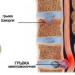
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region 10 mm treatment. Hernia of the lumbar spine: symptoms and treatment. There is only one method of surgical treatment - surgery.
Over the past decade, the number of cases of spinal hernia has almost tripled. Statistics show that timely contact with a specialist is the key to successful treatment.
What is an intervertebral hernia? A spinal hernia (intervertebral hernia) is a prolapse of the nucleus pulposus beyond the intervertebral disc. A hernia of the spine often occurs at the last stage of osteochondrosis, as well as against the background of spinal curvature.
Most often, intervertebral hernias occur in the lumbar spine (65% per 100 patients), due to the greater load on this area, as well as anatomical features. Slightly less frequently, intervertebral hernias occur in the cervical (31%) spine and much less frequently in the thoracic (4%).
Symptoms of intervertebral hernia
The first precursors of the formation of intervertebral hernias can appear as early as 20 years of age and manifest themselves as pain in the lower back or in other parts, and lumbago occurs. Most often, intervertebral hernias occur between the ages of 30 and 50, more often in men and overweight people.
Depending on the location where the herniated disc occurs, symptoms may vary. This disease is characterized by pain, numbness, tingling, weight loss in one arm or leg, muscle weakness and other phenomena.
With almost all vertebral hernias, the first pain appears in adolescence and progresses with age. After 20 years, the spine begins to age, and the risk of intervertebral hernia increases with arithmetic progression.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a spinal hernia, it is important to correctly collect complaints from the patient, determine the nature of the pain, the position in which it occurs, and exclude other diseases. After collecting complaints, tests are carried out; specialists check muscle strength and reflexes, which are disturbed and reduced in case of vertebral hernia. After determining the approximate location of the intervertebral hernia, additional tests are often prescribed: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and x-ray diagnostics.
Treatment
The main problem for doctors is that in 9% of cases, herniated discs cannot be cured by acupuncture, manual therapy, or other conservative treatment methods known to medicine. Then the only hope is for surgical treatment. According to various authors, unsatisfactory results of surgical treatment for disc herniation are observed in 10-20% of cases, and relapses after surgery – in 10-28% of patients. The percentage of complications is no more than 3-5%.
In most cases, if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner, surgical treatment of an intervertebral hernia can be avoided. And if a person consciously wants to avoid neurosurgical surgery, he must be ready to make considerable efforts to work on his health, as well as prepare himself to perform special exercises every day.
Conservative methods include manual therapy, as well as an entire branch of medicine that studies the spine - vertebroneurology. In some cases, high-quality manual therapy can eliminate pain syndromes within a few sessions and stop the progression of the disease.
The spine is the most important and complex organ of the musculoskeletal system and nervous system. Injuries to the spinal column are the most serious injuries, accompanied by various complications.
The most common injury is to the intervertebral discs. One type of injury is an intervertebral hernia.
What is an intervertebral hernia?
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbosacral region is a disease that occurs when intervertebral discs are deformed. As a result of the disease, part of the disc becomes deformed and bulges; prolapse can occur into the cavity of the spinal canal, pinching the nerve roots.
A hernia is accompanied by severe pain and leads to dangerous complications. Without proper treatment, it can cause disability for the patient.

Formation of intervertebral hernia
Types of hernias of the lumbosacral region
Displacement of the intervertebral disc occurs in different directions, so there are several types of hernias:

- Posterolateral– a part of the intervertebral disc prolapses into the spinal canal area. The most dangerous type of hernia.
- Lateral hernias– the disc moves to the left or right relative to the spinal column.
- Anterior hernias– the intervertebral disc protrudes forward.
- Classic hernias– the intervertebral disc protrudes evenly around the entire circumference of the vertebra.
Hernias are also classified by size:
- small– the size of which does not exceed 5 mm;
- average– size ranges from 5 to 8 mm;
- big– range in size from 8 to 12 mm;
- gigantic– whose size exceeds 12 mm.

