Table of irregular verbs English pronunciation. Irregular verbs of the English language: lists of words for different levels of knowledge. main verbs in English
Irregular Verbs in English are verbs that form Past Simple(past simple tense) and Past Participle(past participles) in a special way, that is, they are exceptions to the general rule of formation of these forms. Consequently, irregular verbs and their forms are usually memorized. The list of the most common irregular verbs contains about 200 verbs.
With our service you can quickly find the irregular verb you need. All forms of irregular verbs have transcription and pronunciation. The infinitive, that is, the I form of the verb, has a translation into Russian.
There are also a number of verbs in English that can be either regular or irregular. In the service, such verbs are marked with an asterisk. *
and contain additional information regarding their use in modern English.
Help on verb forms
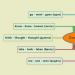
I form of the verb- this is (Infinitive), that is, the indefinite form of the verb or the initial form. The infinitive in English corresponds to the Russian infinitive form of the verb, which answers the questions “What to do? What to do?": read - to read. Particle to is a formal sign of the infinitive, but the infinitive can also be used without a particle to .
II form of the verb is a form of (past simple tense). This form is used to form the past simple tense: read - read, read, read; bought - bought, bought, bought.
III verb form is a form (or Participle II, past participle). The English past participle corresponds to the Russian passive past participle: read - read, bought - purchased. III form is also used to form tenses of the Perfect group (perfect tenses) and to form
Irregular Verbs in English, these are verbs that have special forms (Past Simple) and (Past Participle). Among them there are both very common ones (feel - to feel, speak - to speak) and rare ones (cleave - to cut, forswear - to renounce). The tables below show common irregular verbs.
Read also:
Despite the fact that irregular verbs change in a special way, they still have some regularity. In the table below, the verbs are given with translation and transcription and are distributed based on the coincidence of forms:
- Verbs AAA - all three forms are the same (cut - cut - cut, cut).
- ABA verbs – the 1st and 3rd forms coincide (run – ran – run, run).
- Verbs ABC – the 2nd and 3rd forms coincide (teach – taught – taught, teach).
- ABC verbs – all forms are different (know – knew – known, know).
Inside the table, words are distributed not alphabetically, but by frequency, i.e. the higher the word, the more often it is used. Attached to the tables pdf files– you can print them out, stick them on cardboard and cut out cards for learning words.
| AAA verbs: the same in three forms Download PDF | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Translation | Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| put | put |
put |
put |
| let | let |
let |
let |
| cut | cut |
cut |
cut |
| put (install) | set |
set |
set |
| bet | bet |
bet |
bet |
| throw (cast metal) | cast |
cast |
cast |
| cost | cost |
cost |
cost |
| beat | hit |
hit |
hit |
| to cause a pain | hurt |
hurt |
hurt |
| to knit | knit |
knit |
knit |
| stop | quit |
quit |
quit |
| distribute | spread |
spread |
spread |
| ABA type verbs: forms 1 and 3 match | |||
| run | run |
ran |
run |
| come | come |
came |
come |
| become | become |
became |
become |
| Verbs like ABB: forms 2 and 3 match | |||
| read | read |
read |
read |
| teach (gain knowledge) | learn |
learn (learned) |
learn (learned) |
| think | think [θiŋk] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
| teach (educate) | teach |
taught |
taught |
| smell (smell) | smell |
smelt |
smelt |
| hear | hear |
heard |
heard |
| hold | hold |
held |
held |
| bring | bring |
brought |
brought |
| stand | stand |
stood |
stood |
| lose (lose) | lose |
lost |
lost |
| meet | meet |
met |
met |
| lead | lead |
led |
led |
