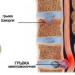
What is the curvature of the spinal column called? Scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine). With all types of scoliosis, a preponderance to the side of the chest is visible
Spinal curvature is a disturbance in the formation of the natural physiological curves of the spine. In the process of development of the human body, four curves are formed - thoracic, cervical and lumbar, and sacral kyphosis. Due to certain pathological processes or as a result of injury, additional bends or disturbances in the natural physiological curvature may form. In this case, you should seek medical help. The problem cannot be ignored, as this is fraught with the development of serious complications.
Etiology
The etiological causes of spinal curvature are divided into two groups - acquired and congenital. Congenital factors include the following:
- genetic abnormalities that have become a provoking factor in pathologies of the connective tissue of the spine;
- hereditary predisposition;
- ailments that lead to metabolic-dystrophic disorders;
- congenital pathologies of the central nervous system.
Acquired etiological factors include:
- muscle inflammation;
- injuries to the spine or other part of the musculoskeletal system;
- long-term with unilateral localization. For example, for kidney disease, education;
- muscle tension, which may be due to the formation of deep soft tissue scars;
- Scheuermann-Mau syndrome - curvature of the spine in the thoracic region;
- pathological lordosis and kyphosis;
In addition, the curvature of the cervical spine can be caused by the specifics of a person’s life activity - sedentary work in an uncomfortable or incorrectly selected chair can also lead to curvature of the spine and associated pathologies.
The lateral curvature of the spine is called. This is one of the most common pathologies, especially among adolescents.
Classification
Clinicians distinguish the following types of spinal curvature:
- scoliosis - pathological lateral bending;
- lordosis - pathological forward bending;
- kyphosis is an abnormal backward bending.
In turn, kyphosis is divided into the following types:
- arcuate - smooth rounded deformation of intervertebral discs;
- angular - protrusion of the corners of one or more intervertebral discs.
Somewhat less often, and only as a complication, a mixed form of several types of spinal curvature occurs.
The development of this pathological process is also distinguished by stages of development:
- first degree - the angle of the arc of curvature is no more than 10 degrees. At this stage there are no special external changes, the patient does not complain of feeling unwell;
- second degree – bending angle from 10 to 25 degrees. With prolonged physical activity, the patient complains of back pain;
- third degree - the angle of curvature varies from 26 to 50 degrees, the deformations are clearly expressed. Shortness of breath both during physical activity and at rest. Painful attacks in the muscles are almost always observed;
- fourth degree – not less than 50 degrees. In this case, problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, and upper respiratory system are observed. Physical activity of a person is minimal, since any movement provokes severe pain.
It should be noted that at the last stage of development of this type of vertebral deformity, massage and exercises will no longer be enough. Therefore, you need to seek medical help in a timely manner and not self-medicate.
Symptoms
The general clinical picture will be supplemented by specific signs, the nature of which will depend on the localization of the pathological process. You can notice the curvature of the spine in children or adults by the following signs:
- if a person stands straight and one shoulder is higher than the other;
- upon physical examination of the back, a protruding scapula is clearly visible;
- when tilted, a clear curvature is visualized.

Subjective clinical signs of spinal curvature include:
- attacks of pain localized in the back, chest, cervical region, which intensify even with minimal exercise;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- muscle weakness;
- when localized in the lumbar region, sexual dysfunction in men and ovarian dysfunction in women;
- deterioration in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system;
At the last stage of development of the disease, the clinical picture of which includes this symptom, signs of the clinical picture of cardiovascular, gastroenterological pathologies, and diseases of the genitourinary system may appear.
It should be understood that only a doctor can tell you how to cure spinal curvature correctly. Self-medication, especially with the use of exercise therapy or massage, can only aggravate the pathology, which will lead to the development of serious complications, including complete paralysis.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor performs a thorough physical examination. To confirm the diagnosis, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs;
- radiography.
In general, the diagnostic program, as well as treatment, is prescribed individually, depending on the current clinical picture, general health and age of the patient.