Classification of hernias
Based on the nature of the prolapsed tissue, hernias are divided into:
- pulpous– occur when the fibrous ring is destroyed or the integrity of the vertebral body is violated;
- cartilaginous– occur when cartilage loses its elasticity due to chronic inflammation or physical activity;
- bone- are mainly observed in the elderly and senile age, when bone growths compress the nerve roots or part of the spinal cord.
Hernias are also divided into primary and secondary. Primary hernia occurs due to trauma in the absence of spinal diseases. A secondary hernia occurs under the influence of spinal deformity or due to other diseases. There is a special type of vertebral hernia - Schmorl's hernia.
Why are hernial protrusions dangerous?
A hernia in the lumbosacral region is dangerous: without treatment, the herniation progresses and the intervertebral disc compresses the roots of the spinal nerves. Depending on which nerve has stopped functioning properly, problems with urination and bowel movements may occur.
When the motor nerves are compressed, the mobility of part of the skeletal muscles of the lower extremities is lost, and gait is impaired. In severe cases, paralysis of one or both legs may develop, leading to disability.
Causes of hernia
The direct causes of the development of pathology include:
- physical stress;
- osteochondrosis;
- vertebral subluxations caused by falls, bruises, sudden movements;
- scoliosis and other diseases of the spinal column;
- diseases of the hip joint;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- lack of calcium in the body and psychosomatics.

Causes of hernia
The risk group includes elderly people leading a sedentary lifestyle, those who are overweight, as well as patients suffering from chronic diseases.
Smoking and poor nutrition also contribute to decreased muscle tone and improper functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
 Stories from our readers!
Stories from our readers!
I want to tell my story about how I cured osteochondrosis and hernia. Finally, I was able to overcome this unbearable pain in my lower back. I lead an active lifestyle, live and enjoy every moment! A few months ago I got a cramp at the dacha; a sharp pain in my lower back didn’t allow me to move, I couldn’t even walk. The doctor at the hospital diagnosed osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, herniated discs L3-L4. He prescribed some medications, but they did not help, the pain was unbearable. They called an ambulance, they put a blockade and hinted at an operation, I kept thinking about this, that I would turn out to be a burden for the family... Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article literally pulled me out of my wheelchair. In recent months I have started to move more; in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day. Who wants to live a long and energetic life without osteochondrosis,
Symptoms of a spinal hernia
The symptoms of a hernia will depend on the location of its occurrence. When a nerve is compressed, radicular syndrome occurs - a sign that helps localize the hernia.
| Localization in the spine | Signs |
| L1 | Lower back pain, loss of sensation in the upper buttocks |
| L2 | Loss of sensitivity on the inner thigh, in the perineum and scrotum, and in women in the labia area |
| L3 | Loss of sensation on the front of the thigh, weakness and involuntary twitching of the muscles in this area |
| L4 | Decreased knee reflex, numbness, difficulty bending the knee |
| L5 | Numbness, pain along the “stripe” on the outside of the leg, inability to lift the foot, loss of balance when resting on the heel |
| S1 | Pain in the back of the thigh, numbness in the calf muscles, inability to stand on the toes |
| S2-S4 | Numbness along the posterolateral surface of the leg on the inside, difficulty defecating, urinating, and in men – decreased erectile function. |
Common symptoms are acute “shooting” pain, a feeling of coldness and tingling in the legs, decreased skin sensitivity in certain areas and muscle weakness.
Treatment
To make an accurate diagnosis, you must contact a qualified specialist. Treatment is carried out both conservatively and surgically. The treatment method chosen depends on the size and location of the protrusion.
Therapy is aimed at relieving pain, normalizing the patient’s well-being and strengthening muscles and ligaments. The main task facing the doctor is to prevent further degenerative changes and enlargement of the hernia.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy complexes - the most important element of treatment - are aimed at stretching the spine and strengthening the muscle corset.
A set of exercise therapy exercises is performed on the floor without shoes:
- The exercise is performed on the floor, lying on your back. Legs are bent at the knees. The abdominal muscles must be tensed, then slowly relaxed, without holding your breath. Perform 10 times.
