Treatment of protrusion of discs of the thoracic spine. Protrusion of the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment What to do for protrusion of the thoracic spine
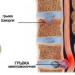
The term “protrusion” refers to a pathology in which protrusion of the intervertebral disc occurs without damage to the fibrous ring. The disc swells and bulges towards the spinal canal.
This pathology is a borderline state between a healthy and herniated spine. Most often, the disease is localized in the lumbar spine, less often in the cervical spine. Separately, thoracic localization is quite rare (but cervicothoracic protrusion often occurs).
1 Causes of protrusions in the thoracic region
There are many reasons for the development of dorsal protrusion of the thoracic spine. For the most part, the disease develops due to intense physical activity, and even physically fit people are not protected from this.
The main causes of protrusions in the thoracic region:
- Intense physical activity, significant overload of the spine (for example, lifting weights).
- Injuries to the spinal column, previous surgical interventions on the spine.
- Age-related changes in the spine, senile destruction of bone and cartilage tissue of the back.
- The presence of concomitant diseases: osteochondrosis, pathological kyphosis, scoliotic disease, arthritis.
- Sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity, general detraining of the body muscles.
1.1 How often do they appear?
Protrusions of the thoracic vertebrae are not uncommon in the general statistics of back diseases. However, of all the departments, the thoracic region is the least affected by this disease. Typically, protrusions affect the lumbar region due to its high mobility and the large load placed on it.
Why is the thoracic spine relatively rarely subject to protrusions?
It's all about its anatomical features. He is inactive and experiences relatively low loads. Even severe thoracic back injuries are tolerated relatively easily in most cases.
1.2 Risk group: who might get it?
Those people who are engaged in intense physical work (for example, builders and loaders) are most susceptible to protrusions of the thoracic region. The disease often develops in those who engage in martial arts, in particular wrestling (due to throwing).
Those who have an unbalanced diet are also at risk. Lack of calcium and various vitamins leads to “fragility” of cartilage and bone tissue. This is also aggravated by a lack of vitamin D, which is produced by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
And it follows from this that homebodies are also at risk. For normal production of vitamin D, you need to stay in the sun for 2-4 hours a day (it doesn’t have to be at its zenith, and weak rays are enough).
1.3 Why is this dangerous?
Protrusion is a borderline pathology. On the one hand there is a healthy spine, on the other there is a herniated disc. And therefore the most obvious danger is the transition of the disease to a hernia.
In addition, protrusion itself can lead to various serious problems. For example, severe protrusion of the spinal disc is fraught with occlusion (stenosis or compression) of the spinal canal.

If the cervical spine is affected, compression of the vertebral arteries is possible, although in reality such a complication is rare. We should not forget about the severe pain syndrome, which occurs quite often (especially when the Th7 and Th8 vertebrae are affected).
2 Symptoms of protrusions in the thoracic spine
There are no specific signs of protrusion in the thoracic region. Any of the symptoms are similar to those of other spinal diseases. The severity of symptoms is also variable: from very moderate (symptoms may not be observed at all for months) to painful.
Symptoms of protrusion in the thoracic region:
- Pain syndrome, from moderate to extremely painful. The longer the disease exists, the stronger the pain syndrome.
- Stiffness in back movements, especially in the first hours after waking up.
- Loss of coordination of movements, paresthesia (numbness) in one or both hands.
- Moderate shortness of breath and/or pain when trying to take a deep breath.
- Increased pain during physical activity or when trying to hunch over/stand up fully.
2.1 Diagnostics
Diagnosis of protrusion of the thoracic spine is carried out exclusively using imaging techniques (CT, MRI, radiography). Why? The fact is that the clinical signs of protrusion are very similar to other back diseases.

