Treatment and prevention of caries of primary and permanent teeth in children at an early age. How to properly treat caries of baby teeth in a child. Caries of baby front teeth is not dangerous.
Hello, dear readers. It's time to talk about how caries in children is treated. This problem can occur in both infants and children aged 5 years. Some parents do not consider it necessary to expose their child to unnecessary stress and treat baby teeth. In this article we will talk about the need for this procedure, possible complications and methods of prevention. We will also consider the causes that provoke caries, characteristic symptoms and diagnosis.
Types of caries
The classification of this disease is based on the depth, localization of the lesion and intensity of pain.
There are: caries on baby teeth and permanent teeth (can occur in children over 5 years of age).
Based on the depth of distribution there are:
- The initial stage of the disease is when white spots of varying sizes appear on the surface of the teeth. During this period, the baby still has no pain. If treatment is not started, these spots will gradually darken, eventually turning black.
- The superficial stage is characterized by superficial damage to the tooth tissue. The child begins to experience pain, usually when eating sweets or something sour or salty.
- Middle stage. Accompanied by intense pain, dentin and tooth enamel are rapidly affected.
- Deep degree. Is the most dangerous stage. At this stage, most of the internal tissues, as well as the tooth enamel, are damaged. The presence of such a condition may be indicated by a complete refusal to eat, the child’s capriciousness, or constant pain.
Primary and secondary caries are considered. In the case of the first, the disease occurs for the first time, as for the second, a relapse of the disease is observed. There are cases when caries develops under a filling, and it is called internal.
According to the speed of development, they are distinguished:
- compensated - the course of the disease is slow, sometimes it can even slow down;
- subcompensated - develops gradually, parents may not notice its appearance for a long time;
- decompensated - a rapid process of destruction of the tooth surface, accompanied by characteristic symptoms, severe pain and the inability to chew food.
Based on the location, they distinguish:
- fissure - occurs in depressions on the surface of the tooth;
- circular - affects the dental tissues along the periphery, in the gum area;
- approximal caries - affects the upper part of the teeth lying on the opposite jaw, that is, those with which the primary infected tooth comes into contact;
- cervical - occurs at the junction of the gum and crown.
Based on how many teeth are damaged, there are:
- generalized - most of the teeth are affected;
- multiple - found on several teeth;
- single - the affected area is on only one tooth.
Features in children

- It is important to understand that children have a low degree of dental mineralization. Unlike adults, wide dentin tubules are present. Pulp activity is low. All this contributes to the accelerated development of caries.
- As a result of infectious processes in the body, a toddler may develop caries.
- In toddlers, there are more forms of manifestation of this disease. Unlike adults, there are superficial and circular.
- The disease can occur even in the smallest children, soon after the appearance of the first tooth.
- Toddlers are characterized by multiple lesions. Caries occurs not on one tooth, but on ten or more at once.
- In children, the presence of even serious defects in dental tissue may not cause any symptoms.
We, like any child, had caries, more than once. I would like to note that the initial experience with the dentist’s office (in a public clinic) was very unpleasant. I was very angry at how the doctors treated little patients rudely and refused to wear gloves. I, of course, controlled the process and made sure that my child was treated with respect, and forced the doctor to put on the sterile gloves that I had purchased in advance. The result of this treatment is the development of inflammation under the filling. We did not return to this clinic; I took my son to a paid one. The conditions and attitude are incomparable. In addition, his favorite cartoon was turned on for my son, which also pleased me. When we got to the first appointment, it turned out that the baby was not brushing his teeth correctly, I mean, I was doing it wrong too. Using a model as an example, the dentist showed what movements should be used to clean the oral cavity. Even though I took my son to the dentist’s office twice a year, caries still had time to form. As our doctor said, this is due to an excessive love of sweets and constant problems with reluctance to brush teeth.
Tooth decay and breastfeeding

Mother's milk has a beneficial effect, is a good means of prevention, and prevents the development of caries. You need to know that breast milk contains specific immunoglobulins that have a protective function and successfully suppress all bacterial activity. If a mother feeds her baby for more than a year and a half, the level of lactoferrin, a protein that kills pathogenic microorganisms, increases in his body. It is important that the baby receives valuable substances from mother’s milk, and in a form that is easily digestible for the child’s body. Thus, breastfeeding has a beneficial effect on strengthening tooth enamel and tissue mineralization.
Needs treatment

- The problem of many young parents is that they do not take the appearance of changes on their child’s baby teeth seriously. A mother may consider that there is no need to treat her 4-year-old son’s teeth if they are already replaced by permanent ones. However, she does not know that bacteria that cause caries can harm the baby’s entire body, and the consequences of this disease can be quite serious.
- Mom must understand that caries is an infectious disease. Microorganisms from the oral cavity penetrate into the digestive organs during swallowing, which leads to abnormalities in their functioning. In addition, the affected teeth become quite sensitive to changes in food temperature, so the baby will react sharply to cold or hot food. Due to pain, the child will begin to refuse to eat. It is believed that a toddler suffering from toothache begins to lag behind in development.
- It is important to understand that the lack of treatment will lead to the infection process affecting the rudiments of the molars. In addition, advanced caries leads to premature removal of the baby tooth, which will lead to the development of malocclusion.
- And do not forget that a neglected tooth can begin to decay, inflammation will spread to the roots - the baby will experience unbearable pain.
Causes
It is important to know what was the factor in the development of caries in order to be able to prevent this process next time. There are various causes of caries in children, let's take a look at the main ones.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy diet of the expectant mother. It must be remembered that the rudiments of teeth are formed during the period of intrauterine development.
- Transfer of carious microbes from a parent to a child through kissing or using the same utensils.
- The lack of solid foods in a child’s diet does not allow the teeth to be cleaned naturally.
- Lack of calcium in the body, which is responsible for tooth enamel (its strengthening).
- Low degree of mineralization of baby teeth.
- Delayed weaning from the pacifier.
- The presence of a pathology such as rickets affects the accelerated destruction of dental tissues.
- The enzymatic composition of saliva can have a negative effect on tooth enamel.
- Anomaly of bite and dentition.
- Lack of oral hygiene.
- Increased fluoride content in foods and drinking water.
- An excess of carbohydrate-containing foods in a child’s diet leads to increased proliferation of bacteria; during the decay of the latter, organic acid is formed, damaging tooth enamel.
- In infants, bottle caries most often occurs, which occurs due to the fact that the baby falls asleep with a bottle in the mouth.
- If the mother suffered a serious illness during pregnancy or was forced to take medications, especially in the first trimester, then there is a high probability that the correct development of the teeth, which begin to form during this period, will be disrupted.
- The occurrence of caries in a child under 3 years of age is most often caused by the effects of medications or the presence of chronic pathologies. It is very important that children at this age do not indulge in snacking, in particular sweets, as this negatively affects their teeth.
Symptoms