- The exercise is performed in a supine position, arms are pressed to the body, legs are straightened. The upper body is raised above the floor for 10 seconds, then slowly returns to its original position. There is a pause of 10 seconds between lifts. Repeat the exercise 5-10 times.
- The exercise is performed while lying on the floor on your back, legs slightly bent at the knees. The right hand is on the left knee. It is necessary to bend your leg while offering resistance with your right hand. The exercise is performed 5-10 times, after which you need to change position and do the same with your right leg, resting on your knee with your left hand.
- Starting position: lying on your back, you can put a flat pillow under your lower back. The legs are freely extended, the arms lie along the body. The shoulder blades and buttocks are pressed to the floor, the head cannot be lifted from the floor. Fix the position for 5-7 seconds; there is no need to hold your breath. Relax your muscles, rest for 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times.

Exercises
Yoga and swimming
You can also use yoga asanas to strengthen your muscles. Yoga is one of the traditional oriental sports, in which sets of exercises are combined with relaxation and breathing techniques. Allows you to strengthen muscles and make ligaments more elastic.
Yoga courses are taught by qualified instructors, but you should consult with your doctor before starting classes. If you have a vertebral hernia, you should not perform deep bends, bends and sharp twists, so as not to aggravate the situation.
Swimming is also a good method - water supports the body, helping to distribute the load on the spine, while enough muscle effort is expended to strengthen the muscles of the back and limbs. For diseases of the spine, it is recommended to swim breaststroke or on the back.
Exercise equipment
When treating hernias, specially designed simulators and gymnastics are used.
The following devices are used:

- Bubnovsky simulator;
- spinal trainer KC-500;
- elliptical trainer;
- exercise bike.
The work of the devices is aimed at strengthening the back muscles and improving blood supply.
Wearing a corset
For a hernia of the lumbosacral region, a special corset-belt is used, 30-40 centimeters wide, with special inserts. The product ensures complete immobility of the lower spine and relieves part of the load from the spinal column.
You need to wear a corset while performing sedentary or physical work as prescribed by your doctor. Corsets are selected individually and adjusted to your figure for better fit. To treat a hernia, the corset must be worn for at least six hours a day; it is better to put the product on while lying down.
Corset Corset Chest-Belt Corset for the spine
Spinal traction
Spinal traction during a hernia is performed in order to return the vertebrae to their normal position and prevent further development of the disease. Treatment is carried out in a horizontal position in two versions: dry and water.
Indications for traction treatment are:
- severe back pain;
- pronounced radicular syndrome;
- violation
- difficulty moving limbs and muscle weakness.

Spinal traction using hardware
The traction method is not used for the following pathologies:
- with high blood pressure, with severe diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- in the presence of acute infection or inflammatory process;
- severe obesity;
- cancer diseases;
- surgery performed on the spine any time ago.
Massage
Before traction, the muscles are warmed up with a massage, then traction itself is performed - during traction, some points of the body are fixed, influencing the desired areas and stretching the spine.
Several types of massage are used to treat hernia:
- hand massage;
- can;
- hardware.

Cupping massage scheme
One massage session takes from 10 minutes to half an hour, while the rule is observed: the spine itself is not affected, so as not to displace the intervertebral disc even more. The course consists of 10-15 procedures lasting about 30-40 minutes.
The duration of the massage course varies from ten days to a month - the effect is achieved only with a course of treatment; single irregular procedures will not only not give an effect, but can worsen the patient’s condition.
The method of acupuncture is used as part of complex therapy for vertebral hernias, pursuing the following goals:

- release of nerve roots when they are pinched;
- removal of swelling;
- elimination of muscle spasm;
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- improvement of blood supply.
The procedure is prescribed in conjunction with massage sessions and physiotherapeutic procedures. The number of procedures is at least ten during the course. During the procedure, long sterile needles are inserted into the skin at various angles. The injections are quite painful, but relief occurs by the middle of the course.