Based on the symptoms, protrusion can easily be confused with banal osteochondrosis or spondylosis. To confirm the protrusion, radiography is initially performed. But this is only a primary diagnosis; magnetic resonance or computed tomography is used to clarify.
Preference is given to MRI, since this technique is both accessible and absolutely safe for health. In complex cases, computed tomography using contrast agents and three-dimensional modeling of the spinal column may be required.
3 Treatment of protrusion of the thoracic spine
How to cure protrusion of the thoracic spine? Treatment of this pathology is exclusively complex, involving the use of several techniques simultaneously. It is pointless to treat the disease with folk remedies - this will only lead to a worsening of its course.
For the treatment of thoracic protrusion, the following is used:
- therapeutic physical education (physical therapy) and gymnastics - this includes medical physical education and some yoga exercises (basic and only the most gentle);
- massage (including manual) - usually a superficial classic massage is performed, but with a moderate course of the disease, manual therapy is also possible;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - acupuncture (acupuncture) and heat are most effective for eliminating pain;
- medications - warming patches, painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
3.1 Exercises
Physical exercise is the basis of treatment for most back diseases. And this is true in the case of protrusion. But gymnastics for this pathology is prescribed only in between exacerbations. If there is an exacerbation, gymnastics is contraindicated due to the fact that it can lead to rupture of the fibrous ring.

What exercises are best to do? Standard physical therapy is usually used. It is prescribed by a neurologist, traumatologist or therapist (if there are no other specialists). But in general, in the absence of contraindications, ordinary gymnastics is also effective.
You can also use yoga exercises or other therapeutic complexes. But only after consulting with your doctor.
3.2 Massage
Massage procedures are not an independent method of treating thoracic protrusions. They should be considered only as a method of symptomatic treatment to eliminate pain and swelling (this also has its place).
Typically, classic superficial massage is used. It is not necessary for a doctor to do it - you can also rely on relatives. In the simplest cases, even self-massage is suitable, if possible (for this you need to buy special devices).

Manual therapy is allowed for use in patients with moderate protrusion. It can be done only after obtaining an image of the spinal column and eliminating contraindications.
3.3 Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures, like massage, should also be considered as symptomatic treatment. Their goal is to reduce the severity of pain and, if possible, reduce inflammatory processes in the tissues of the back.
It is best to use acupuncture and heat on the back. Firstly, both of these procedures are extremely safe. Secondly, they do not create excessive pressure on the tissues of the spine (like, for example, shock wave physiotherapy).
In some cases, mud baths can help, but, unfortunately, they are carried out only during sanatorium-resort treatment. Therefore, acupuncture and thermal effects are a priority (but the second procedure has a lower priority, as well as effectiveness).
3.4 Treatment of thoracic protrusion (video)
3.5 Medicines
Along with physical exercise, drug therapy is the basic treatment for thoracic protrusion. Unfortunately, for many people who do not tolerate “chemo”, in 90-95% of cases it is impossible to cure thoracic protrusion without medications.
What is this therapy? A prerequisite is to prescribe painkillers to the patient (from Paracetamol to) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesil).
Anti-inflammatory and warming patches can also be prescribed, which need to be fixed on the pathological area of the back for 6-12 hours a day. In some cases, injections may be prescribed (for example, blockades for very severe pain).
Protrusion is a pathological change in which the intervertebral disc occupies an incorrect position, but the fibrous ring remains intact. Treatment of protrusion of the thoracic spine should be comprehensive and aimed at reducing pain and restoring the normal position and structure of cartilage tissue.
In the early stages of development, the disease occurs without a clear clinical picture. Over time, pinching of the nerve trunks occurs. At this time symptoms appear:
- Pain in different parts of the spine - cervical, thoracic, lumbar.
- Decreased elasticity of the muscles of the back and neck.
- Weakening of the muscular corset.
- Changes in sensitivity - numbness, goosebumps, tingling.
- Deterioration of limb functions.
- Feeling of stiffness in the back.
- Discomfort in internal organs – pain in the chest, abdomen, shortness of breath.
- Burning in the spine.
- Headache and dizziness.
- Decreased hearing and vision acuity.
The clinical picture in each individual patient depends on the location of the damage.
Why does a protrusion form?
Typically, such damage to the spine develops against the background of advanced forms of osteochondrosis. Other causes and triggers may include:
- excessive physical stress on the vertebrae or tension due to prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- bad habits leading to water-electrolyte imbalance - abuse of fatty and salty foods, etc.;
- mechanical injuries of the spine - bruises, falls, surgical interventions, damage during childbirth;
- genetically determined pathology of the musculoskeletal system;
- inflammatory lesions of the intervertebral discs;
- scoliosis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- in women – difficult labor.
How to identify pathology