How to determine in time that a baby has caries? Sometimes the process goes unnoticed, and parents find out about the disease when it is in a fairly advanced state.
- The appearance of white spots on the surface of the tooth, which leads to a change in uniform color.
- Pain while chewing food, acute reaction to cold or hot, sour, salty.
- Bad breath.
- The appearance of crater-shaped cavities.
It is important that in the early stages the disease is asymptomatic and the whole complex of symptoms is present only at the most advanced stage of the disease. Therefore, it is so important to visit the dental office twice a year, without waiting for the child to experience pain.
If we consider dental caries in young children, we can distinguish bottle and cervical types. In children under 3 years of age, microorganisms actively damage the cervical area of the canines and incisors on the upper jaw, while the lower jaw remains intact due to the fact that during breastfeeding or bottle feeding, the teeth located below are cleaned naturally (by the tongue).
Signs of cervical caries:
- localization of the lesion at the base of the gums;
- no hypersensitivity;
- due to thinning of the enamel, the color of the affected area changes;
- the stain increases, which leads to the formation of a hole in the tooth cavity, causing severe pain;
- At the beginning of the disease, only a specialist will be able to notice any changes.
Signs of bottle caries:
- the appearance of plaque on the upper canines and incisors;
- two or more teeth are damaged at once;
- the spots are characterized by a yellowish or whitish tint;
- there is a multiple nature;
- the baby has increased sensitivity;
- the lesions are localized in the area of the tooth neck;
- as the disease progresses, the color of the spots will change to dark brown;
- The baby experiences pain when coming into contact with food of different temperatures or chemical composition.
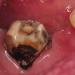
About how caries manifests itself in children, photos of this disease:


Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease at an early stage, often invisible to the normal eye, the following procedures can be performed:
- examination of the toddler’s oral cavity by a specialist using a mirror and probe;
- X-ray, which allows you to examine the initial stage of caries;
- transillumination - the baby’s teeth are scanned;
- photopolymerization;
- electroodontometry - a pain symptom is determined using a weak discharge current;
- drying is a method for diagnosing the early stage of the disease;
- vital staining - blue is applied to the tooth, the affected areas are painted blue;
- fluorescent stomatoscopy - diagnosis is carried out using ultraviolet radiation. At the same time, healthy areas are painted blue, and affected areas are dark.

Possible complications
If caries is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious consequences.
- The child may develop.
- The occurrence of periodontitis. Inflammation of nearby tissues occurs and can lead to the complete death of the permanent tooth germ. Such a case will be the answer for parents who have the question “”.
- If the teeth are not treated, an extensive infection process may begin, which will lead the tooth to such a condition that it will need to be removed. Due to premature removal, there will be a high probability of malocclusion, and even deviations in jaw development.
- If the baby has pain or a tooth is pulled out, this will lead to problems with chewing food, which in turn will cause a disruption in the digestion process.
Treatment

It is important that the baby’s parents understand the need for medical procedures even if they have disease in their baby teeth. In addition, you need to understand that the sooner you see a dentist, the less painful the preparation will be.
If this is your first time visiting a doctor, make sure that he is a good specialist who loves children. It is important that the baby does not get scared and accepts this doctor normally.
The treatment process includes:
- Carrying out anesthesia in two stages, the gel is applied to the mucous membrane, after which an injection is given;
- after the local anesthesia has taken effect, drilling of the cavity affected by caries begins, if no other method can be used.
Parents should understand that the proposed treatment method depends on the stage of development of the disease:
If the initial stage of the disease is observed, the child will be offered:
- silvering. Popular among children under 3 years old. Silver has an antibacterial effect and helps prevent enamel destruction. The procedure is carried out by applying silver nitrate to a cotton ball, followed by treatment of the teeth. However, it must be taken into account that during this procedure, the tooth is painted black.
- remineralization therapy. It is the penetration of calcium preparations into the tooth structure, while the crystal lattice is restored. There is a wide variety of remedies in this area, so the drug is selected individually for each child, depending on his age, the characteristics of the course of the disease and the level of its intensity. The difficulty is that the course of treatment is long, visits to the dentist are carried out daily. The baby needs to be supervised, because a large amount of fluoride in the body can lead to serious poisoning.