Treatment
Treatment of spinal curvature in a child or adult should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Basic therapy is selected based on the diagnosis. Treatment almost always includes a course of exercise therapy. In advanced stages, surgical intervention is performed.

Drug therapy includes the following:
- painkillers;
- chondroprotectors;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamin complexes.
As additional medical measures, special exercises for spinal curvature, massage, and manual therapy courses are prescribed.
Spinal curvature can be corrected at home only in the initial stages of deformation through the following measures:
- elimination of physical activity;
- developing correct posture;
- arranging the right workplace - the chair should not only be comfortable, but also correct, from a physiological point of view.
A set of exercises that can be done at home should be agreed upon with your doctor.
Prevention
Avoiding pathological curvature of the spine is much easier than eliminating the consequences of such a pathological process and accompanying ailments. There are no specific preventive measures, since this is a symptom and not a separate disease. To prevent such pathology, preventive measures regarding etiological factors should be applied in practice.
Our spinal column is not just a straight line. Starting from the birth of a person, physiological curves gradually form on the spinal column; their main purpose is to soften the daily load on our spine.
In addition to the necessary natural curves, people can also develop pathological ones, they are called curvatures. When they form, the main danger is not only a noticeable physical defect, but also a deterioration in the functioning of the most basic organs - the lungs, heart, and parts of the digestive system.
Types of spinal curvatures
Normally, a person, starting from birth and over the next few years of life, develops four physiological, that is, natural curvatures in the spinal column. They are found in humans in the sacrum, cervical, lower back and thoracic spine.
Curvatures are usually called those bends that abnormally deviate from the axis of the spine forward, backward or to the sides.
The physiological curves listed above deviate only backward or forward; deviation to the side from the axis is designated in medicine by the term scoliosis. Kyphosis and lordosis are always considered normal only if their curvature does not exceed certain values.
The photo shows types of spinal curvatures
As soon as these curvature indicators begin to deviate from the norm, pathological kyphosis or lordosis occurs, requiring a special course of treatment.
Scoliosis
The photo shows the curvature of the cervicothoracic spine against the background of kyphosis

There are two forms of this pathology; with the arcuate one, a uniform arc of curvature is noted. Angular kyphosis occurs due to protrusion of several adjacent vertebrae with the formation of an angle. Mild forms of kyphosis in humans include stooping.
Causes
Deviation of the spinal column from the normal axis can be due to two groups of reasons - acquired during life and congenital.
Under the influence of provoking factors, structural or non-structural abnormal curvatures are revealed in the spinal column. The term structural refers to various changes in the structure of the vertebral body or the entire spinal column in general.
There are many reasons for such anomalies, the most basic and common of which include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Genetic abnormalities that lead to pathologies of connective tissue elements in the spine.
- Injuries, benign or malignant neoplasms of the spine.
- Diseases of the central nervous system (congenital or acquired during life). These are cerebral palsy, polio, conditions after cerebral strokes.
- Diseases with metabolic-dystrophic processes in the body - osteoporosis, rickets.
- Bone tuberculosis, late stages of syphilis.
- Rheumatism.
Among adult patients, the development of pathological curvatures is often detected against the background of several years of ongoing and in people with.
Various non-structural curvatures of the spine are secondary, that is, they arise due to pathology of the organs or skeletal system. The main causes of such spinal curvatures are:
- Congenital anomalies of the bone structures of the pelvis and lower extremities, most often these are flat feet, congenital dislocation of the hip, shortening of one limb, clubfoot.
- Injuries to the spine and pelvic bones.
- Unilateral long-term or frequently recurring intense pain syndrome. A similar symptom can occur with kidney diseases, gallstones, and liver diseases.
- Deep scars of soft tissue on one side of the body, leading to muscle tension.
- Myositis, that is, muscle inflammation.
In children, curvature of the spinal column often occurs with rapid growth of the skeleton and the initial weakness of the muscular corset. In the occurrence of pathology in schoolchildren, the leading role is played by constant incorrect body position in classes and when doing homework.