The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that in the early stages the protrusion occurs unnoticed. The sequence of measures to identify the disease includes:
- Questioning the patient and taking anamnesis. The doctor clarifies in detail the nature of the complaints, the events preceding the onset of pain - injuries, heavy lifting, etc.
- External examination and description of the neurological status - allows you to see the forced position of the body, in which a person experiences less pain.
- Determination of muscle strength and tone, assessment of pain and tactile sensitivity, reflexes.
- Radiography is a research method that detects structural anomalies of bones and joints, phenomena of injury or osteochondrosis, and curvature.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to see the protrusion of the intervertebral disc.
- Electroneuromyography is a study of the functional state of muscle tissue and the conductivity of nerve trunks.
Treatment methods
Therapy for protrusion of the thoracic spine is aimed at eliminating pain and suppressing the progression of the process. To combat the disease, drug treatment, physiotherapy, surgical methods and traditional recipes are used.
Medications
Medicines are prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation, improve the condition of cartilage tissue and restore nerve conduction. The most commonly used groups are:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – Diclofenac, Movalis, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, etc.
- Diuretics for relieving edema during exacerbation - Lasix, Furosemide, Hypothiazide.
- Corticosteroid hormones (in cases where NSAIDs are ineffective) - Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone. Typically, such drugs are prescribed in the neurology department of the hospital.
- Muscle relaxants – Mydocalm, Tolperisone, Baclofen.
- Chondroprotectors – Terraflex, Alflutop, etc.
- Vitamin complexes that help improve nerve conduction - Neuromultivit, Milgamma.
- Means for improving local blood circulation - Pentoxifylline, Eufillin.
If drug therapy is ineffective, an epidural block is performed. To do this, local anesthetics and hormones are injected into the affected area.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where there is compression of the nerve trunks or spinal cord by bone tissue. For protrusions, this method is used quite rarely.
Traditional neurosurgery involves removing parts of the vertebral arches or damaged discs. An implant made from tissue taken from the pelvic bone is installed in this place.
Microsurgical treatment is considered less traumatic. After this, the recovery period is minimal. Endoscopic intervention using a laser is effective and relatively safe.
Gymnastics and exercise therapy
Physical therapy complexes are widely used outside the acute stage. Properly selected physical exercises can relieve muscle spasms, strengthen the muscle corset, and improve blood supply and nutrition to the discs. Movements should be soft, without jerking or significant stress on the spine. The complexes from Dr. Bubnovsky earned good reviews.
You can learn about other effective exercises by watching the video.
Magnetotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used in the acute period and in remission. Magnetic therapy helps relieve pain and swelling, helps restore spinal mobility and prevents further exacerbations. After this procedure, blood supply to the affected area improves and the rate of cartilage regeneration increases.
Manual therapy
This type of non-drug treatment is prescribed to restore the natural position of bones and cartilage. There are 2 types of manual therapy - structural and PIR (post-isometric relaxation). In the first case, work is carried out with ligaments and bones, aimed at correcting the abnormal position of the spine. The second method allows you to create tension and relaxation of muscles in the right places.
Massage
To treat protrusion of the thoracic spine, different types of massage are used:
- classic therapeutic – aimed at relieving spasms and pain, unloading the disc core, creating a muscle corset to support the spine;
- segmental-reflex – impact on individual parts of the body that are connected to the spinal nerves;
Effective for the treatment of thoracic protrusion is considered to be the effect on biologically active points of the body using traditional oriental medicine (shiatsu).
Laser therapy
In the complex treatment of osteochondrosis, laser beam exposure to the affected areas of the back is widely used. This procedure helps normalize metabolic processes in tissues, increases collagen production, and stimulates the regeneration of the fibrous ring in the intervertebral disc. In the acute period, this type of therapy can treat inflammation and pain.
Folk remedies
You can reduce discomfort and restore mobility in the thoracic spine using traditional medicine recipes.
The affected area of the ridge can be rubbed with alcohol tincture of St. John's wort. To prepare, take 100 g of dry grass and pour in 500 ml of vodka. Infuse for a week in a dark place, then filter. The prepared liquid is used to treat the affected area for a month.
Turpentine baths have a stimulating effect, relieve pain and swelling, and promote tissue regeneration. To prepare it at home, first make a mixture of a grated piece of baby soap, a glass of turpentine and 30 ml of salicylic acid. All ingredients are dissolved in 1 liter of hot water. To treat the back, prepare a bath by adding 3 tablespoons of the mixture to it. The water temperature should be about 45 degrees. The course of treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- From days 1 to 5, the procedure is used daily.
- From 6 to 20 - done every other day.
- From 21 to 40 - 2 times a week.

