Features of the treatment of reflux esophagitis with homeopathy and drugs
Since reflux esophagitis can be due to various reasons, the therapeutic approach is complex. It includes dietary and postural therapy, treatment with medications and aids, and surgical correction. The choice of drug, dosage and duration of its use also depend on many factors. Therefore, it is necessary to take medications after consulting a specialist.
The main principles of treatment of reflux esophagitis are:
- the introduction of restrictions in the diet and the maintenance of a certain lifestyle;
- reducing the acidity of the contents of the stomach by prescribing appropriate drugs;
- stimulation of the motility of the digestive tract, increased evacuation activity;
- the appointment of drugs that provide restoration and protection of the gastric mucosa.
It should be noted that all principles of treatment are closely interconnected. Failure to comply with one of them significantly reduces the effectiveness of therapy.
The main course of medical therapy
The duration of the main course of therapy for reflux esophagitis is 4 weeks. If an erosive form of the disease is observed, then the duration of treatment is increased to 8 weeks, while it is possible to increase the dosage of drugs. If there are changes outside the esophagus (especially in elderly patients), then therapeutic treatment can last up to 12 weeks. When the effect is achieved, the patient is prescribed maintenance therapy.
It should be noted that in many patients with reflux, the disease is chronic and is accompanied by relapses. In this case, if the symptoms of esophagitis are not observed, then drugs are prescribed as needed.
At the erosive stage
In the presence of minor and single erosions, the treatment of reflux esophagitis can also last 4 weeks. Otherwise, the duration of treatment is 2 months. Prescribe proton pump inhibitors (morning and evening). Additionally, the reception of omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole is indicated. These drugs are also taken twice a day. The most effective in this case is rabeprozole, which is enough to take once a day.
Even after successful treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis, the vast majority of patients remain at risk of recurrence throughout the year. Such people need long-term therapy with PPIs taken in half doses. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor, taking into account many individual parameters (age, complications, and others).
At non-erosive stage
If there are no erosions, then the PPI is taken once a day for 4 weeks. The amount of the drug taken depends on the intensity of inflammation and is in the range of 10-40 mg. Without fail, after the main course, maintenance therapy is indicated, the duration of which is determined by the attending physician and can last up to six months.
Possible treatment regimens
In the treatment of reflux esophagitis, the following schemes can be used.
- The same drug is used. Accompanying symptoms, complications and changes in the mucous membrane are not taken into account. This is an inefficient approach.
- It implies diet therapy, taking antacids. Medications are prescribed with varying degrees of exposure, depending on the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Effective in the treatment of severe forms of the disease. First, the reception of strong PPIs is shown. After the removal of the inflammatory process, weak prokinetics are prescribed.
The choice of the scheme is carried out by the attending physician based on the clinical picture and examination data.
Classic scheme in 4 stages
The classic treatment regimen for reflux esophagitis, presented in 4 stages, depends on the degree of the disease.
As can be seen from the table, the higher the degree of development of the disease, the stronger the drugs.
Important milestones
Drug treatment is carried out in 2 stages. The first is aimed at eliminating provoking factors and ensuring the healing process of the mucous membrane of the organ. At the second stage, the goal of therapy is to achieve remission. In this case, 3 treatment options are possible:
- taking PPI for a long time in a high dosage;
- as needed, short-term (5 days) intake of PPIs;
- the drug is taken only if symptoms appear.
The doctor chooses the necessary option, after agreeing it with the patient.
Preparations
For drug treatment of reflux esophagitis, different groups of drugs are used, which differ from each other in many factors. They may have a different mechanism of action, the duration of the onset of the effect, vary in time of administration, price, and so on.
Antacids and alginates
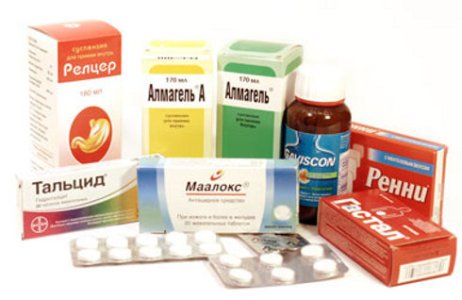 The purpose of antacids is to neutralize hydrochloric acid. In addition, they promote the release of bicarbonates, bind bile acids, and inactivate pepsin. Preference is given to non-systemic preparations that contain aluminum and magnesium, for example: Gastal, Phosphalugel, Maalox. Experts recommend using drugs in liquid form for the treatment of reflux esophagitis.
