with Windows XP SP2, the administrator could configure the service to run in the context of one of the built-in accounts, a local account, or a domain account. However, most Windows itself services still run in the Local System context. But even aside from this, the situation when several services are running in the context of the same account leads to the fact that a successful attack on one service, even without administrative privileges, potentially exposes any other resources to which the attacker has access. compromised service account.
Windows Vista introduced several mechanisms to increase service isolation. I'll stop at two.
The first mechanism is the service's unique security identifier (Service SID). This SID is generated for each service by hashing the service name using the SHA-1 algorithm. The result is prefixed with S-1-5-80-. You can view the SID of a service using the sc showsid command with the name of the service as a parameter (see Figure 1).
Rice. one
You can experiment with, for example, the W32Time service. For any folder on NTFS in the permissions settings (permissions), you only need to enter the username in the format NT SERVICE\<имя службы>, in our case NT SERVICE\w32time (see Figure 2). 
Rice. 2
Click Check Names, then OK and see the user (see Fig. 3), which can be assigned rights. 
Rice. 3
Again, w32time is not a user object. This is a SID, but if so, it can be used in ACLs, both in the graphical interface and on the command line and programmatically. Moreover, service SIDs can be used in the Windows Firewall settings, applying certain rules to a specific service, or rather a specific Service SID.
The second change introduced in Vista is a new type of SID, the Write Restricted SID. If a service is marked with the Write Restricted SID type, then its SID is added in its own access token to a special list - Restricted SID list. When such a service tries to write something to a file, the access rights check algorithm changes somewhat. Namely, a service will only be able to write to a file if the Write permission is explicitly granted to the service's SID, or to the Everyone group.
For example, ServiceAccount1 of some Service1 is a member of Group1. Group1, and only Group1, has Write permission on Folder1. What happens if the service tries to change something in Folder1? Under normal circumstances, ServiceAccount1 will be able to write to the folder at the cost of being a member of Group1. But if Service1 is marked with the Write Restricted SID type, then its access token is handled differently and it can't write anything to the folder because it hasn't been explicitly given the Write permission, nor has it been given the Everyone permission.
You can view the SID type using the sc qsidtype command (see Figure 4). 
Rice. 4
In particular, in fig. 4, you can see that the Windows Firewall service belongs to the mentioned type. Naturally, this type was introduced in order to further limit the capabilities of the service (the ability to erase or overwrite something) in the event of a successful hack. It should also be added that this mechanism is intended primarily not for system administrators, but for service developers. Just to use it.
In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, work on service isolation has continued. There are virtual accounts (virtual accounts) and managed service accounts (managed service accounts). And actually what is the problem? We need to isolate services - let's create the required number of local (or domain) user accounts. Each critical service has its own account. Yes, this is the solution. But for local services that do not need network access to resources, you must manually set passwords that are long and complex. And also manually update them periodically. Well, since we're all for safety. For services that need to access resources over the network in the context of domain accounts, plus you also need to register a Service Principal Name (SPN), which is different for each service. It is not comfortable. But the inconvenience becomes a real problem when a service cannot start due to an expired password. And the admin just forgot to change the password for her.
So for local services, you can use virtual accounts. The virtual account is only used to run a specific service, more specifically, to create a security context for a specific service. You will not find this entry among users in Computer Management. And yet, this is an account, with its own unique SID, with its own user profile. And therefore, you can assign permissions to it and, thereby, differentiate access rights and clearly control them. But just like with Local System, Local Service and Network Service, the operating system takes over the tasks of managing passwords for virtual accounts. We isolate the necessary services, and we do not have a headache about passwords.
To create a virtual account, you need to specify in the service settings as an account: NT SERVICE\<имя службы>(see figure 5) 
Rice. 5
After starting the service, the virtual account will be displayed in the Services console (Fig. 6), and in the Users folder you will notice the appearance of a new user profile.
Rice. 6
The format is very similar to the service SID. But I emphasize that this is not just an additional unique SID for the service as in Vista, this is a separate account and, accordingly, a different isolation level. By default, virtual accounts are used, for example, for application pools in IIS 7.5 on Windows Server 2008 R2. Keep in mind that virtual accounts are for local use. If a service running in the context of a virtual account is accessed over the network, then this access occurs on behalf of the account of the computer on which the service is running. If it is necessary that a service, for example SQL Server, work over the network on behalf of a domain account, then managed service accounts will help here. However, there are more subtleties associated with them, and their consideration is beyond the scope of this post. Learn more about MSA
- What was taught to women who became guards in concentration camps Torture used by the Nazis
- Singer Alex Malinovsky: biography, career, personal life, photo Let's start the story again
- Do I need to shave the testicles and how to do it right at home How to shave the eggs
- Chinese girls with small breasts
- Famous girls with small breasts
- Shoulder girdle: why you can’t sympathize with Russian truckers
- How to clean your computer from junk and speed up its work
- Wedding predictions for guests: funny and funny ideas Comic fortune-telling of a gypsy in prose
- Business on coffee grounds or how to open a mobile coffee shop on wheels?
- Congratulation of a gypsy on a woman's anniversary
- Define the concepts: choir, vocal ensemble, trio, duet, solo
- Guy's Room Design: Ideas and Examples
- General rules for drawing up a foundation plan House foundation drawings
- modern art deco bedroom small art deco bedroom
- Pansies: characteristics and photos of flowers
- Making an art deco bedroom: the choice of materials Beige art deco bedroom
- Bedroom interiors in art deco style Bedroom art deco style beige
- Young: planting and care in the open field Young planting and care in the open
- Varieties for open ground
- Pansies: cultivation and care in the open field