The main advantage of acupuncture is the ability to restore nerve function without resorting to surgery, that is, treatment with needles becomes an alternative to surgery.
Manual therapy
Another effective method for eliminating a herniated disc is manual therapy. The method allows you to alleviate the patient’s condition at almost any stage of hernia formation. The treatment method is selected individually for each patient depending on the location and size of the hernia.
The use of manual therapy together with massage and acupuncture allows not only to correct subluxations of the intervertebral discs, but also to saturate the cartilage tissue with oxygen, improve blood supply and restore the lost elasticity of the cartilage.
Physiotherapy procedures
Complex therapy includes such physical procedures as:
- EHF - the impact of extremely high frequencies on the area affected by the disease, improves blood supply.
- Electromyostimulation – improves muscle tone and relieves spasm.

Physiotherapy for hernia
The use of physiotherapy helps restore muscle activity and prevents tissue atrophy. All manipulations are performed under the supervision of a specialist in courses of 10 or more procedures.
The use of physiotherapy is contraindicated: 
- for acute pain;
- in case of untreated inflammatory processes;
- at elevated temperatures;
- with decompensated heart failure;
- after myocardial infarction;
- with a pacemaker installed.
IMPORTANT! To clarify individual contraindications, it is recommended to undergo a full examination before starting treatment.
Drug treatment
When vertebral discs are pinched, drug treatment is aimed at suppressing inflammatory processes and improving the general condition of the patient.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments and creams:
- Diclofenac, Ibuprofen or Indovazin– these drugs have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, reduce swelling by suppressing inflammatory mediators.
- Apply ointments 1-2 times a day in a thin layer, rub in circular movements until completely absorbed. The duration of treatment ranges from 1-2 weeks.
Diclofenac in gel form Ibuprofen ointment Indovazin
Chondroprotectors:
- Teraflex, Chondroguard or Mucosat. The composition of chondroprotectors includes collagen obtained from animal bones. This substance is close in structure to the collagen of cartilage in the human body. It restores the tissue of the intervertebral discs, preventing degenerative changes in the tissue.
- Teraflex used in the form of ointment or tablets with the addition of peppermint essential oil.
- Mucosat is prescribed in tablet form for ease of use.
- Chondrogard Available in the form of a solution for injection. The drug, course duration, and dosage of injections are selected by the doctor individually for each patient, depending on the severity of the disease.
Teraflex Advance Chondroguard Mucosat tablets
To relieve pain it is performed novocaine blockade. Novocaine injections are possible if the fibrous ring is preserved and the size of the hernia does not exceed 8 mm. The blockade is performed only in a medical hospital and is effective for 3-4 hours after the administration of the painkiller.

Surgery
Surgical treatment for a herniated disc involves removing the hernial body and can cure many pathologies associated with the herniation.
Surgery is prescribed in the following cases:
- with multiple compression of the nerves of the cauda equina;
- if the size of the hernia is more than 10 mm;
- with sequestered hernia;
- if conservative treatment measures have failed and the disease progresses rapidly.

Endoscopic surgery
The success rate of the operation is 90-95%; in approximately 6% of cases, a repeat hernia develops in the operated area. The newest method of surgical intervention is laser microsurgery - the laser not only destroys the body of the hernia, but also solders the surrounding tissues, preventing the re-formation of the protrusion.
Traditional methods of treating hernia
Traditional folk remedies are used to relieve pain and swelling. Products of plant origin are used.
Compresses
Compresses are applied directly to the area where the hernia appears: 
- Compress with ointment based on calendula tincture. In order to make a compress, alcohol tincture of calendula is mixed with Vaseline or any fatty cream in a ratio of 1:3, clean gauze is soaked in the ointment and fixed on the lower back. The compress is left overnight. This composition will help relieve inflammation and reduce swelling.
- Honey compress with aloe. To prepare a compress you will need three parts alcohol or vodka, two parts fresh aloe juice and one part honey. The compress is soaked into gauze, which is fixed on the leg for 40 minutes in the morning or evening. The procedure is applied for 1-2 weeks, then you should take a break.