If a child has medium or deep caries, then, as a rule, classic preparation options with further filling are used. However, there is an alternative:
- preparation with a drill - drilling occurs with a tip at fairly low speeds, after which water cooling occurs;
- art technique - using hand tools to remove various tissues. This method is very painless;
- laser preparation - this method is easy to use, the action is aimed exclusively at the affected area of the tooth, and also does not cause pain;
- ozonation - tissues are nourished with ozone, which helps actively fight microorganisms;
- depophoresis - active substances penetrate into dental tissues under the influence of electric current.
If the condition is neglected, the tooth may not respond to treatment and will have to be removed.
You need to know that composites, glass ionomer cements, compomers and sealants are used for the filling procedure. Compomers, which are fillings of different colors, are very popular among young children. The kid chooses the paint he likes with interest, and then happily shows off the new filling to his friends.
Help at home

- Along with medical actions in the dentist's office, it is important to carry out therapy at home. The doctor will prescribe a special rinse or children's toothpaste that has an anti-caries effect.
- If we are talking about a child who is not yet 4 years old, then this product must be selected without fluoride. At this age, it would be correct to use active calcium ions and antibacterial components. It is important that the baby rinses his mouth after every meal, only if he can cope with this procedure.
- A toddler who is over 2 years old may be prescribed the following mouth rinse:
- a weak solution of sea salt (a teaspoon per glass of warm water);
- infusion of pharmaceutical chamomile (for preparation you need a tablespoon of dried plant per glass of boiled water; the solution is adjusted within half an hour);
- sage decoction (to prepare, add a tablespoon of crushed dry plant to a glass of hot water).
Prevention