Electrophoresis with the drug Karipazim is used to treat diseases of the spine. Using a weak electric current, the drug penetrates the tissue. As a result, the elasticity of ligaments and cartilage improves, inflammation and swelling resolve.
Possible complications and contraindications in the treatment of protrusions
During the treatment of protrusion, undesirable side effects may occur. Their nature depends on the method of treatment:
- When taking medications, allergic reactions may develop. In addition, each drug has its own list of side effects. For most medications, contraindications for use include renal and liver failure, pregnancy and breastfeeding, and individual intolerance.
- Incorrectly and untimely massage, manual therapy or exercise therapy can not only worsen the patient’s condition, but also lead to the formation of a hernia and complete prolapse of the disc. Contraindications to these procedures are acute infectious diseases, skin lesions, and severe heart failure.
- Complications during surgery can be general surgical (reaction to anesthesia, bleeding, thrombosis, secondary infection), neurological (impaired function of the limbs), associated with the implantation. Contraindications to surgery may include acute infectious diseases, decompensated pathology of internal organs, pregnancy, and bleeding disorders.
- When using folk remedies, individual intolerance reactions are possible.
Is it possible to cure protrusion of the thoracic spine?
The prognosis for this pathology depends on the stage of development and on what therapeutic measures were taken.
Protrusion in itself is not a death sentence. Timely treatment can stop the process. It must be comprehensive and regular.
To combat spinal pathology, it is extremely important to normalize body weight, give the body dosed physical activity and try to maintain correct posture.
Prevention of disease
To prevent the development of protrusion in the thoracic spine, it is important to follow simple rules:
- Balance the diet - the tissues of the vertebrae and discs need nutrients, calcium, and vitamins.
- Regularly give moderate physical activity to your back muscles.
- Quit smoking and alcohol. These bad habits contribute to the accumulation of toxins in the body and worsen tissue respiration, which negatively affects the spine.
- You should lift weights carefully, keeping your back straight and your legs slightly bent at the knees.
- Watch your posture and gait, and avoid curvature of the spine.
- Choose an orthopedic mattress and pillow for night sleep.
Conclusion
The sooner the fight against the disease is started, the more favorable the prognosis. To treat protrusion of the thoracic spine, conservative methods are used (medicines, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy, folk remedies) as well as surgical methods.
Protrusion of the thoracic spine is a diagnostic sign that characterizes a number of pathological processes occurring in the intervertebral disc. This deviation is the initial stage of osteochondrosis, followed by a hernia.
Symptoms of protrusion of the thoracic spine are mild, and about 80% of all people have it, but most do not even suspect it.
Diagnosis is carried out by X-ray or MRI, and this often happens randomly, because this deviation does not show any external signs.
What is protrusion
Protrusion of intervertebral discs is not a separate disease, but a stage of a degenerative disorder such as osteochondrosis. Taking this into account, the treatment will be carried out comprehensively, and it is aimed at restoring the balance of nutrients in the intervertebral discs.