The purpose of antacids is to neutralize hydrochloric acid. In addition, they promote the release of bicarbonates, bind bile acids, and inactivate pepsin. Preference is given to non-systemic preparations that contain aluminum and magnesium, for example: Gastal, Phosphalugel, Maalox. Experts recommend using drugs in liquid form for the treatment of reflux esophagitis.
Alginates are also designed to reduce the acidity of the stomach contents. They contain alginic acid. These include: sodium alginate, Gaviscon, Topolkan. They are preferred over antacids containing aluminum.
PPI - proton pump inhibitors
Proton pump inhibitors - PPIs - drugs designed to reduce the acidity of gastric juice by blocking the release of hydrochloric acid by the cells of the body. They have a number of advantages:
- fast action;
- are not absorbed into the bloodstream;
- have a minimum of side effects.
The most common inhibitors are: Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole.
H2-histamine receptor blockers
H2-histamine receptor blockers are drugs whose purpose is also to reduce the acidity of gastric juice. They act on H2-histamine receptors, block them, as a result of which the release of hydrochloric acid stops. To date, there are 5 generations of drugs in this group, the most preferred of which are: Ranitidine and Famotidine.
NOTE! A characteristic feature of H2-histamine receptor blockers is to cause a backlash in the event of a sharp cessation of their intake (rebound syndrome).
Prokinetics
Prokinetics include drugs that increase the motility of the stomach and its evacuation activity. In addition, they operate in the following areas:
- reduce the time of contact of the contents of the body with the inner wall of the esophagus;
- contribute to the cleansing of the esophageal mucosa;
- increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Often, prokinetics are prescribed concomitantly with PPIs. Among them are: Domperidone, Itoprid, Tegaserod.
Cytoprotectors
This group of drugs includes drugs whose action is aimed at increasing the protective properties of the inner wall of the esophagus and stomach. Their use allows:
- increase the secretion of mucus and enhance its protective properties;
- improve blood circulation in the mucous membrane of the esophagus;
- reduce stomach acid (misoprostol);
- accelerate the healing of erosions and ulcers on the mucosa of the esophagus and stomach.
Among the drugs can be noted: Dalargin, Misoprostol.
Symptomatic treatment
Reflux esophagitis can be caused by another disease or occur with concomitant pathology against its background. In this case, the treatment will be symptomatic:
- If the cause is nervous, neurological or psychological problems, then consultation of the appropriate specialist is required. Sedatives, antidepressants, and others may be prescribed.
- In the presence of a stomach ulcer, antibiotics are additionally indicated.
- If the mucous membrane of the esophagus is subject to third-party effects on the background of reduced immunity, then it is recommended to take immunostimulating agents in parallel.
According to the same principle, treatment is carried out if any other disorder is a prerequisite for reflux esophagitis.
Homeopathy for reflux esophagitis
 When prescribing homeopathic medicines, the symptoms present at the moment and the prescribed medicines are taken into account without fail. The task of homeopathy in this case is to preserve and maintain the ongoing therapy, accelerate the regeneration of the tissues of the esophagus and stomach, as well as normalize the motor function of the digestive tract. In the course of treatment, the following means can be used:
When prescribing homeopathic medicines, the symptoms present at the moment and the prescribed medicines are taken into account without fail. The task of homeopathy in this case is to preserve and maintain the ongoing therapy, accelerate the regeneration of the tissues of the esophagus and stomach, as well as normalize the motor function of the digestive tract. In the course of treatment, the following means can be used:
- magnesium phosphate (pain relief);
- iris versicolor, veratrumalbum (for heartburn and chest pain);
- potassium bichromicum (heartburn, increased secretion of hydrochloric acid);
- belladonna, argentumnitricum (severe inflammation, erosion in the esophagus).
Homeopathic remedies are selected in strict accordance with the characteristics of the patient's constitution. Pay special attention to the physical and mental state, the intensity of the disease. At the first stage, symptomatic drugs are selected, and then, as the condition improves, the main drugs are prescribed, usually in high dosages (no more than three drugs).
Multivitamins
To accelerate tissue regeneration, restore general and local immunity and ensure a speedy recovery, vitamins and macro- and microelements are needed. The usual diet does not provide sufficient intake of these compounds in the body, especially in diseases of the digestive tract. Therefore, you also need to take multivitamin complexes.
Approaches
To date, there are various approaches to the medical treatment of reflux esophagitis. The choice of either method is determined by the severity of the disease, morphological changes in the esophageal tissue, secretion features and other factors:
- According to Sheptulin. The essence of the approach: the appointment of drugs of varying degrees of aggressiveness in several stages.