It is important to teach your child to take care of his teeth from childhood. What can be done to reduce the risk of dental caries?
- Maintaining hygiene. Very important from a very young age. At first, the mother does this using special devices, then she accustoms the child to a children's toothbrush.
- After each meal, you need to rinse your mouth.
- You need to reduce your consumption of carbohydrate-containing foods.
- If there is a lack of fluoride, special medications are prescribed, and the use of fluoridated water is recommended.
- Your baby's diet should include solid foods every day, such as carrots and apples. They will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the teeth and gums. In addition, chewing solid food has a positive effect on neutralizing the acid contained in the oral cavity, thereby preventing the development of carious microorganisms.
- It is important to visit your dentist for a consultation at least twice a year.
Now you know what the condition of caries in children is. Remember the need for medical procedures in children of any age if there are any changes in the structure of the tooth. Make sure that your child is not afraid of meeting with the dentist and treats it normally. Spend more time on preventive measures, because it is always easier to follow special rules than to then torment your child with the sight of a drill.
Caries of primary teeth in children has recently become a very pressing problem for both parents and dentists. This pathological process is increasingly being found in children under 2 years of age.
According to some medical data, the incidence of caries at the age of 1 year and above has increased sharply, and nowadays 80% of children under the age of four have at least one damaged (“carious”) tooth. To prevent the development of caries in preschool children, caring parents need to learn as much information as possible to help them recognize the insidious disease in time and contact a specialist, thereby preventing the child’s health from deteriorating.
Causes of caries in baby teeth
Caries of primary teeth is the development of a pathological process in the hard tissues of a child’s teeth, leading to the gradual destruction of tooth enamel, as well as internal tissue damage. This pathological process manifests itself in several forms and stages. At the very beginning, caries manifests itself as superficial damage to the tooth enamel, but if timely treatment is not carried out, it can form a deep cavity inside the tooth, and then penetrate into its tissues and cause an inflammatory process. First of all, the baby's upper primary incisors, as well as the surface of the enamel of the molars, which perform the chewing function, can suffer from caries.
The onset of caries development is observed during the prenatal period if the fetus has damaged tooth buds, which usually form in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is for this reason that the expectant mother is advised to exercise special caution during this period. The main cause of the occurrence and development of caries in children is considered to be a violation of the structure of tooth tissue. Typically, expectant mothers experience diseases such as rheumatism, hypertension, all kinds of infections and viral infections, as well as various diseases of the endocrine system, or a severe form of toxicosis. Factors that provoke the development of early caries may be smoking by the pregnant mother, or excessive use of various medications by the woman throughout pregnancy.
During the period of eruption of the child’s first teeth, it is necessary to remember to maintain oral hygiene. What are the causes of caries in baby teeth? The main factors that cause caries are:
- non-compliance or neglect of the rules of hygiene of the child’s oral cavity and gums;
- poor nutrition with excessive consumption of carbohydrate foods and sweet foods;
- using pacifiers, as well as bottles with nipples to feed the baby for a long period (falling a child to sleep with such a bottle in the mouth provokes the rapid progression of the so-called “bottle” caries);
- artificial feeding of an infant due to an infectious or hemolytic disease;
- lack of microelements (in particular fluoride) in the children's diet, which are important for the growth processes of the child's body.
The above “bottle” caries deserves special attention. It can quickly destroy a baby’s teeth, preventing them from further developing fully. This type of caries initially manifests itself in the form of a characteristic brown coating on the enamel, and after that it provokes rotting and almost complete destruction of the child’s teeth. The reason for this negative process is the contact of the baby's teeth for a long period with the sweet mixture contained in the feeding bottle.
Thus, a special environment is formed in the baby’s mouth, which is very favorable for the proliferation of harmful bacteria. For such bacteria, a natural source of energy is carbohydrates, as a result of the processing of which acid appears, which literally “corrodes” the enamel of children's milk teeth.
Symptoms of caries in baby teeth
Caries of primary teeth has several stages of development. Therefore, if any pathologies occur in the form of unremovable plaque, white or brown spots on the child’s tooth enamel, it is necessary to urgently show the child to a pediatric dentist.
The main symptoms of caries in childhood can be the child’s complaints about various unpleasant sensations while eating food, especially cold or hot - in such cases it is quite possible that caries has already penetrated into the deeper tissues of the tooth. Therefore, parents need to pay special attention to such complaints of the child so that they can provide him with timely help. Often it is difficult for a child to formulate his thoughts, and he cannot explain in detail what exactly is bothering him. However, even a child’s refusal to eat a specific food or food in general should immediately alert parents. A child chewing food on one side of the mouth may also indicate that the baby has tooth pain.
Determining caries of baby teeth in young children is not so difficult. Visually, you can notice spots (most often white or brown) on carious teeth, and you can also observe the baby’s painful reaction to eating certain foods. In addition, the child may have an unpleasant odor from his mouth (this is due to decay processes resulting from rapidly developing caries).
The first symptoms of caries in primary teeth should cause an immediate reaction from parents, because This process can develop very rapidly, instantly affecting several teeth at once. If you do not sound the alarm for a long time and do not take appropriate measures, then the child’s entire dentition may be affected by caries.
What does caries look like in baby teeth?
Caries of primary teeth can be divided into several types, depending on its visual manifestation, the depth of damage to the enamel and dental tissue, as well as symptoms. Parents often ask the question, “What does caries look like in baby teeth?” To answer this question, it is necessary to list the main stages of the development of the disease:
- Initial degree of caries. Characteristic signs of this process are the appearance of white spots of various sizes on the tooth enamel, but there is still no pain. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the next stage in the development of initial caries will be the darkening of the spots (they will turn brown or black). It should be noted that at the initial stage of development, caries can still be completely prevented.
- Superficial appearance of caries. This type of pathological process is characterized by defects in the tissues of a damaged tooth, which initially appear exclusively on its surface. The baby is already experiencing pain, but mainly when eating something sweet, sour, or salty.
- Average degree of caries. It is accompanied by severe pain in the tooth, including that which occurs when it is exposed to cold or too hot food. In this case, caries quickly affects both the enamel and dentin (i.e., internal tissues) of the teeth.
- Deep degree of caries. This is the most dangerous stage of the disease. Both the enamel and most of the internal tissues of the tooth are affected. Such caries causes a child’s reluctance to eat, loss of appetite, and frequent whims. Most often this is due to constant toothache.
It should be taken into account that caries of primary teeth quite often affects the entire dentition. Sometimes the number of carious teeth in a child reaches 20. In addition, several cavities can form in one tooth at once, because In young children, due to their anatomical characteristics, the layer of enamel, as well as the internal tissues of the tooth, is much thinner. This detail allows the process to spread deeper into the tooth much faster.
Caries of primary anterior teeth
Most often, caries of baby teeth in young children begins with the process of damage to the front teeth, since they are the ones who are most in contact with milk formulas and sweet foods. This kind of caries is called “bottle caries” because a small child mainly gets food through a bottle. Bottle caries is a rather serious problem, because as a result of rapid progression, both in its distribution and depth, this pathological process can affect even neighboring teeth.
Caries of primary front teeth forms dark spots on the tooth enamel, which are visible during a visual examination of the child’s mouth. Typically, the dentist checks the baby's front teeth for caries by backlighting them. To clarify the clinical diagnosis of “caries of the anterior teeth,” enamel probing is carried out, and using the results of targeted radiographic tests, it is possible to identify the depth of carious lesions in primary teeth. If the disease is in its initial stage, then fluoridation must be used for therapeutic purposes, as well as changing the child’s eating habits and improving hygiene procedures for oral care.
In more advanced stages of caries of primary anterior teeth, it is suggested that the child be treated under intravenous anesthesia. In this case, the process of restoring anterior primary teeth includes the use of glass ionomer materials, as well as filling material intended for the restoration of a damaged tooth.
Initial caries of primary teeth
Initial caries of primary teeth manifests itself in two stages: first, the so-called. “stain stage”, and then the stage of superficial carious lesion of the tooth develops. The occurrence of caries “in the stain stage” is associated with the appearance of white chalky spots on the baby’s teeth (usually on the upper incisors) - they have different sizes and shapes. The child still has no pain. Carious spots without certain clear boundaries grow over time and form the so-called. "carious cavities". Thus, the initial caries from the first stage gradually develops into its other stage - superficial damage to the tooth. Sometimes this process is determined by such signs as softening of tooth enamel, the appearance of roughness on the surface of a carious stain, increased sensitivity of teeth when a child eats salty, sweet or sour, as well as hot or cold foods.
Initial caries of primary teeth must be distinguished from other diseases, for example, fluorosis or enamel hypoplasia. To establish a clinical diagnosis, stomatoscopy is performed under special ultraviolet lighting. If a tooth is damaged by caries, then there is no glow of the tissues; The tissues of a healthy tooth give off a light green glow, but if a child has enamel hypoplasia, it is gray-green. Another method allows you to determine the presence of a carious process in the initial stage: for this, tooth tissue is wetted in an aqueous solution of methylene blue (2%) and a solution of methylene red (1%). To do this, the enamel surface, previously cleaned of plaque, is dried, and then a dye solution is applied to it. After a couple of minutes, the demineralized areas of the tooth become stained with varying intensities.
Deep caries of baby teeth
Caries of primary teeth develops gradually, affecting the dental tissues deeper and deeper. With deep caries, destruction of the bulk of dentin is observed. In this case, only a thin layer separates the pulp from the carious cavity. The child often complains of severe pain when eating cold or hot food.
It should be noted that deep caries of primary teeth is a particularly serious disease that develops rapidly and in most cases turns into inflammation of the dental pulp. Diagnosis of deep caries in children includes, first of all, studying the condition of the pulp. Diagnostic results directly influence the choice of treatment. This can be a session with the installation of a medicated pad, or treatment using antibiotics and corticosteroids. Often in such cases, filling of the affected tooth is used with the application of odontotropic pastes under the filling.
There are cases when the condition of the pulp in deep caries cannot be determined, then a control filling is used in the form of burnt asbestos, which is left in the carious cavity after its careful treatment. If the child does not experience any pain within a week, the cavity can be filled. Odontotropic paste is applied to its bottom. Unfortunately, caries of primary teeth in the deep stage in children is quite common. The main thing in this matter is to prevent its complications in time.
Circular caries of primary teeth
Circular caries of primary teeth usually develops in children with weakened immune systems: first of all, premature babies, those suffering from rickets, tuberculosis, etc. This type of caries also occurs in children who have had infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, etc.) . In this case, damage to the upper frontal teeth is mainly observed.
In the initial stage, circular caries covers the frontal surface of the baby tooth, namely the area of its neck, and then spreads throughout the entire crown of the tooth and penetrates deeper. Naturally, under the influence of a pathological process, the crown of the tooth is destroyed and broken. Caries affects the pulp, so most often during a dental examination, a picture of destruction of the dental crown is observed. Usually, the death of the pulp is asymptomatic, and only an x-ray shows the advanced process of chronic granulating periodontitis.
Circular caries of primary teeth very often occurs without the presence of an inflammatory response to the pathological process, which indicates a low level of children's immunity. Timely remineralization therapy is effective when, with the help of replacement dentin, the root pulp is isolated from the coronal pulp. Of course, therapeutic manipulations, first of all, should be aimed at improving the child’s well-being. Initial damage to teeth by circular caries is treated with remediation, and deeper damage is treated with filling.
Children with varying degrees of caries should be observed at the dispensary. Clinical examination helps to timely identify the initial stage of circular caries, as well as apply preventive measures for the development of complications.
Is it possible to treat caries in baby teeth?