In itself, such a violation is not dangerous, but when there is a predisposition to pathologies of the musculoskeletal system or various risk factors are present, the protrusion progresses, which already ends in dangerous conditions.
Why does it occur
Long-term influence of negative factors on the spine in the form of high load, poor nutrition, muscle tension leads to pathological processes in the disc.
Its inner part, namely the nucleus pulposus, consists of collagen fibers and proteoglycans that retain moisture. These molecules (proteoglycans) provide the main function of the disc - shock absorption. If water balance is disturbed, this affects the condition of the entire spinal column.
The outer part of the disc is represented by the fibrous ring, and it also consists of collagen fibers, but of high strength. Its function will be to maintain the position of the nucleus pulposus and maintain its shape. During protrusion, it becomes deformed, and over time it may crack, which will lead to the release of the core. The latter, migrating along the spinal canal, compresses nerve fibers and roots, and the greatest danger is damage to the spinal cord.

The disc is nourished by the absorption of substances from nearby tissues, mainly muscles. Diffusion occurs only during the movement of the spine, and lack of activity causes this process to fail. Following metabolic disorders, atrophic processes begin, the intervertebral disc becomes thinner, loses strength, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, which can cause compression of the roots.
If the pathological changes do not stop, protrusion develops. Displaced vertebrae put pressure on the disc, causing it to protrude beyond the spinal column.
The protrusion stage ends when the annulus fibrosus ruptures.
Changes in the thoracic region are accompanied by a number of other degenerative processes. The patient may be diagnosed with concomitant abnormalities such as curvature, subluxation, spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis.
How does the violation manifest itself?
Degenerative changes can only be observed with radiography or magnetic resonance imaging. Protrusion is an x-ray sign that does not cause unpleasant symptoms. But in almost every case, disc damage is combined with other pathologies of the spine, and then a number of complaints appear.

TOWhat phenomena are alarming when the structure is disrupted?disc in the thoracic segment:
- mild pain syndrome;
- discomfort and stiffness in the area of the shoulders and shoulder blades;
- muscle weakness, numbness of the skin of the hands;
- increased pain when moving and maintaining one body position for a long time;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- swelling of tissues.
Treatment options
TOcomplex treatmentprotrusionin the thoracic spine includes:
- medications;
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- Exercise therapy (physical therapy);
- diet;
- osteopathy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.

When starting treatment for protrusion of the thoracic spine, risk factors should be eliminated, that is, those phenomena and conditions that could cause the disease and continue to aggravate it.
ABOUTgeneral rules and restrictions whenprotrusiondiscs in the thoracic region:
- avoid back injuries, impacts, pressure on the spine;
- add vitamin foods to your diet, take microelements;
- do physical therapy daily, devoting 20-40 minutes to it;
- give up alcoholic beverages, get rid of the smoking habit;
- keep your back straight, don’t slouch;
- sleep on a firm mattress and orthopedic pillow;
- spend less time sitting.
Pathologies of the spine can lead to dysfunction of internal organs, especially the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In this regard, the treatment of intervertebral protrusions is combined with the elimination of associated health problems and their prevention.

The attending physician refers you to other specialists for a preventive examination. Patients with spinal pathologies usually need help from specialists such as a neurologist, gastroenterologist, and nutritionist. After consulting with several doctors, it will become clearer how to treat the spine without harm to other organs and systems.
Folk remedies
Unconventionalmedicine offers the following recipes forprotrusion:
- Aloe juice, comfrey and honey. Comfrey is crushed, mixed with a glass of honey and three tablespoons of aloe juice. The mixture is stored in the refrigerator. The product is taken orally, one tablespoon at a time, on an empty stomach for 14 days. The course of treatment is repeated after 2 weeks.
- TOgarlic ashitsa. A glass of peeled garlic is crushed and poured with 100 ml of vodka. The product is infused for 10 days. The prepared mixture is applied to the thoracic region of the back for an hour until a burning sensation appears. The course of treatment continues until the condition improves.
- NastoykaSt. John's wort. A glass of the plant is filled with 200 ml of vodka, and the mixture is infused for a week. The finished product is used to rub the back before bed. The procedure can be repeated every evening for a month.
Drug therapy
It is necessary to treat protrusion with the use of medications for oral and local application. The main groups of drugs for improving the condition of the intervertebral disc are NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, antispasmodics, chondroprotectors, and painkillers.
TOwhat kindmedicinestwawill be useful for disc pathology in the thoracic region:
- Xondrosamine - chondroprotector, stimulates the growth of cartilage tissue, improves the regeneration of damaged structures;
- Glucosamine- chondroprotector, activates metabolic processes, improving nutrition of the diseased disc;
- Amedial - combined chondroprotector of a new generation;
- Dmelt - affects metabolic processes in bone and cartilage tissue;
- Xondromax - chondroprotector, slows down the aging process of cartilage, promotes the restoration of a diseased disc;
- TOarbamazepine - anticonvulsant, eliminates pain of neuropathic origin;
- Awhovegin - the drug improves peripheral blood flow;
- Midocalmus - injections and tablets eliminate muscle spasms and relieve pain;
- B vitamins- normalize the functioning of the nervous system, restore nerve conduction.
In parallel with pathogenetic treatment, symptomatic therapy is also carried out. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in combination with chondroprotectors (Diclofenac and Chonroitin).