- Combination of antacids with diet therapy and lifestyle changes.
- Use of prokinetics or blockers of H2-histamine receptors.
- The use of proton pump inhibitors or H2-histamine receptor blockers in conjunction with prokinetics.
- According to Grigoriev Therapy is based on the stage of the disease and its form.
- According to Titgat:
- At the initial stage of development of reflux esophagitis, diet therapy is indicated in combination with antacids. The latter can be replaced with a short course of H2-histamine receptor blockers.
- In the second degree, a long course of prokinetics and H2 blockers is prescribed. A short course of treatment with proton pump inhibitors is possible.
- In the third stage of the disease, H2 blockers are combined with PPIs. Another option: prokinetics and blockers in high dosages.
If the effect of drug therapy is absent, then surgical intervention is indicated. In the event of a deterioration in the psychological state of the patient, Eglonin or Grandaxin with Teralen are prescribed.
Supportive care
The tasks of maintenance therapy include reducing the aggressive effects of drugs. In the first two stages of the disease, this function is performed by prokinetics in the usual dosage. With a more severe course of reflux esophagitis, strong H2-blockers are added to the prokinetics. Admission is permanent, under diagnostic control of the state of the mucous membrane.
Pregnancy and GERD
During pregnancy, the appointment of high doses of antacids with aluminum, as well as sodium bicarbonate, is contraindicated. Taking antacids with magnesium will result in a mild laxative effect. For treatment, you can use such medicinal and herbal remedies as:
- chamomile flowers;
- alginates;
- starch;
- alder seedlings.
The greatest effect is achieved with a combination of alginates and astringents.
Children
Drug therapy of reflux esophagitis in children should be carried out only under the supervision of a physician. The diagnosis is made after a thorough examination. With a mild degree of the disease, antacids or H2-histamine receptor blockers (Ranitidine, Famotidine) are most often prescribed. When used independently, it must be remembered that these remedies eliminate only the symptoms of the disease, and not the cause.
Early age
In infants, reflux is a normal physiological phenomenon, but its course also requires special attention. In the event of its transition to a pathological form, urgent measures will need to be taken to prevent the further development of the disease. Treatment of reflux esophagitis in infants is not schematized, as it is performed only according to strict indications and in accordance with a specific case. Basically, postural therapy, antireflux mixtures, correction of diet are used.
older age
For older children, as well as for infants, the treatment of reflux esophagitis begins with a change in diet, diet therapy, and the use of herbal decoctions. If non-drug therapy does not lead to relief of the condition, then drugs are used. At an older age, according to the testimony of a doctor, it is possible to use drugs such as:
- antacids and alginates;
- blockers of H2-histamine receptors.
The main drugs for treatment in this case are antacids. If the symptoms of reflux esophagitis in a child appear regularly, then the use of PPIs and blockers is additionally indicated.
ATTENTION! The choice of the drug, its dosage and the duration of the course of treatment is carried out only by a doctor!
Conclusion
Treatment of reflux esophagitis is a long process that requires a medical stage. If the drugs and the treatment regimen are chosen correctly, then this contributes to a faster recovery and prevention of relapses. Otherwise, the disease may take a chronic form and / or go to the next stage. Therefore, it is very important to contact a specialist in time and follow his instructions in a timely manner. To date, there is a sufficient number of medications and methods that allow you to get rid of pathology at any age.
Read more you will like:
- Intercostal neuralgia - what is it and how to treat
- How to quickly get rid of dry corns on the legs
- How to treat left ventricular hypertrophy
- Rating of the best drugs for rotavirus for children
- Making tea from currant leaves, the benefits and harms of the drink
- How to drink hydrogen peroxide according to Neumyvakin - an oral regimen
- Features of the treatment of plantar fasciitis with folk remedies
- The composition and beneficial properties of parsley root
- How to get pregnant quickly? Folk remedies
- Herbs-ants in the "pot-bellied" period or the use of herbal medicine during pregnancy
- Why does a sore throat and dry cough occur, and what treatment is required?
- Guy's Room Design: Ideas and Examples
- General rules for drawing up a foundation plan House foundation drawings
- modern art deco bedroom small art deco bedroom
- Pansies: characteristics and photos of flowers
- Making an art deco bedroom: the choice of materials Beige art deco bedroom
- Bedroom interiors in art deco style Bedroom art deco style beige
- Young: planting and care in the open field Young planting and care in the open
- Varieties for open ground
- Pansies: cultivation and care in the open field