Quite often, adults do not know whether to treat caries of baby teeth in their children. Parents of a teething child should remember that caries of baby teeth over a long period of time can develop almost asymptomatically and unnoticed. This indicates the particular importance of regular examination of the baby by a dentist.
If childhood caries is not treated at all, this disease can cause a number of serious complications. First of all, it should be noted the damage to the deep tissues of a carious tooth, and subsequently the development of periodontitis (the process of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth), as well as pulpitis (the process of inflammation of the soft dental tissues). This point is due to the fact that the enamel of a child’s baby teeth is much thinner than the enamel of an adult’s teeth. Thus, baby teeth are much more susceptible to the negative effects of pathogenic microflora and destruction. That is why it is imperative to treat caries of baby teeth, and in no case put off this problem “for tomorrow.”
Complications caused by caries in a child indicate a lack of responsibility and proper attention of the father and mother to the health of the baby. Untimely treatment of childhood caries or its complete absence is the main factor leading to the need to remove affected baby teeth. This phenomenon in itself is negative, since a baby tooth removed at the wrong time is the cause of various diseases, as well as future pathologies in the development of a permanent tooth. The need to remove a baby tooth, destroyed as a result of deep caries, leads to the installation of a special prosthesis in its place, which eliminates the development of dental anomalies in the child in the future. Of course, it is best to avoid such a situation, because installing a prosthesis is a very uncomfortable procedure for a small child.
Preventing the development of caries through preventive measures and effective treatments in the initial stages is the best way to solve this problem. It is necessary to remember that the health of the entire child’s body depends on the health of the teeth.
What to do about caries of baby teeth?
Caries of primary teeth is the rapid spread of a bacterial infection in the oral cavity, developing against the background of a decrease in the resistance of the child’s body.
What to do about caries of baby teeth? In general, the appearance of caries is directly related to the cariogenic streptococcal microflora, which multiplies in the child’s oral cavity literally at lightning speed, especially in weakened children. At the first suspicion that a child has caries in baby teeth, it is necessary, without delay, to seek help from a pediatric dentist, who will promptly prescribe a course of treatment. After all, caries is, first of all, a source of a spreading pathogenic infection, which can cause various diseases of the baby’s internal organs.
Complications caused by the development of early caries can lead to complete destruction and even death of the rudiments of permanent teeth. It must be remembered that caries of primary teeth can develop very rapidly and, most often, asymptomatically. At the same time, a damaged baby tooth may not hurt at all and may not cause any discomfort in the baby. This is explained, first of all, by the absence of nerve endings in the baby tooth.
Modern medicine today, in order to timely prevent the development of childhood caries, uses various preventive measures, in particular, triple coating of a child’s healthy baby teeth with fluoride varnish. This procedure is carried out at intervals of six months. During the period when a child has permanent teeth, it is recommended to carry out another procedure called “fissure sealing”, which gives very effective results and prevents the development of carious processes in 90%.
How to stop caries of baby teeth?
Today, caries of primary teeth is observed in almost every child, so there is an urgent need to stop the development of infection as quickly as possible. Modern medicine knows how to stop caries of baby teeth and uses several well-proven methods for this purpose, in particular silvering of teeth. The procedure consists of covering baby teeth with a special solution that contains silver nitrate. This substance has a strong bactericidal effect and the ability to stop the process of exposure of tooth enamel to pathogenic microbes.
The procedure for silvering baby teeth does not require the use of drills, is carried out quite quickly and is absolutely painless for the child. In addition, this method of preventing caries is safe for the baby and does not cause allergic reactions or food poisoning. Typically, the silvering procedure is prescribed to children with the initial stage of caries, associated with the appearance of dark spots on the tooth enamel. This method favors the preservation of baby teeth until they are replaced by permanent ones. The disadvantage of silvering children's teeth is the visual effect: usually such teeth become black. The use of silver in cases of deep tooth damage with the formation of carious cavities will not bring the desired result. On the contrary, this procedure in this case can simply harm the baby, because Silver nitrate, consisting of a nitric acid salt of the silver metal, can cause a burn to the dental nerve. In turn, the child will be in great pain.
Caries of primary teeth should be treated exclusively under the supervision of a pediatric dentist, using professional equipment. In addition to silvering, which is currently under debate, there are no less effective ways to stop childhood caries. Among them, the most popular are mineralization (i.e. deep fluoridation of teeth) and ozonation (so-called disinfection of the oral cavity). The specialist decides which of these methods will be most effective in a particular case.
Treatment of caries of baby teeth
Modern medicine has various alternative methods for treating caries of primary teeth. They are aimed at eliminating all the unpleasant aspects associated with treatment, in particular, treating a damaged tooth with a dental drill.
Decay in primary teeth is treated using methods that involve treating cavities with special chemicals and hand instruments. Recently, laser dental units have also appeared, the work of which is aimed at treating caries of baby teeth. Unfortunately, so far none of the alternative methods of treating caries gives such an effective result as the use of a time-tested drill in this process. When treating childhood caries using professional dental equipment, several stages can be distinguished.
First, the affected baby tooth undergoes a thorough cleaning of demineralized, softened tissues infected with bacteria. Then the baby tooth is sterilized, as well as the carious cavity is hermetically sealed using special materials. Thus, the cured baby tooth can last until the child has it replaced with a permanent one. This is precisely the main goal of pediatric dentistry.
The decision to treat or remove a baby tooth is made by the dentist, who, based on personal experience, determines the best option based on the specific situation. It is especially important to make the right decision if the child has no pain, because treated milk teeth, like sick ones, will sooner or later fall out. Therefore, filling itself in most cases does not bring much benefit, but this process causes fear and discomfort in the child.
When observing the first signs of caries development in a child, you should immediately contact a pediatric dentist. It is important for parents to understand the fact that caries can be cured only at the stage of a “white spot” occurring. For this purpose, the child is prescribed vitamins (B1, B6, A, D, C), as well as calcium and phosphorus preparations (Calcium gluconate, Calcitonin, Sibacalcin, etc.).
Regarding folk methods aimed at treating caries of baby teeth, it is necessary to take into account the fact that folk remedies in such cases are used only for preventive purposes. They are not able to completely heal caries. Prevention of caries using folk remedies mainly comes down to rinsing the child’s mouth with decoctions of medicinal plants and ingesting restorative herbal preparations. Such prevention can be carried out at home, while treatment (in particular, filling) of baby teeth is possible only in a medical facility and is carried out by a qualified specialist. Traditional medicine recipes aimed at relieving pain in a carious tooth include the following:
- You need to put a pea-sized amount of propolis on the sore tooth and cover the area with a cotton swab for 20 minutes. Propolis has analgesic properties, but can destroy teeth, so it should not be used for a long time.
- To temporarily relieve pain, apply a cotton swab soaked in garlic juice to a tooth affected by caries.
- To rinse the child’s mouth, use an infusion of sage or chamomile: 1 tbsp. add a spoonful of medicinal herbs to a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour.
According to the recommendations of pediatric dentists, parents need to show their child to doctors, starting from the age of one, at least once every six months. Thus, you can control the baby’s development process, as well as prevent caries of baby teeth in a timely manner.
Prevention of caries in baby teeth
Caries in primary teeth can develop in children starting from a very young age. It is advisable to carry out preventive measures to prevent this pathological process together with the eruption of the child’s first milk teeth.
Using special products designed for oral care, it is necessary to regularly remove microbial plaque and food debris from the baby’s baby teeth. Such means, first of all, include a regular toothbrush. The use of children's toothpaste is recommended for children starting from the first year of age. This is the main prevention of caries in baby teeth. An important factor is the suitability of the composition of the toothpaste for children. This is primarily indicated by the information on the packaging. For example, it is better not to buy toothpaste containing fluoride for a child under three years of age. Young children are not able to properly brush their teeth and rinse their mouth; they often swallow large amounts of toothpaste. Regular swallowing of paste with fluoride by a child can cause serious consequences in the future and thereby undermine the baby’s health, because fluorine is the active element.
From the age of four, children partially acquire the skills of brushing their teeth, they know how to spit out the remains of toothpaste and, thus, can easily use toothpaste with fluoride for prevention - a substance that reduces the risk of the occurrence and development of caries in baby teeth.
As for the choice of toothbrushes, at first the mother should learn how to carefully remove plaque from the child using a special finger brush. Parents need to teach their child to brush their teeth on their own as early as possible, starting from the age of 2.5-3 years.
In addition to using toothpaste and brushing, preventive measures to prevent the development of childhood caries include a balanced diet for the child. Such a diet should include fats, carbohydrates, proteins, as well as minerals and vitamins necessary for the full formation and development of dental tissues in sufficient quantities.
Breastfeeding is one of the most important aspects of preventing caries in primary teeth. Older children should be given fluoridated salt and water, for which there are no special indications. Additional sources of calcium are primarily fermented milk products, potatoes, cheese, cottage cheese, legumes, and mineral water.
Contrary to the opinion of some mothers that baby teeth do not need to be treated because they will soon fall out, baby tooth caries discovered in a baby should not be left to chance.
Healthy and intact baby teeth are the key to the appearance of healthy permanent teeth in a teenager, which means his self-confidence and a beautiful smile.
Today dentistry has various methods for treating baby teeth.
A safe, reliable and least painful treatment option for the child’s psyche is individually selected for each child. Treating initial caries, without filling and preparation, is much easier than subsequently subjecting the child to complex procedures for a deeply damaged tooth.
Reasons for appearance
It has been proven that the main cause of carious destruction of baby teeth is microorganisms of the genus streptococci, which the baby, as a rule, first receives from the mother.
Bacteria can enter the child’s mouth when sharing dishes with parents, or when the mother licks a spoon or a pacifier that has fallen to the ground, which is especially unacceptable during the teething of baby teeth.
A child's first baby teeth have weak, delicate enamel that is easily destroyed by bacterial infection.
However, the presence of streptococci in the baby’s saliva will not cause caries of a baby tooth to develop. The destruction of children's teeth, in addition, is due to a number of predisposing factors:
- diet and eating habits;
- cleanliness of the oral cavity;
- the chemical composition of the child’s saliva;
- heredity;
- the general health of the baby.
 Sucking on a bottle of sweet juice, compote, milk or other sugar-containing drink is especially conducive to caries.
Sucking on a bottle of sweet juice, compote, milk or other sugar-containing drink is especially conducive to caries.
Microorganisms feed on carbohydrates and actively reproduce.
During their life, organic acids are released, which accumulate on baby teeth in the form of plaque and corrode their fragile enamel.
Caries can occur regardless of whether the child is breastfed or bottle-fed. Normal, regular feeding does not contribute to the development of caries. The disease can be triggered by frequent and prolonged feeding at night in the absence of subsequent cleaning of the oral cavity.
So, the main reasons for the activation of microbes that cause caries of baby teeth:
- frequent and long night feedings of sweet foods;
- sucking on a pacifier that has been previously dipped in sugar or jam;
- neglect of hygienic oral care after the child eats food.
The child should receive sweets as rarely as possible, and after eating he should be taught to rinse his mouth. Or give him unsweetened water to drink if he is still very young.
First signs
 Typically, caries in children is first detected on the front incisors.
Typically, caries in children is first detected on the front incisors.
Carious lesions of various sizes and shapes look like white, reddish or yellowish spots. This is the so-called “spot stage”.
The affected areas can be located on the cervical area of the tooth, on the lateral surfaces in contact with each other, or cover its entire crown. At the spot stage, the child still does not have any sensations.
If no treatment is carried out, the process progresses, the light spots darken, and the stage of superficial tooth destruction begins. Carious spots grow and gradually cavities form in their place. This stage is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the surface of the stain becomes rough;
- the enamel softens;
- the tooth becomes sensitive to sweet, sour, hot and cold.
The carious spot gradually covers the entire thickness of the enamel, forming a shallow and then a deep hole. When caries moves to the dentin layer, the tooth begins to hurt.