Symptoms
 The patient's complaints with various curvatures of the spinal column will depend not only on the type of pathological curvature, but also on its location, and even more on the degree of curvature of the arch.
The patient's complaints with various curvatures of the spinal column will depend not only on the type of pathological curvature, but also on its location, and even more on the degree of curvature of the arch.
- The first degree during examination is set if the arc angle is no more than 10 degrees. There are no special changes in well-being with this degree of curvature, and there is no noticeable external defect. You can pay attention to stooping, uneven height of the shoulder blades and raised shoulder girdle on one side when a person is without clothes.
- The second degree of curvature is set at angles ranging from 10 to 25 degrees. Structural abnormalities in the vertebrae are detected by the type of twisting. There is unequal tone of muscle groups on the back or front of the chest. When sitting for a long time, back pain occurs and physical activity is poorly tolerated.
- The third degree of curvature ranges from 26 to 50 degrees. The deformation of the chest and spinal column is immediately noticeable. A person has almost constant painful spasms in the muscles of the back, cannot tolerate even the most moderate physical activity, and is bothered by shortness of breath, both during exercise and at rest.
- If the arc angle is determined to be more than 50 degrees, then we are talking about the most severe degree of curvature - the fourth. Severe deformation also negatively affects the functioning of the heart, bronchi, lungs, liver, and stomach.
Symptoms of a violation of the normal, natural position of the spinal column also depend on where the curvature itself is formed. If pathology develops in the neck, then the person is often bothered by headaches, dizziness, and various movement disorders.
With curvature of the lumbar spine, motor and sensory disturbances occur in the legs, women develop ovarian dysfunction, and men may experience sexual dysfunction.
How to determine the presence of a disease?
Deformation of the spine is revealed by a careful external examination, this applies even to the first degree of curvature. You can independently assume that you have a pathology based on the following signs:
- If you stand straight, one shoulder will be lower than the other.
- When examining the back, you can see the protruding angle of the shoulder blade, and if you bend forward downwards, the curvature of the spine will be noticeable.
- In a straight standing position, you need to lower your arms down and look at the distance between them and your waist. If it is very different, then an abnormal curvature of the spine is often detected.
Subjective signs of pathological changes in the spinal column include pain in the back, neck, chest, numbness and decreased strength in the limbs.
Courses are used to reduce pain and relieve muscle spasms. With the help of physiotherapy, they improve blood circulation and relieve inflammation from tissues.
Corseting is another auxiliary method for eliminating curvatures. Corsets can be supportive or corrective. The latter are most often prescribed to children, since at this age it is quite possible to reduce the degree of scoliosis.
Supportive corsets of various types do not allow the pathology to worsen. The type of corset is selected in each case individually.
Prevention
 Curvature of the spine is not only an externally noticeable defect, but also a disruption of the functioning of many organs and systems.
Curvature of the spine is not only an externally noticeable defect, but also a disruption of the functioning of many organs and systems.
In a severe form of pathology due to a disorder of the most important functions in the body, a person quickly becomes disabled and often dies at a young age.
Therefore, the prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system should be observed from childhood and in fact it is not difficult.
Necessary:
- Since childhood, I have been constantly involved in various sports.
- Develop correct posture.
- Eat fully and only healthy food.
- Treat all diseases related to metabolism and the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
Do they take you into the army?
The issue of military service worries many young men with scoliosis. With the first degree of curvature, identified in childhood and successfully treated, they are accepted into the army without restrictions. With the second degree of curvature, a young man can serve in certain troops by decision of the commission.
The degree of curvature of the spine also influences the decision about suitability for service. Also, in case of scoliosis, a temporary deferment may be given. In case of severe degrees of pathology, they are released from service.
The commission makes a decision on whether or not to serve on the basis of X-ray data and previous entries in the medical record. Therefore, it is in the interests of young people to always undergo prompt examination if scoliosis is suspected.
Which doctor should I contact?