Tinctures
Tinctures are made both for lotions and for internal use.
The most popular is cinquefoil tincture: 
- To prepare the tincture you will need 100 grams root per liter of alcohol.
- Infuse for three days in a cool, dark place, then strain.
- Take the tincture three times a day after meals a tablespoon per glass of water or rub into the area of the damaged disc.
Dried fruit remedy
To relieve inflammation and strengthen joint tissue, professional athletes recommend using a mixture of dried fruits in the diet - dried apricots, prunes and figs in a 5:2:1 ratio.
The mixture should be consumed in small quantities after each meal. The mixture of champions not only acts as a medicine, but is also an effective prevention of herniated discs.
Possible complications and consequences
The most important consequences of an untreated lumbar hernia are paralysis and atrophy of the leg muscles, gait disturbance and dysfunction of the pelvic organs. If the nerves of the cauda equina are pinched for a long time, the reproductive function of the body may be impaired.
The most serious complication is complete paralysis of the lower extremities - this pathology develops with multiple hernias in the absence of treatment.
Disability due to hernia
Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient may be assigned a disability group: 
- First disability group assigned in the event of paralysis of the limbs, as well as in the case of uncontrolled emptying of the bladder or intestines.
- Second disability group assigned to patients with severe pain that is not relieved by medications.
- For small hernias assigned the third disability group– a person leads an almost full life, but prolonged sedentary activity and physical overexertion are contraindicated for him.
With the current level of hernia treatment, disability of the first and second groups is rarely assigned.
Precautionary measures
Patients with a lumbar hernia should lead a gentle lifestyle that does not complicate their existence: 
- You cannot sit in one position for a long time;
- lifting heavy objects is contraindicated;
- Painful;
- Compression;
- Vertebrate.
- Directions of disc protrusion and its dimensions;
- The degree and type of tissue compression;
- The nature of associated complications (tissue swelling, blood stagnation).
- Gibbosity;
- Slouch;
- Lateral displacement of the axis of the spinal column (scoliosis);
- Unsteady movements;
- Loss of skin sensitivity.
- Impaired sensitivity of the skin of the lower back (paresthesia);
- Pain in the buttocks and lower extremities;
- Urinary disorders;
- Irregular periods (in women);
- Loss of sexual function.
- Weakness of the muscles of the lower limb (hips, legs, feet);
- Decreased muscle tone in the posterior group;
- Leg atrophy;
- Impaired sensitivity of the skin;
- Numbness of fingers;
- Dryness and sweating of the skin;
- Paralysis and paresis of the legs.
- X-ray of the lumbar region in two projections (direct and lateral);
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan.
- Injections of anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ketorol);
- Wearing an orthopedic corset (to prevent further curvature of the spine);
- Manual therapy;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapeutic and sanatorium-resort treatment.
An intervertebral hernia forms in the spine when the cartilage disc located between the vertebrae protrudes beyond its anatomical location posteriorly, anteriorly, or in the lateral plane.
A classic intervertebral hernia (dorsal) is directed towards the spinal canal. If the size of the protrusion exceeds 10 mm, there is a high probability of compression of the spinal cord with consequences in the form of paralysis (immobility due to lack of muscle innervation).
When the formation is 5 to 10 mm long, acute pain is rare. The pathology manifests itself only by periodic pain in the spine at the level of localization of the hernial sac. With sharp turns or bends of the body, the pain intensifies due to irritation of the spinal nerves exiting the spinal cord through the openings in the processes of the vertebrae.
In medical language, the clinical picture that occurs as a result of compression of the spinal nerves is called compression (radicular) syndrome. In addition to this, pathology also causes vertebral syndrome.