Caries on incisors
Thus, the following first signs are characteristic of caries:
- Stains on the tooth.
- Painful sensations and changes in sensitivity.
- Involvement of several baby teeth in the carious process at once. In addition, several lesions can form in one tooth. For an early age, due to the weakness of tooth enamel, multiple caries is characteristic.
- An unpleasant odor that is the result of bacterial activity. Under their influence, lingering food remains rot in the child’s mouth.
The task of parents is to regularly (at least once a week) examine their baby’s teeth and pay attention in time to unusual stains that suddenly appear on them. At this stage, it is still possible to prevent further development of the disease and cure the tooth without a drill.
Kinds
Depending on the location, external symptoms and depth of destruction of dental tissues, caries of primary teeth can be classified into several types.
Initial caries
Caries always begins with a "stain stage", first light, then dark. Gradually the spots darken and enlarge.
Superficial caries
This type of pathology is characterized by enamel defects. The child feels slight pain when eating sweet or sour foods.

Average caries
Average caries
Characterized by severe pain in the affected tooth when it is exposed to cold water or sweet food. The carious process destroys the enamel and spreads to dentin (the inner layer of dental tissue lying under the enamel).
In the diseased tooth, a cavity with a loose dark bottom and uneven edges is clearly visible.
Deep caries
This is the most dangerous type of disease. All layers of enamel and most of the dentin are affected. The tooth hurts almost constantly, the child is capricious, cries and refuses to eat.
"Bottle" caries
 This pathological process got its name due to the fact that it owes its appearance to the bottle from which a small child receives food or drinks.
This pathological process got its name due to the fact that it owes its appearance to the bottle from which a small child receives food or drinks.
This type of caries develops in children, starting from the appearance of the first milk teeth.
Bottle caries primarily affects the front teeth, because they are the ones that come into contact with sweet milk formulas and juices. Rapidly progressing, both in breadth and depth, this pathological process easily spreads to adjacent teeth.
Only an experienced doctor can determine; it is almost impossible to independently identify the destructive process. With early diagnosis, dental drilling can be avoided.
Read about how to treat swollen gums in a child.
With pulpitis, the tooth can hurt very much. If you experience such symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist to avoid losing your tooth and preventing the development of dangerous processes. Follow the link to learn all about the symptoms and treatment of pulpitis.
Circular caries
 This is a variant of the bottle tooth, when the latter develops in the cervical region of the front milk teeth and partially or completely surrounds the crown.
This is a variant of the bottle tooth, when the latter develops in the cervical region of the front milk teeth and partially or completely surrounds the crown.
Circular caries begins on the frontal surface of a baby tooth in the area of its neck, and then covers the entire circumference of the crown and deepens.
Due to the reduced immunity of children, circular caries of primary teeth often occurs without signs of inflammation.
As a result of exposure to a destructive pathological process, the crown of the tooth breaks off, and pulpitis begins - inflammation of the dental nerve.
Usually the pulp of a baby tooth dies asymptomatically, and only an x-ray can reveal advanced chronic periodontitis.
Multiple or “blooming” caries
 Due to the chemical composition of the enamel of primary teeth, the pathological process easily passes from one tooth to another; In young children, almost the entire dentition is often affected by the disease.
Due to the chemical composition of the enamel of primary teeth, the pathological process easily passes from one tooth to another; In young children, almost the entire dentition is often affected by the disease.
Typically, multiple types of caries occur in babies with weakened immune systems, premature babies, patients with rickets or tuberculosis.
This type of caries can develop in children who have had an infectious disease (measles, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, mumps).
Multiple and circular types of caries are a rather serious problem, so the disease cannot be allowed to develop to the point of irreparable consequences.
In addition to dental treatment, you may need the help of an immunologist, pediatrician and endocrinologist.
Treatment of caries of baby teeth
In case of initial caries, when one enamel is damaged, remineralization is usually sufficient. Demineralized areas are first cleaned without using a drill, and then a varnish is applied to restore the enamel.
The ICON method is also widely used. The damaged area of the tooth is covered with a special composition. It fills the pores formed by caries and hardens.