Several doctors should be involved in the treatment of spinal curvatures. If you suspect such a pathology, it is best to first contact a neurologist, who will issue referrals for examination and subsequently refer the patient to an orthopedist. This specialist already deals with pathologies of the skeletal system.
In addition to an orthopedist, treatment of spinal curvatures is impossible without an exercise therapy instructor or a chiropractor. At the last stages of scoliosis, surgeons are also involved in treatment.
If you suspect a curvature, it is necessary to undergo a full examination as soon as possible. At the initial stage, eliminating the changes will require a minimum amount of your own efforts and finances.
Interesting video about beneficial and harmful exercises on the spine:
CURVATION, curvature, cf. 1. Action under Ch. bend warp and warp warp. 2. Curved place, bend, curvature. There are many bends in the pipes. || Deviation from the correct position, curvature. Rachiocampsis. 3.… … Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary
Distortion, deflection; curvature, bending, warping, distortion, curvature, deviation, bending, gyrus, retreat, distortion, scoliosis, curvature, figure eight, disfigurement, skew, distortion, distortion, lordosis, curvature, ... ... Synonym dictionary
CURVATION, I, cf. 1. see bend, sya. 2. A curved place, a curved part of something. Curvatures on a tree trunk. 3. transfer Evasion, deviation from the right direction in activity, behavior. Ozhegov's explanatory dictionary. S.I.... ... Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary
curvature- deformation - [A.S. Goldberg. English-Russian energy dictionary. 2006] Topics energy in general Synonyms deformation EN hoggingwarping ... Technical Translator's Guide
curvature- CURVATION, i, cf Part of something l., curved, indirect shape, curved, curved place. A bend in the wire can be easily straightened with a hammer... Explanatory dictionary of Russian nouns
Wed. 1. process of action according to ch. bend, bend 1., 2. 2. The result of such an action; bend, curvature. 3. transfer Deviation, deviation from something correct; violation of the norm. Ephraim's explanatory dictionary. T. F. Efremova. 2000... Modern explanatory dictionary of the Russian language by Efremova
Curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature, curvature (Source: “Full accentuated paradigm according to A. A. Zaliznyak”) ... Forms of words
Straight surface... Dictionary of antonyms
curvature- curvature, I... Russian spelling dictionary
curvature- (2 s), Ex. about curvature... Spelling dictionary of the Russian language
curvature- Syn: distortion, deflection Ant: straightening... Thesaurus of Russian business vocabulary
Books
- About the most important thing. Keep your child healthy! (3DVD), Pelinsky Igor, 1. No! childhood scoliosis! Massage and gymnastics Scoliosis (from the Greek skoliosis - curvature), or lateral curvature of the spine, is a disease that most often occurs in children aged… Category: Sports and health Series: Educational games and techniques for children Publisher: Sova-Film,
- Gen. Model of the universe, Lyakhovitskaya Henrietta, Scientific approach to religious and esoteric views: a new form of the periodic system of chemical elements; structure and evolution of the universe; curvature of time; "myrometry" instead... Category:
Spinal scoliosis is a fairly common pathology in childhood and adolescence: approximately a quarter of musculoskeletal diseases are caused by this disease. In adults, scoliosis is much less common and is often a consequence of injuries or surgical interventions on the structures of the spinal column.
The main problem is the late diagnosis of scoliotic curvature of the spine, when the deformation of the spinal column becomes clearly noticeable.
What it is?
The human spine is normally not perfectly straight and has physiological curves (and kyphosis). However, in the frontal plane (front or back), the vertebrae are aligned in a straight line. If this line deviates sideways with the formation of one or more arcs, then in this case they talk about.
It is important to know that true scoliosis is characterized by some signs that are detected in combination:
- Frontal curvature of the spinal column.
- Vertical torsion (twisting) of the vertebrae, their deformation.
- Persistent (organic) fixation of the spinal column.