Thus, the pathogenetic picture of intervertebral hernia consists of a triad of symptoms:
Each person with an intervertebral hernia has an individual severity of compression, pain or vertebral syndromes. Symptoms depend on many factors:
Pain syndrome with intervertebral hernia
Pain syndrome due to intervertebral hernia can have an acute or chronic course. Sharp pain in the lower back, in which a person takes a forced posture, is observed with radiculitis (inflammation of nerve fibers). This condition occurs in patients with protrusion of the intervertebral disc in the lower lumbar region. This area of the spine bears the maximum load when walking and lifting heavy objects.
Radiculitis is a common disease among builders and general workers who lift heavy objects as part of their professional activities.
Chronic pain in the lower back is characteristic of the early stages of a hernia, when the formation does not compress the nerve root, but can irritate it with a sharp turn of the body or change of position. The course of the disease with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation occurs due to the addition of inflammatory changes and swelling of the vertebral tissues to the disease.
This situation is observed against the background of concomitant diseases (osteochondrosis, scoliosis, spondylosis). At this stage, the progression of the disease can be stopped. Otherwise, over time, persistent compression of the spinal cord nerve roots will occur, which can lead to disability. In such a situation, the pain will become aching rather than “shooting.” It will radiate to the gluteal region and lower limbs.
Spinal syndrome due to hernia of the lumbar spine
Spinal syndrome occurs when there is a hernial protrusion in the lumbar region due to spasmodic muscle contraction. Nerve fibers pass through their thickness, which are pinched in this condition. The consequence of these changes is limited mobility of the lower extremities. If the pathology continues for a long time, accompanying symptoms occur:
For humans, a hernial protrusion is typical at the level of the lumbar region in the L4-L5-S1 segments. It is this area that bears the maximum load when lifting heavy objects and walking. With such localization of intervertebral hernia, specific symptoms are formed:
Compression syndrome with hernial protrusion in the lower back
Radicular syndrome with a hernia of the spine at the lumbar level causes the maximum number of symptoms:
The above symptoms of a hernia lead to disability. In severe cases of the disease, a violation of the innervation of the pelvic organs, potency in men, and gynecological diseases in women are formed.
Diagnosis of intervertebral hernia
In addition to the above-described clinical manifestations of a hernia of the lumbar spine, diagnosis of the disease is based on the following radiological methods:
Using these clinical and instrumental methods, it is possible to establish not only the type and direction of the hernial protrusion, but also to identify complications of the pathology.
Myelography is used to determine the level and degree of spinal cord compression. This method involves studying the condition of the spinal canal by injecting a contrast agent into it under fluoroscopic control.
Treatment of intervertebral hernias
Treatment of intervertebral hernias depends on the severity of structural changes and the nature of the clinical symptoms of the pathology.
In the initial stages of hernial formation with periodic aching pain in the lower back, it is rational to use conservative methods aimed at eliminating inflammatory changes, eliminating pain and preventing the progression of the disease. For these purposes, the following procedures are prescribed:
If the effectiveness of medical procedures is low, the issue of surgical removal of the hernia is decided. The operation can be performed using open access or using laser technology.
Thus, intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine manifests itself with various clinical symptoms. For some people, the disease is characterized by periodic lower back pain throughout their lives, while for others it is characterized by limited mobility of the lower extremities. In any case, there is no etiological treatment for spinal hernias, so the pathology must be treated immediately after detection.
Over the past decade, the number of cases of spinal hernia has almost tripled. Statistics show that timely contact with a specialist is the key to successful treatment.
What is an intervertebral hernia? A spinal hernia (intervertebral hernia) is a prolapse of the nucleus pulposus beyond the intervertebral disc. A hernia of the spine often occurs at the last stage of osteochondrosis, as well as against the background of spinal curvature.
Most often, intervertebral hernias occur in the lumbar spine (65% per 100 patients), due to the greater load on this area, as well as anatomical features. Slightly less frequently, intervertebral hernias occur in the cervical (31%) spine and much less frequently in the thoracic (4%).
Symptoms of intervertebral hernia
The first precursors of the formation of intervertebral hernias can appear as early as 20 years of age and manifest themselves as pain in the lower back or in other parts, and lumbago occurs. Most often, intervertebral hernias occur between the ages of 30 and 50, more often in men and overweight people.