Treatment of caries using ICON technology
When the enamel is destroyed and dentin begins to decay, the carious area is excised, disinfected and filled with a filling. In many clinics, cleaning a carious hole is done using a jet of a special substance, without a drill.
Some dental offices use a laser. The appointment of laser cleaning of a carious cavity should be made taking into account the patient’s age and the picture of the disease.
There are cases when there is no point in treating a baby tooth: if caries has developed on an already loose tooth and has a sluggish course.
Complications
A carious tooth is a source of infection, and with a decrease in immunity, for example, with a cold, it can cause complications in the following organs:- ears - otitis media;
- throat – tonsillitis;
- nose – runny nose, sinusitis;
- periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum;
- osteomyelitis – inflammation of the bone and bone marrow.
Untreated caries of a baby tooth can cause underdevelopment or death of the permanent rudiment developing above it.
The loss of the chewing function of several teeth leads to malocclusion, indigestion and a deterioration in the child’s general well-being.
There are several. Superficial tooth defects often go unnoticed, but the disease is already beginning to progress to the point of tooth decay.
Do you want to know what medications help relieve gum inflammation? Read.
Prevention
What should parents do to prevent caries in children?
- Limit sweets and increase the amount of hard vegetables and fruits in the children's diet.
- Do not give your baby a “sweet” pacifier to help him fall asleep faster.
- Feeding formula from a bottle should not last longer than 15 minutes - during this time the child will have enough time to get enough.
- With the appearance of the first milk tooth, accustom the child to oral hygiene: teach him to rinse his mouth after eating, for starters, take water into his mouth and spit it out. Until the baby knows how to rinse his mouth, give him unsweetened warm water to drink after eating.
- Dairy products and greens should be present on the children's table every day.
- Teach your child to maintain oral hygiene. Your child will be less likely to get dental caries if he has his teeth brushed by an adult before the age of 7.
The best motivation for dental hygiene is a parental example.
Photo
If you discover caries in a baby tooth in a child, you should immediately contact a pediatric dentist. The doctor will decide how to treat the tooth and how to make the treatment convenient for the baby. It must be remembered that the health of children's teeth depends entirely on the responsibility of adults, on how parents will protect and care for them.