In addition, destructive and fibrous changes in the intervertebral discs are often detected, worsening the normal functioning of the vertebrae and aggravating the pathological manifestations of the disease.
If the lateral deviation of the spine is leveled out when the body position changes (for example, lying down or when pulling the head) and there are no deforming changes in the vertebrae, they speak of.
This pathology has been known for a very long time. Even ancient doctors mentioned a “crooked spine” in their manuscripts. Actually, the term “scoliosis” is translated from ancient Greek as “crooked, twisted spinal column.”
Major functional changes
Of course, organic metamorphoses in the vertebrae and surrounding tissues during scoliosis are reflected in the body as a whole. Consequently, with scoliotic curvature of the spine one can observe:
- Pathological contraction or overstretching of the trunk muscles.
- Damage to the ligamentous apparatus and back muscles.
- The appearance of functional intervertebral blocks with subsequent imbalance of the surrounding muscles. This ultimately leads to the development of excessive mobility (mobility) of the vertebrae.
- Disturbance of movements of the spinal column.
- Displacement or compression of spinal cord structures with the development of corresponding neurological symptoms as a result of vertebral deformation and damage to the intervertebral discs.
- Compression of the lung tissue with subsequent progressive deterioration of respiratory function.
- Displacement of the anatomical position of the heart and large vessels. This can lead to the formation of hypertrophic changes in the right parts of the heart and the development of progressive cardiopulmonary failure.
- Lumbar localization of scoliosis causes problems with the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and also leads to a distortion of the pelvic axis.
Taking into account the diverse influence of lateral curvature of the spinal column on almost all organs and systems of the human body, the term “scoliotic disease” was proposed.
When should you see a doctor?

You can diagnose the initial signs of scoliosis at home. It is enough to carefully monitor the child’s posture and, if suspicion arises, carry out some simple tests. All of them are performed in various positions of the body: sitting, standing, lying down and bending forward with arms down. You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- Slouch.
- The location of the shoulder blades, shoulder girdle and elbows is not at the same level or at the same distance from the axis of the spine or torso.
- Visible lateral displacement of the spine.
- The appearance of muscle ridges in the chest or lower back when the body is tilted to the side.
- Visible bone deformities in the chest area.
In addition, frequent manifestations of scoliosis are: headaches, fatigue (especially during physical activity), discomfort in the chest, back or pelvis.
If you have the slightest suspicion of scoliosis, you should immediately consult a doctor, since treatment of this pathology is most effective in the initial stages of the development of the disease.
Types of scoliosis
Spinal scoliosis can be of congenital or acquired origin. If a pathology of the spinal column is detected in a newborn or in the first months of a child’s life, then most likely we are talking about a congenital form of the disease. The frequency of this form of scoliosis is low and is about 3%.
Acquired scoliosis usually occurs in. Its formation is influenced by many reasons, which can be roughly grouped into the following groups:
- Traumatic – after previous injuries or surgical interventions on the spinal column or surrounding structures.
- Static (for pathologies of the lower extremities, in which compensatory pathological bending of the spine occurs. For example,).
- Rachitic.
- Neurogenic - for diseases accompanied by a disorder of the function of motor neurons of the spinal nerves (for example, poliomyelitis or cerebral palsy).
- Idiopathic - the true cause cannot be determined.
In a significant number of cases (more than 80%), it is idiopathic scoliosis that is detected, which most often develops in girls aged 10–13 years.
Forms and types

There are right- or axes of the spinal column. In addition, there can be one arc of curvature or several (two or three). Based on this, scoliosis is distinguished:
- C-shaped.
- S-shaped.
- Z-shaped.
Depending on the location of the curvature, the following types of scoliosis are distinguished:
- Upper thoracic (or cervicothoracic).
- The thoracic one is formed most often.
- Thoracolumbar.
- Lumbosacral.
Regardless of the location and shape of the lateral curvature of the spine, it is necessary to determine the angle of the deformity and the clinical severity of the disease.