| understand | understand [ʌndə’stænd] |
understood [ʌndə’stud] |
understood [ʌndə’stud] |
| win | win |
won |
won |
| buy | buy |
bought |
bought |
| send | send |
sent |
sent |
| sell | sell |
sold |
sold |
| catch | catch |
caught |
caught kɔ:t] |
| fight | fight |
fought |
fought |
| put (lay) | lay |
laid |
laid |
| sit | sit |
sat |
sat |
| bind | bind |
bound |
bound |
| bleed | bleed |
bled |
bled |
| build | build |
built |
built |
| burn | burn |
burnt |
burnt |
| deal with | deal |
dealt |
dealt |
| dig | dig |
dug |
dug |
| feed | feed |
fed |
fed |
| hang | hang |
hung |
hung |
| hide | hide |
hid |
hidden [‘hɪdn] |
| lean | lean |
lean (leaned) |
lean (leaned) |
| lend (to someone) | lend |
tape |
tape |
| illuminate | light |
lit |
lit |
| ride | ride |
rode |
ridden [‘rɪdn] |
| sew | sew |
sewed |
sewed (sewn) |
| spell or spell | spell |
spelled |
spelled |
| shed | spill |
spilt |
spilt |
| spit | spit |
spat (spit) |
spat (spit) |
| spoil | spoiler |
spoilt |
spoilt |
| stick | stick |
stuck |
stuck |
| strike | strike |
struck |
struck |
| sweep | sweep |
swept |
swept |
| cry | weep |
wept |
wept |
| twist | wind |
wound |
wound |
| Verbs likeABC: all forms are different |
|||
| go | go |
went |
gone |
| know | know |
knew |
known |
| take | take |
took |
taken [‘teik(ə)n] |
| see | see |
saw |
seen |
| give | give |
gave |
given |
| write | write |
wrote |
written [‘ritn] |
| speak | speak |
spoke |
spoken [‘spouk(e)n] |
| drive a car | drive |
drove |
driven [‘drivn] |
| break | break |
broke |
broken [‘brouk(e)n] |
| wear clothes) | wear |
wore |
worn |
| There is | eat |
ate |
eaten [‘i:tn] |
| drink | drink |
drank |
drunk |
| draw (draw) | draw |
drew |
drawn |
| steal | steal |
stole |
stolen [‘stəulən] |
| throw | throw [θrəu] |
threw [θru:] |
thrown [θrəun] |
| blow | blow |
blew |
blown |
| fall | fall |
fell |
fallen [‘fɔ:lən] |
| start off | begin |
began |
begun |
| forget | forget |
forgot |
forgotten |
| forgive | forgive |
forgave |
forgiven |
| fly | fly |
flew |
flown |
| freeze (freeze) | freeze |
froze |
frozen [‘frouzn] |
| grow | grow |
grew |
grown |
| call | ring |
rank |
rung |
| shake | shake [ʃeik] |
shook [ʃuk] |
shaken [‘ʃeik(ə)n] |
| sing | sing |
sang |
sung |
| stink | stink |
stank (stunk) |
stunk |
| try | strive |
strove |
striven [‘strɪvn] |
| to swear | swear |
swore |
sworn |
| tear | tear |
tore |
torn |
| wake | wake |
woke up |
woken [‘wouk(e)n] |
Pay attention to the words read And wind. In the 2nd and 3rd forms read is read as . And the verb wind - to twist, should not be confused with the noun wind - wind.
The ten most basic irregular verbs
Among the commonly used irregular verbs we can distinguish the most basic. You need to know them first. Start learning verbs from them, and not in alphabetical order. You can learn them in literally 5 – 10 minutes.
| Translation | Infinitive (1st form) | Past Simple (2nd form) | Past Participle (3rd form) |
|---|---|---|---|
| go | go |
went |
gone |
| know | know |
knew |
known |
| think | think [θiŋk] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
| take | take |
took |
taken [‘teik(ə)n] |
| see | see |
saw |
seen |
| give | give |
gave |
given |
| write | write |
wrote |
written [‘ritn] |
| speak | speak |
spoke |
spoken [‘spouk(e)n] |
| hear | hear |
heard |
heard |
| buy | buy |
bought |
bought |

These verbs need to be learned first
Notes:
- Over time, some verbs have almost turned from irregular to regular. For example, even in not very old textbooks it is written that the verb to work– irregular, it has the forms: work – wrought – wrought. Now the form wrought is hardly used except in established expressions like “wrought iron,” so I have not included it in this table.
- Verbs to learn(learn), to lean(lean) are also more often used as correct: learned, leaned, especially in the USA.
- Pay attention to the forms read – read – read. The word is written the same, but read differently.
- Don't confuse the verb wind(twist) and noun wind- wind. They are written the same, but have different pronunciation and meanings.