Depending on the location where the herniated disc occurs, symptoms may vary. This disease is characterized by pain, numbness, tingling, weight loss in one arm or leg, muscle weakness and other phenomena.
With almost all vertebral hernias, the first pain appears in adolescence and progresses with age. After 20 years, the spine begins to age, and the risk of intervertebral hernia increases with arithmetic progression.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a spinal hernia, it is important to correctly collect complaints from the patient, determine the nature of the pain, the position in which it occurs, and exclude other diseases. After collecting complaints, tests are carried out; specialists check muscle strength and reflexes, which are disturbed and reduced in case of vertebral hernia. After determining the approximate location of the intervertebral hernia, additional tests are often prescribed: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and x-ray diagnostics.
Treatment
The main problem for doctors is that in 9% of cases, herniated discs cannot be cured by acupuncture, manual therapy, or other conservative treatment methods known to medicine. Then the only hope is for surgical treatment. According to various authors, unsatisfactory results of surgical treatment for disc herniation are observed in 10-20% of cases, and relapses after surgery – in 10-28% of patients. The percentage of complications is no more than 3-5%.
In most cases, if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner, surgical treatment of an intervertebral hernia can be avoided. And if a person consciously wants to avoid neurosurgical surgery, he must be ready to make considerable efforts to work on his health, as well as prepare himself to perform special exercises every day.
Conservative methods include manual therapy, as well as an entire branch of medicine that studies the spine - vertebroneurology. In some cases, high-quality manual therapy can eliminate pain syndromes within a few sessions and stop the progression of the disease.
If you have constant aching or “shooting” pain in the back, lower back, or neck that does not go away for quite a long time, you should pay serious attention to your health. Perhaps such pain indicates that you have an intervertebral hernia. This is an unpleasant, dangerous disease that requires surgical treatment, otherwise the disease can progress and cause serious damage to a person’s health and well-being. Intervertebral hernia occurs when the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc is displaced with rupture of the fibrous ring.
Where does a vertebral hernia occur?
Intervertebral hernia can be localized in different parts of the spine. The most common type of hernia occurs in the lumbosacral spine. In this case, the pain can radiate to the back, lower back, hips, legs, feet, and buttocks. Disturbances in the functioning of the intestines and bladder may occur, and men may experience problems with potency.
Less common is intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine. Headaches may appear, pain in the arms and shoulders may occur, frequent dizziness may occur, and memory functions may be impaired. With an intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region, pain also occurs in the thoracic region, in the interscapular region, and scoliosis may appear.
Intervertebral hernia appears, as a rule, from an uncomfortable workplace and incorrect position during the performance of professional duties of drivers, surgeons, welders, etc. Intervertebral disc defects often arise from regular heavy lifting. Those who suffer a spinal injury due to an unsuccessful fall or various fractures are also at risk of intervertebral hernia.
Treatment methods based on the size of the vertebral hernia
Treatment of a hernia must begin as soon as it is discovered. The more the intervertebral hernia gets worse, the more time and effort it will take to relieve the pain. If an intervertebral hernia is suspected, the doctor will prescribe a CT or MRI. Basically, experts recommend using magnetic resonance imaging as a method for diagnosing intervertebral hernia - it is the safest for health and provides the most accurate data on the location of the hernia and its size.

Intervertebral hernia is treated in various ways: conservative and surgical. The treatment method is determined by the size of the spinal hernia. If the displacement has just begun to occur, and the size of the vertebral hernia is about 2 mm, they can get by with medication, manual therapy, spinal traction, etc. A medium-sized protrusion, for example, a 5 mm intervertebral hernia, can also be treated non-surgically. For a large spinal hernia of 8 mm, treatment is prescribed, including surgery. However, surgical intervention in this case is not the final stage of treatment for a spinal hernia. After the operation, the patient is prescribed medication, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and sanatorium treatment is recommended.