Severity

The main method for diagnosing lateral curvature of the spinal column is x-ray, which has not yet lost its value. The most common methods for determining scoliosis curvature are two: Chaklin or Cobb. Depending on the angle of the deformity, there are four degrees of severity of scoliosis:
- First. Mild lateral displacement of the spinal column, which is usually not accompanied by any clinical manifestations. The primary arc angle is up to 10 degrees (Cobb). Vertebral torsion manifests itself as a slight deviation of the spinous processes from the midline.
- Second. The scoliosis angle ranges from 11 to 30 degrees. A compensatory arc appears. The radiograph clearly reveals torsion and deformation of the vertebrae with maximum manifestations at the apex of the scoliotic arch. Upon examination, muscle ridges are visible in the chest and lower back, which are caused by pathological muscle tone.
- Third. A pronounced rib hump and visible deformation of the chest appear. The retraction of the intercostal spaces is visualized on the concave side of the arcuate curvature and protrusion on the opposite side. The angle of scoliosis is 31–60 degrees. A wedge-shaped deformity of the vertebrae and a change in the width of the intervertebral fissures are revealed. The spinal cord is compressed by pathologically altered vertebrae, which is accompanied by the development of various spinal symptoms.
- Fourth. Severe deformities of the chest develop, a distortion of the pelvic axis and the entire torso towards the main arc of curvature. The costal hump becomes pronounced. The normal functioning of internal organs is disrupted: lungs, heart, etc. X-rays reveal serious deformation of the vertebral bodies and vertebral joints. Compression of the spinal cord structures occurs and the formation of progressive paresis of the lower extremities. The angle of curvature is over 60 degrees.
Depending on the severity of the lateral deformation of the spinal column and pathological changes in nearby structures and organs, the method of treatment for scoliosis is determined, as well as the prognosis of the disease.
Treatment

Both conservative and surgical methods for correcting scoliosis are used. For each of them there are clearly defined indications and contraindications. Conservative treatment is most effective in the initial stages of scoliosis. In case of severe deformities (third or fourth degree), it is often necessary to resort to surgical correction.
The choice of treatment method for scoliosis directly depends on the following factors:
- The reasons that caused the curvature of the spinal column.
- The severity of the pathological process.
- The presence and rate of progression of spinal deformity.
The main goals of treatment are: improving the quality of life of a patient with scoliosis and preventing the progression of the disease.
The complete formation of the spinal column ends at approximately 21 years of age. Therefore, the earlier treatment is started, the faster and more effective it is.
Treatment of scoliosis should begin with eliminating the cause that caused the curvature of the spinal column. So, when the lower limb is shortened, it is necessary to wear special orthopedic shoes or insoles. In case of traumatic damage to the vertebrae, treatment begins with their surgical correction, etc.
Conservative

For this type of treatment of scoliotic curvature of the spine, the following methods are used:
- Special corrective gymnastics and. This treatment method is prescribed to absolutely all patients with scoliosis and should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In the initial stages of the disease (scoliosis angle up to 15 degrees), the use of only this type of treatment may be sufficient for a complete recovery.
- Treatment by position. The essence of this method is to periodically or constantly wear a special derotation corset that straightens the spine. In cases of severe scoliotic curvature (scoliosis angle 20–25 degrees), as well as after surgical interventions, it is recommended to use the corset almost around the clock (removing it only during hygiene procedures and gymnastics).
- Massage and manual therapy are prescribed with caution and for specific indications. And, of course, they must be carried out by an experienced specialist.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - electro- and phonophoresis, electromyostimulation, exposure to a magnetic field, electric current, etc. The choice of a specific method of exposure to physical factors is determined by the doctor and serves more as an auxiliary method of treatment.
- Drug treatment consists of prescribing vitamin and mineral complexes, general strengthening drugs and improving microcirculation, etc. Symptomatic treatment of emerging pathological manifestations is also carried out.
Therapy with conservative methods is most effective for such spinal curvatures, characterized as the first and. If the deformity is more pronounced, complex treatment is used, combining surgery with wearing a corset and doing gymnastics.