- In the British version the verbs sew pronounced like
There are correct (regular) and incorrect (irregular). When using irregular verbs, their forms are formed in different ways than regular verbs (by adding –ed to the infinitive).
The Irregular Verbs table consists of three forms:
- (this is the initial form of the verb without the particle to).
- (verb in past tense).
- (past participle).
Unfortunately, there is no such rule that helps determine which verb is correct and which is not.
In total in English there are about . Naturally, you won’t be able to learn them right away, and there’s no need to: many of them are not used in speech, as they are considered outdated.
Ways to quickly memorize Irregular Verbs
There are some ways you can speed up learning Irregular Verbs:

Group No. 1. The verb in all three forms has the same pronunciation and spelling.
For example:
| cut | cut | cut | cut |
| hurt | hurt | hurt | hurt |
Group№ 2 . Past Simple and Past Participle are identical in spelling and pronunciation. For example:
Group№ 4 .The verb form is formed by adding -old to the first group of the infinitive:
Group№ 6. The form of the verb in the Present Simple and Past Participle is the same:
Group№ 8 .The Past Simple form is formed using –ew, and the Past Participle form is formed using -own:
Group№ 9 . ABOUT The Past Participle form is formed using the ending -n added to the infinitive:
Group№ 11 . The vowel in each form changes according to the i-a-u principle, for example:
Note. Verbs formed with the prefixes re-, dis-, over-, un-, mis-, out-, under- and others will also be irregular. Their Past Simple and Past Participal forms are the same as the verbs from which they were derived. For example, set – reset, stand – understand.
Table of irregular verbs (Irregular Verbs)
Below is a table of Irregular Verbs with the 117 most common and most used.
| Infinitive | Past simple | Past participle | Translation |
| be | was, were | been | be |
| beat | beat | beaten ['bi:tn] | beat |
| become | became | become | become |
| begin | began | begun | start off |
| bleed | bled | bled | bleed |
| blow | blew | blown | blow |
| break | broke | broken [‘brouk(e)n] | break |
| bring | brought | brought | bring |
| build | built | built | build |
| burn | burnt | burnt | burn |
| burst | burst | burst | break out |
| buy | bought | bought | buy |
| catch | caught | caught | catch, grab |
| choose | chose [ʃəuz] | chosen | choose |
| come | came | come | come |
| cost | cost | cost | cost |
| creep | crept | crept | crawl |
| cut | cut | cut | cut |
| do | did | done | do |
| draw | drew | drawn | draw, drag |
| dream | dream | dream | dream, doze |
| drink | drank | drunk | drink |
| drive | drove | driven [‘drivn] | drive |
| eat | ate | eaten [‘i:tn] | There is |
| fall | fell | fallen [‘fɔ:lən] | fall |
| feed | fed | fed | feed |
| feel | felt | felt | feel |
| fight | fought | fought | fight |
| find | found | found | find |
| fit | fit | fit | fit to size |
| fly | flew | flown | fly |
| forget | forgot | forgotten | forget |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven | forgive |
| freeze | froze | frozen [‘frouzn] | freeze |
| get[get] | got | got | receive |
| give | gave | given | give |
| go | went | gone | go |
| grow | grew | grown | grow |
| hang | hung | hung | hang |
| have | had | had | have |
| hear | heard | heard | hear |
| hide | hid | hidden ['hidn] | hide |
| hit | hit | hit | hit the target |
| hold | held | held | hold |
| hurt | hurt | hurt | hurt |
| keep | kept | kept | contain |
| kneel | knelt | knelt | kneel |
| know | knew | known | know |
| lay | laid | laid | put |
| lead | led | led | lead |
| lean | leant | leant | tilt |
| learn | learn | learn | learn |
| leave | left | left | leave |
| lend | tape | tape | occupy |
| let | let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain | lie |
| light | lit | lit | illuminate |
| lose | lost | lost | lose |
| make | made | made | produce |
| mean | meant | meant | to mean |
| meet | met | met | meet |
| mistake | mistook | mistaken | make a mistake |
| pay | paid | paid | to pay |
| prove | proved | proven | prove |