During long-term drug therapy, the patient is also shown drugs to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (Gastal, Maalox).
Massage and exercise
Psample set of exercisesatprotrusionthoracic discs:
- Standing, arms down, legs brought together. As you exhale, raise your arms up, bending your back back. While inhaling, return to the starting position, then slowly bend forward. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Sitting on a chair, hands behind your head, spine in contact with the back. Slowly bend back, lowering your head. Repeat 5-7 times.
- Standing on all fours. Arch your back, throwing your head back. Stay in one position for up to 5 seconds, then relax. Repeat 5-7 times.
- Lying on your stomach, palms facing the floor. Leaning on your hands, raise your torso, bending backwards as much as possible. Repeat 3-5 times.
- Lying on your back, legs extended. Raise your head and shoulders. Stay in one position for 5-10 seconds. Repeat until fatigue appears.
Therapeutic massage for protrusion is prescribed by a doctor and performed by a professional. The course usually consists of 10-20 procedures, which are carried out at intervals of 2-3 days.

Between massage sessions, the patient may be recommended to simultaneously undergo a course of manual therapy. The latter will be effective for vertebral displacement and muscle spasms. Manual therapy involves a gentle impact on the spine, and when performed by a professional, there are no risks.
Complications
Without the treatment described above, protrusion of the discs of the thoracic spine can result in a number of pathologies. It is important to understand that this disease cannot be completely cured, because it is a disease with irreversible damage. Therapy is aimed only at slowing down pathological processes so that changes do not progress, leading to other disorders.
TOwhat can it lead toprotrusiondisks withouttreatment:
- rachiocampsis;
- compression fracture;
- vertebral displacement;
- hernia;
- disc sequestration;
- inflammation and pinching of nerve roots.