Surgical

Surgical intervention is usually indicated for obvious deformities of the chest and torso, in which the functions of vital organs are noticeably affected. Also, indications for surgery are the obvious ineffectiveness of conservative treatment and the rapid progression of the disease.
In addition, there are types of scoliosis, the root cause of which can be eliminated through surgery.
There are a lot of surgical methods for treating scoliotic curvature of the spine, but they all boil down to two areas:
- Creation of spinal fusion of individual vertebrae. The essence of the operation is the alignment of the curved part of the spine, followed by a fixed connection of the involved vertebrae with each other. For this purpose, various metal structures or autografts are used.
- Plastic correction of individual pathologically changed vertebrae.
The optimal age for surgical treatment is no earlier than 13–15 years. Carrying out an operation at a younger age, when the processes of growth and formation of the spine are not yet fully completed, can lead to an unsatisfactory result and the development of complications.
Treatment of scoliotic curvature of the spinal column is a long and stressful process for both the patient and the doctor. The patient is required to strictly and routinely comply with all medical prescriptions. Only in this case the chances of successful correction of deformity and improving the quality of life increase significantly.
In an adult, the formed spine has some bends. Their purpose is to absorb vertical loads that affect the body from the outside. These are physiological curves. The side ones are called scoliosis. The disease is characterized by a persistent deviation from the physiologically straightened position.
Brief description of the disease
So, lateral curvatures of the spine are called, according to medical terminology, scoliosis. The disease can be easily identified on your own. Just look carefully at the back. With scoliosis, the spine has one or more curves that are not normal.
Girls are more susceptible to severe forms of the disease. The photo below clearly demonstrates the curvature of the spine. The onset of scoliosis in adults is associated with inactivity in childhood. As a rule, the disease was not diagnosed in a timely manner and, as a result, it was not subjected to the necessary treatment. In some cases, degenerative diseases of the spinal joints can lead to this diagnosis.

Etiology of scoliosis
Many factors can trigger the development of scoliosis. Let's look at the main ones. So, the main causes of spinal curvature are as follows:
- Congenital disease. Pathology occurs as a result of underdevelopment of the vertebrae. Sometimes additional joints are laid in the column. In some cases, an abnormal condition is noted. The disease can also develop as a result of connective tissue weakness.
- Rickets. This disease is characterized by soft bones and muscle weakness. Against the background of such pathologies, lateral curvatures of the spine may appear. They are called rachitic scoliosis.
- Paralysis. This pathology is based on a nervous disease, unilateral muscle damage. Scoliosis can occur as a result of childhood
- Poor posture. These scolioses received the appropriate name - “school”, since they mainly arise as a result of an incorrectly selected desk (table), ignoring backpacks and carrying briefcases (bags on one shoulder). Constantly holding the baby by one hand can lead to pathology.
- Injuries. It is especially worth focusing on generic ones. According to statistics, about 90% of children develop scoliosis as a result of difficult births.
- Physiological pathologies. When one of the legs is shortened, the spinal column tries to compensate for the position of the body. As a result, permanent curvature develops.
- Ailments of other systems and organs. Such pathologies cause painful discomfort in the child. As a result, the muscle tissue that supports the spinal column weakens. Such children develop lateral curvatures of the spine. Such pathologies are called visceral scoliosis.
- Emotional tension, stress. Introverts and withdrawn children are susceptible to this form of curvature.

Most often, scoliosis occurs due to a combination of several factors. As a rule, the first manifestations of the disease are observed in children 7-9 years old. The next dangerous age at which scoliosis can appear is adolescence. After all, the body is experiencing the most rapid growth.
You can identify the pathology yourself. But the best way not to miss the onset of the development of the disease is for the child to undergo periodic medical examinations.
Classic signs of scoliosis
As noted above, the curvature of the spine (see photo above) can be determined visually. There is a group of external signs that accurately indicate this pathology.