We will tell you in more detail about the treatment of a hernia, based on the size of the displacement. The sizes of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar and thoracic spine are divided as follows: small protrusion from 1 to 5 mm. A medium protrusion is considered to be more than 6 mm of protrusion of the intervertebral disc, and a large protrusion is considered to be more than 9 mm. Dimensions of a hernia of the cervical spine: small - 1-2 mm, large protrusion - 5-6 mm. Thus, the need for surgical intervention is most often determined based on the size of the vertebral hernia.
Dimensions of lumbar intervertebral hernia
A 3 mm lumbar intervertebral hernia requires outpatient treatment, home treatment, which involves spinal traction, and therapeutic exercises.
A lumbar disc hernia of 6 mm is considered medium, and therefore requires more serious outpatient treatment using additional methods. Manual therapy, physiotherapeutic treatment (massage, ultrasound, spinal traction), physical therapy. However, when asked whether surgery is necessary to treat a 6-7 mm lumbar disc herniation, doctors answer that surgery is not required.

But with an intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region measuring 12 mm, surgical intervention is required if symptoms of compression of the spinal cord appear and when elements of the “cauda equina” appear.
Dimensions of cervical hernia
An intervertebral hernia up to 2 mm in the cervical spine is considered small; manual, medicinal, and physiotherapeutic methods are provided for its treatment. A hernia of the cervical spine measuring 3 mm, like an intervertebral hernia of 4 mm, requires urgent outpatient treatment to avoid further injury to the area. An intervertebral hernia in this area of 5-6 mm still allows outpatient treatment. But if an intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine larger than 6 mm is detected, urgent surgical intervention is required.
Regardless of what size and in what part the intervertebral hernia is found, the sooner treatment begins, the better. If a spinal hernia is detected in time, there is every chance of getting rid of the disease or at least relieving the symptoms, ensuring the proper level of quality of life. In addition to outpatient treatment, it is effective to use. But only as a supplement, without replacing conservative treatment (medication, manual and physical therapy).
| Dimensions of intervertebral hernia | ||
|
Lumbar and thoracic spine |
||
| Size of intervertebral hernia | Characteristic | Treatment |
| 1-5mm | Small protrusion size | Outpatient treatment is required, probably home treatment - spinal traction, therapeutic exercises |
| 6-8mm | Average size of vertebral hernia | Outpatient treatment is required, surgery is not necessary |
| 9-12mm | Large protrusion size | Prompt outpatient treatment is necessary; surgical intervention is indicated for symptoms of compression of the spinal cord and elements of the cauda equina. |
| More than 12 mm | Large prolapse or sequestered hernia | Outpatient treatment is possible. But if symptoms of spinal cord compression appear, the patient must undergo surgery |
|
Cervical spine |
||
| Size of intervertebral hernia | Characteristic | Treatment |
| 1-2mm | Small size intervertebral hernia | Urgent outpatient treatment |
| 3-4mm | Average protrusion size | Urgent outpatient treatment required |
| 5-6mm | Large size of the vertebral hernia | Outpatient treatment possible |
| 6-7mm and more | Large size of intervertebral hernia | Surgical treatment required |
- The most effective remedies for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia - symptoms, types of VSD and treatment
- What is partial pressure of oxygen
- The effect of low partial pressure of oxygen in the air on the body and adaptation processes
- Time it takes for alcohol to leave the human body
- Pyogenic granuloma as an interdisciplinary problem
- Cheek biting - causes and treatment Inner cheek disease
- Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease
- Neutralization reaction: definition, examples, application
- All about Duchenne myopathy: genetic factors and a complete list of symptoms Progressive Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart: what is it, symptoms, treatment The last ECG did not show left ventricular hypertrophy
- Lumbar disc herniation: symptoms and treatment
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) - symptoms, treatment and consequences of borreliosis
- News of health, medicine and longevity
- Pain worse after physical therapy
- Scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine)
- Osteochondrosis is the result of fatty degeneration
- Protrusion of the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment What to do for protrusion of the thoracic spine
- Manual therapy of the spine for hernia reviews
- Why does arthritis get worse?