| put | put | put | put |
| quit | quit | quit | go out |
| read | read | read | read |
| ride | rode | ridden [‘ridn] | ride a horse |
| ring | rank | rung | ring |
| rise | rose | risen [‘rizn] | get up |
| run | ran | run | run |
| say | said | said | speak |
| see | saw | seen | see |
| seek | sought | sought | search |
| sell | sold | sold | sell |
| send | sent | sent | send |
| set | set | set | put |
| sew | sewed | sewn | sew |
| shake [ʃeik] | shook [ʃuk] | shaken [‘ʃeik(ə)n] | shake |
| show [ʃəu] | showed [ʃəud] | shown [ʃəun] | show |
| shrink [ʃriŋk] | shrank [ʃræŋk] | shrunk [ʃrʌŋk] | reduce |
| shut [ʃʌt] | shut [ʃʌt] | shut [ʃʌt] | close |
| sing | sang | sung | sing |
| sink | sank, sunk | sunk | drown |
| sit | sat | sat | sit |
| sleep | slept | slept | sleep |
| slide | slide | slide | slide |
| sow | sowed | south | sow |
| speak | spoke | spoken [‘spouk(e)n] | speak |
| spell | spelled | spelled | to spell |
| spend | spent | spent | spend |
| spill | spilt | spilt | shed |
| spoiler | spoilt | spoilt | spoil |
| spread | spread | spread | spread out |
| spring | sprang | sprung | jump |
| stand | stood | stood | stand |
| steal | stole | stolen [‘stəulən] | steal |
| stick | stuck | stuck | prick |
| sting | stung | stung | sting |
| sweep | swept | swept | sweep |
| swell | swelled | swollen [‘swoul(e)n] | swell |
| swim | swam | swum | swim |
| swing | swung | swung | sway |
| take | took | taken [‘teik(ə)n] | take, take |
| teach | taught | taught | learn |
| tear | tore | torn | tear |
| tell | told | told | tell |
| think [θiŋk] | thought [θɔ:t] | thought [θɔ:t] | think |
| throw [θrəu] | threw [θru:] | thrown [θrəun] | throw |
| understand [ʌndə’stænd] | understood [ʌndə’stud] | understood [ʌndə’stud] | understand |
| wake | woke up | woke [‘wouk(e)n] | wake up |
| wear | wore | worn | wear |
| weep | wept | wept | cry |
| wet | wet | wet | wet |
| win | won | won | win |
| wind | wound | wound | wriggle |
| write | wrote | written [‘ritn] | write |
Let's see clearly how the forms of irregular verbs change in sentences:
- I write a letter to my Grandmother. — My father wrote a bestseller last year.— This story was written by unknown soldier of the Second Worlds War.
- I see my best friend every day. I saw my cousin three days ago at my uncle Bens birthday party. – I have already seen this comedy.
By following the rules described in the article, it will become much easier to learn the wrong ones. Good luck!
Most grammar reference books pay little attention to the topic of regular English verbs. In fact, these words have their own characteristics that all students need to become familiar with.
Main characteristics of regular verbs
This group of words is distinguished by the way they form the past tense. Regular verbs add the ending -ed to the stem. The remaining cases are considered exceptions, calling those words incorrect. When attaching an ending to a stem, it is important to remember some cases of its interaction with final consonants and vowels:
- if the verb ends in -e, it is removed: manage – managed (to cope, to succeed);
- the final consonant is doubled if it is preceded by a short stressed vowel: knit – knitted (knit);
- if there is a consonant before the final -y, this letter is replaced by -i: study – studied (to study, study);
- When the letter -y at the end of a verb is preceded by another vowel, -y remains: play – played (play).
The rules for adding the ending -ed are necessary to prevent errors in writing. But the pronunciation of such verbs also varies depending on the final sound of the stem:
- the ending -ed is read as [d] if it is preceded by a vowel or a voiced consonant: allow – allowed [əˈlaʊd] (to allow), stay – remained (to remain), worry – worried [ˈwʌrid] (to worry);
- -ed conveys the sound [t] after voiceless consonants: work – worked (work), discuss – discussed (discuss);
- -ed is pronounced as when the verb ends in t or d: admit – admitted [əd’mɪtid] (to admit).
There are more regular verbs in English than irregular ones, but there is no need to remember them all. It is enough to learn the features of adding the ending of the past tense and its pronunciation.