Doctors have identified eight classic symptoms that characterize scoliosis. Let's look at them:
- The child's shoulders are at different levels. One is significantly higher than the other.
- Incorrect head position. Draw a mental vertical axis, starting from the middle of the pelvis. If the position of the head deviates away from this line, there is a possibility of developing scoliosis.
- Uneven hip placement. One of them is slightly higher than the other, and may even protrude a little forward.
- The halves of the chest differ in their location in the horizontal direction.
- Slanted or curved waist.
- Changes in the structure or appearance of the skin along the spinal line.
- The body position is slightly tilted to one side. In this case, a displacement is always observed in the same direction.
- When bending forward, it is visible from one side.

If you notice at least one of the above signs, and even more so if several are observed at once, you should definitely visit an orthopedist.
Degrees of curvature
There are many classifications of this pathology. We will look at the degrees of curvature of the spine. There are 4 of them. The division into such categories depends on the size of the angle of the curvature arc.
Scoliosis degrees:
- The angle of curvature is no more than 10 degrees. Visually, this asymmetry is almost invisible. The presence of pathology can be suspected by stooping and uneven shoulder levels.
- Angle - 11-25 degrees. This pathology is clearly visible visually. It is observed in the shoulder and pelvis area. Pathological muscle tension leads to the formation of muscle ridges in the lumbar and chest areas.
- The curvature takes on dimensions of 26-50 degrees. Clearly visible. An internal hump often forms.
- Angle greater than 50 degrees. The pathology is clearly expressed. Inability to tolerate even minimal physical activity. With this degree, internal organs suffer.
Treatment methods
It should be remembered that lateral curvature of the spine is a serious pathology, which, if ignored, can significantly reduce the quality of life and lead to unforeseen complications. Therefore, be sure to periodically undergo the recommended medical examination with your child.

If a pathology is detected, the orthopedist will recommend adequate treatment. Control methods are based only on the individual characteristics of the patient. The child’s age, maturity, gender, family history, and angle of curvature (shown by x-ray) are taken into account.
Wearing a corset
This method is prescribed to growing children whose curvature angle is 20-40 degrees. Of course, a corset will not correct or “remove” the curvature of the spine. Treatment in this way will prevent the progression of scoliosis. It is necessary to strictly understand that this measure will only be beneficial if prescribed by a doctor.
Physiotherapy
An effective method of combating the disease is a complex of exercise therapy. Such gymnastics will strengthen the muscle tissues that support When the stage is not advanced, it is possible to “remove” the curvature of the spine.

Massage
If necessary, the child will be prescribed this procedure along with therapeutic exercises. This is an additional method of training and strengthening muscle tissue. As a rule, massages in combination with physical therapy exercises quite effectively remove curvature of the spine. Treatment is aimed at stopping and reversing the progression of scoliosis.
Surgery
This measure is resorted to if it is more than 40-50 degrees. It should be remembered that this pathology will continue to progress. In such a situation, manual therapy, massage, and therapeutic exercises are powerless. Only surgical intervention can return the child to normal life.
- The most effective remedies for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia - symptoms, types of VSD and treatment
- What is partial pressure of oxygen
- The effect of low partial pressure of oxygen in the air on the body and adaptation processes
- Time it takes for alcohol to leave the human body
- Pyogenic granuloma as an interdisciplinary problem
- Cheek biting - causes and treatment Inner cheek disease
- Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease
- Neutralization reaction: definition, examples, application
- All about Duchenne myopathy: genetic factors and a complete list of symptoms Progressive Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart: what is it, symptoms, treatment The last ECG did not show left ventricular hypertrophy
- Lumbar disc herniation: symptoms and treatment
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) - symptoms, treatment and consequences of borreliosis
- News of health, medicine and longevity
- Pain worse after physical therapy
- Scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine)
- Osteochondrosis is the result of fatty degeneration
- Protrusion of the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment What to do for protrusion of the thoracic spine
- Manual therapy of the spine for hernia reviews
- Why does arthritis get worse?