If the pain syndrome is severe, the patient will be given anesthesia in the hospital, after which an examination will be scheduled.
Diagnosis includes MRI or X-ray. In the image (MRI), the radiologist will be able to examine the tissue layer by layer, describing all the pathological processes.
Once the diagnosis is made, the attending physician will be able to prescribe medications and treatment procedures. Treatment of the spine is usually a lengthy process, so the patient undergoes regular examinations to assess the effectiveness of therapy and its correction.
One of the most unpleasant and sometimes severe complications of osteochondrosis is protrusion of the intervertebral disc. The word protrusion comes from the Latin protrusion - protrusion, protrusion. This literally means protrusion, extension of the intervertebral cartilaginous disc beyond its position in the intervertebral space. Most often this happens towards the intravertebral canal, where there are fewer obstacles from ligaments and muscles.
Protrusion itself is not a disease, but a syndrome associated with spinal osteochondrosis, or rather, its complication. This occurs due to a combination of the following factors:
- reducing the height and elasticity of the disc with osteochondrosis;
- the presence of cracks in the fibrous ring surrounding the disc;
- increased pressure of the nucleus pulposus of the disc during physical activity;
- weakening of the connection between the disc and the vertebral body.
All this happens with osteochondrosis - a disease of cartilage discs. Other causes may be spinal injuries, tumors, or tuberculous lesions of the vertebrae and discs. The trigger point for protrusion can be lifting heavy objects or sudden movements of the body.
Important: The concepts of disc protrusion and disc herniation should not be confused. If during protrusion the disc only protrudes, then with a hernia due to rupture of the fibrous ring, the nucleus pulposus of the disc comes out, and this is a more severe pathology.
Symptoms of disc protrusion in the thoracic region
In the thoracic spine, protrusions and disc herniations are much less common because it is less mobile and there is less likelihood of vertebral destabilization. However, the pain syndrome is quite pronounced and has its own characteristics. Here, autonomic nerve fibers emerge from the spinal cord and go to the organs of the chest and upper abdominal cavity.
Therefore, in addition to pain in the spine itself, a pain syndrome can develop, as with angina pectoris, gastritis, cholecystitis, or peptic ulcer. Along the intercostal nerves, pain can radiate (give) to the anterior chest, to the sternum area. Without a special examination, it is impossible to find out the cause of such pain and make a differential diagnosis.
Important: Compression of the autonomic nerves in the thoracic region can also produce such atypical symptoms as vascular crises, muscle weakness and numbness of the limbs without severe back pain. In these cases, a spinal examination is also necessary.
Protrusion of the lumbar spine is a disease accompanied by protrusion of the spinal disc tissue beyond the spinal column without damage to the fibrous ring. The main cause of the disease is osteochondrosis, and its treatment is carried out both in a medical hospital and at home.
Diagnosis of protrusions
In order to detect changes in the discs, conventional radiography of the spine is not enough. More informative examination methods are:
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT-MRI is a method that combines computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- radioisotope study (scintigraphy);
- myelography is a contrast study of the spinal canal and spinal cord to determine the degree of disc displacement and possible compression of the spinal cord.

Treatment of protrusions in the thoracic spine
Treatment after identifying disc protrusion in the thoracic spine consists of 2 stages: relieving acute symptoms of the disease and undergoing a course of complex treatment taking into account the cause of the protrusion. In the acute stage, physical rest, drug treatment (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs), acupuncture, paravertebral novocaine blockades are prescribed.
The video shows exercises to treat protrusion
After the acute symptoms have subsided, a course of treatment is prescribed:
- drug therapy (analgesics, antispasmodics, chondroprotectors - drugs that improve the condition of the cartilage tissue of the discs);
- physical therapy to strengthen the muscular corset of the chest;
- physiotherapy, reflexology;
- diet therapy;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- laser therapy;
- surgery.
The treatment program and indications for surgery are determined individually for each patient. It is extremely important to perform special exercises for protrusions in the thoracic spine. They need to be agreed upon with a specialist in the field of exercise therapy and performed constantly and daily to increase the elasticity and strength of the muscle corset. It is its condition that affects the stability of the spine and the likelihood of protrusions and disc herniations.

Disc protrusions in the thoracic region are the “first signs” on the path to the formation of hernias, and their treatment is mandatory. Much depends on the patient himself - on his diet, lifestyle and physical activity.
- The most effective remedies for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia - symptoms, types of VSD and treatment
- What is partial pressure of oxygen
- The effect of low partial pressure of oxygen in the air on the body and adaptation processes
- Time it takes for alcohol to leave the human body
- Pyogenic granuloma as an interdisciplinary problem
- Cheek biting - causes and treatment Inner cheek disease
- Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease
- Neutralization reaction: definition, examples, application
- All about Duchenne myopathy: genetic factors and a complete list of symptoms Progressive Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart: what is it, symptoms, treatment The last ECG did not show left ventricular hypertrophy
- Lumbar disc herniation: symptoms and treatment
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) - symptoms, treatment and consequences of borreliosis
- News of health, medicine and longevity
- Pain worse after physical therapy
- Scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine)
- Osteochondrosis is the result of fatty degeneration
- Protrusion of the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment What to do for protrusion of the thoracic spine
- Manual therapy of the spine for hernia reviews
- Why does arthritis get worse?