Table of regular verbs in English
For informational purposes, students should pay attention to a small summary table of these words. It also covers the basic rules of regular verbs in English.
| Initial form | Transcription | Past tense | Transcription | Translation |
| agree | [əˈɡriː] | agreed | [əˈɡriːd] | agree |
| allow | [əˈlaʊ] | allowed | [əˈlaʊd] | let |
| answer | [‘ɑːnsə] | answered | [‘ɑːnsəd] | reply |
| arrive | [əˈraɪv] | arrived | [əˈraɪvd] | arrive |
| believe | believed | believe | ||
| borrow | [ˈbɒrəʊ] | borrowed | [ˈbɒrəʊd] | occupy |
| call | called | call, call | ||
| change | changed | change | ||
| confess | confessed | to acknowledge | ||
| cook | cooked | prepare | ||
| cry | cried | cry, scream | ||
| decide | decided | decide | ||
| dry | dried | dry | ||
| explain | [ɪkˈspleɪn] | explained | [ɪkˈspleɪnd] | explain |
| express | [ɪksˈpres] | expressed | [ɪksˈprest] | to express |
| finish | [ˈfɪnɪʃ] | finished | [ˈfɪnɪʃt] | end |
| greet | greeted | to greet | ||
| handle | handled | address | ||
| help | helped | to help | ||
| invent | [ɪnˈvent] | invented | [ɪnˈventid] | invent |
| judge | [ʤʌʤ] | judged | [ʤʌʤd] | judge |
| knit | knitted | to knit | ||
| locate | located | settle down | ||
| love | loved | be in love | ||
| marry | married | marry | ||
| manage | managed | manage | ||
| neglect | neglected | neglect | ||
| offer | [ˈɒfə] | offered | [ˈɒfəd] | suggest |
| open | [ˈəʊpən] | opened | [ˈəʊpənd] | open |
| play | played | play | ||
| promise | promised | promise | ||
| return | returned | come back | ||
| stop | stopped | stop | ||
| talk | talked | speak | ||
| use | used | use | ||
| want | wanted | want |
If you studied English as a child, then you are familiar with long tables with three forms of irregular verbs from school. But the regular verbs of the English language, despite their frequent use in speech, for some reason are always ignored and not studied in tabular form. And in vain, because they also have special grammatical cases. In addition, by memorizing a whole list of regular verbs, we will expand our vocabulary and feel more confident when constructing sentences, without a doubt putting any verb into the form required by the context. But first, let’s remember once again what rule gave the name to such verbs.
Forms of regular English verbs
As you remember, in English grammar there are only four verb forms. Two of them do not require close study: we become familiar with the infinitive when we work on learning new words, and the present participle (Participle I) is invariably formed by adding the ending –ing. There remain two forms, according to which the division into regular English verbs and irregular ones occurs.
According to the grammatical norm*, the formation of the Past Simple (simple past) and Participle II (past participle) occurs by adding the ending –ed to the stem of the word. Accordingly, the appearance of these verb forms is the same.
*Exceptions to this rule are precisely the class of irregular verbs.
But not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. Adding an ending has its own phonetic and grammatical nuances associated with linguistic features. The following grammar table will help you avoid incorrect formation and pronunciation of past tense forms.
| Grammar rules | |
| Rule | Example |
| For verbs ending in -e, the final vowel is not doubled, i.e. only the letter d is added. | ti e-tie d (tie)
lik e– like d (like) queu e–queue d (stand in line) |
| If a word has one syllable and it ends with a consonant, then it is doubled. | kni t–kni tted (to knit)
pla n– pla nned (to plan) ro b–ro bbed (rob) |
| The final l when adding an ending always requires duplication. | travel l– travel lled (travel) |
| Verbs ending " consonant+y", replace the last letter with i. | t ry-t Ried (try)
hur ry– hur Ried (hurry) car ry– car Ried (carry) |
| Words ending in –y with a preceding vowel add the ending –ed as standard. | enj oh– enj oyed (enjoy)
st ay– st ayed (stand) pray – pra yed (pray) |
| Pronunciation nuances | |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiced d if it is preceded by a voiced sound. | live-li ved (live)
phone - phon ed (call) |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiceless t if it is preceded by a voiceless sound. | swap – swap ped (exchange)
finish – finish shed (end) |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiced id if preceded by the letters d or t. | study – stu died (study)
wait-wai ted (wait) |
Now we are familiar with all the important points related to the correct formation of verb forms. It's time to get acquainted with the popular representatives of this class of verbs. The table below will present the most common regular verbs with translation and their pronunciation in English.
Regular English verbs – 50 words with transcription and translation
So, we bring to your attention the basic regular verbs in English with transcription and translation.
| Top 50 Regular English Verbs | |||
| Infinitive | Past Simple=
Past Participle |
Transcription | Translation |
| agree | agreed | [əˈɡriː – əˈɡriːd] | agree |
| allow | allowed | [əˈlaʊ – əˈlaʊd] | allow |
| answer | answered | [‘ɑːnsə - ɑːnsəd] | reply |
| arrive | arrived | [əˈraɪv – əˈraɪvd] | arrive |
| believe | believed | believe | |
| call | called | call, call | |
| close | closed | close | |
| cook | cooked | prepare | |
| copy | copied | [ˈkɒpi – ˈkɒpid] | copy |
| cry | cried | scream, cry | |
| decide | decided | decide | |
| defend | defended | protect | |
| discuss | discussed | discuss | |
| dry | dried | dry | |
| explain | explained | [ɪkˈspleɪn – ɪkˈspleɪnd] | explain |
| happen | happened | [ˈhæpən — ˈhæpənd] | happen, occur |
| help | helped | to help | |
| invite | invited | [ɪnˈvaɪt - ɪnˈvaɪtɪd] | invite |
| jump | jumped | jump | |
| listen | listened | [ˈlɪsn – ˈlɪsnd] | listen |
| look | looked | look | |
| love | loved | be in love | |
| manage | managed | manage, cope | |
| marry | married | marry | |
| move | moved | move, move around | |
| need | needed | need | |
| offer | offered | [ˈɒfə – ˈɒfəd] | suggest |
| open | opened | [ˈəʊpən — ˈəʊpənd] | open |
| play | played | play | |
| prefer | preferred | prefer | |
| prepare | prepared | ready | |
| promise | promised | promise | |
| reach | reached | achieve | |
| realize | realized | [ˈriːəlaɪz – ˈriːəlaɪzd] | understand, realize |
| remember | remembered | remember, recall | |
| return | returned | come back | |
| save | saved | keep | |
| smile | smiled | smile | |
| start | started | start off | |
| stop | stopped | stop | |
| surprise | surprised | surprise | |
| switch | switched | switch | |
| talk | talked | talk, chat | |
| thank you | thanked | [θæŋk - θæŋkt] | thank |
| translate | translated | transfer | |
| use | used | to use, to use | |
| want | wanted | want, desire | |
| watch | watched | look | |
| work | worked | work | |
| worry | worried | [ˈwʌri – ˈwʌrɪd] | worry, worry |
Congratulations, we have studied over 50 words if we take into account the example verbs used in the theoretical part. Now you not only know what regular English verbs are in theory, but you can also give many practical examples of them. Be sure to continue to improve your English and see you in new classes!
Views: 398
- The height of the main building of Moscow State University on Sparrow
- Temple-chapel of Boris and Gleb on Arbat Square
- Botanical gardens, their scientific profile and tasks The role of botanical gardens in the world
- Strastnoy Boulevard 5 building architecture
- Imprisoned in a sewer: The history of the Gorodnya River
- Press release of the grand opening of the memorial sign “Memorial complex dedicated to the cities of military glory” on Poklonnaya Hill
- De Tolly, who deceived Napoleon (1 photo)
- This street, this house: st.
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Period of independent development
- Ghee ghee recipe with photo Preparation of ghee with water
- From the history of Moscow hospitals - pharmacy order
- Irregular verbs in Spanish Spanish irregular verbs
- How to tell time in French
- Irregular verbs of the English language: lists of words for different levels of knowledge
- Degrees of comparison of adjectives – Die Steigerung der Adjektive
- Degrees of comparison of adjectives – Die Steigerung der Adjektive
- A Sports Center
- Modal verbs in German
- Phrasal verbs: GET and its derivatives
- Davydov Denis Vasilievich