Caries of incisors

Damage to the upper primary incisors
Video on the topic
Dental caries continues to be a serious problem for many children and the most common infectious disease of childhood.
Decay in primary teeth has become an urgent problem for both parents and dentists. Children under the age of two suffer from this pathological process more and more often. Currently 80% of preschool children have at least one damaged tooth.
Eighty percent of dental caries is found in only 25 percent of children. Below we will look at what dental caries of primary teeth is, its main causes, symptoms and treatment.
What is dental and early childhood caries?
Dental
This infection, which causes tooth decay by acid-producing bacteria found in plaque.
The most important information to remember is that tooth decay is a dynamic disease process and not a static problem. Secondly, before a cavity is formed, the tooth decay infection can actually be reversed.
The progress of caries or its retreat is determined by the balance between protective and pathological factors in the mouth. Development of dental caries is a dynamic process: demineralization of hard dental tissue by acidic products of bacterial metabolism - alternating with periods of remineralization.
sporadically, periods of demineralization alternate with periods of remineralization. Lactic acid, produced by cariogenic bacteria, dissolves the calcium phosphate mineral of tooth enamel through the process of demineralization.
A child's teeth have thinner enamel than permanent teeth, making them very susceptible to tooth decay. Dental caries in children was first observed clinically as a “white spot lesion.” If the tooth surface remains intact and slightly hollow, then possible remineralization of enamel. If subsurface enamel demineralization is extensive, it will eventually cause the surface of the overlying tooth to collapse, resulting in a “cavity.”
Saliva plays an important role in preventing tooth decay. It provides calcium, phosphate, proteins, lipids, antibacterial agents and buffers. Salivation can reverse the low pH of dental plaque, and at a higher pH, calcium and phosphate can be released back into the tooth enamel.
One factor that reduces the risk of cavities is normal saliva flow. Anything less than 0.7 ml/min increases the risk of developing a cavity.
Early childhood
A dangerous form of dental caries that can destroy the teeth of preschool children and toddlers. Early childhood caries can also be defined as the appearance of any signs of dental caries on any tooth surface during the first 3 years of a child's life.

Economically disadvantaged children are the most vulnerable to RCD.
Caries of primary teeth is progressive pathological process s, which leads to the gradual destruction of enamel and damage to internal tissues. Tooth decay begins as a superficial lesion of the tooth enamel. However, if appropriate treatment is not carried out, decay can provoke the development of a deep cavity inside the tooth, penetrate into its tissues and cause an inflammatory process.
Early childhood caries is an infectious disease, and the bacteria Streptococcus mutans (Streptococcus mutans) is the main causative agent. Not only does S. mutans produce acid, the bacterium also thrives in acid. High sugar levels in the mouth increases acid levels in teeth. In children with RDC, levels of mutans streptococci typically exceed 30% of the cultured plaque flora.
Caries first affects the primary upper anterior teeth, and then the upper primary molar teeth. The initial manifestation of early childhood caries is white areas of demineralization on the enamel surface along the gum line of the upper incisors. These white spots are affected so that they later become cavities that were discolored.
The mandibles are protected by saliva and the position of the tongue during feeding. The RCD process can be so rapid that teeth develop cavities “from the moment they occur.”

The first event in the natural history of RDC is a primary infection with S. mutans. The second event is the accumulation of S. mutans to pathological levels due to prolonged exposure to sugars. The third event is demineralization of the enamel, which leads to the formation of cavities in the teeth.
Early S. mutans infection is an important risk factor for future caries development. Colonization of a child's mouth with these bacteria is usually the result of transmission from the child's mother. S. mutans can apparently colonize the mouths of infants before their teeth begin to emerge and grow.
Children at high risk for early childhood caries may develop carious lesions on their upper front teeth soon after they erupt. As the disease progresses, decay appears on the surfaces of the primary upper first molars.
Causes
The caries process should be considered as a dynamic change in the phases of demineralization and remineralization. This represents a competition between pathological factors(such as bacteria and carbohydrates) and protective factors(such as saliva, calcium, phosphate and fluoride).
Streptococcus mutans bacteria
The main causes of caries are the bacteria Streptococcus Mutans. An important risk factor associated with RCD is the early acquisition of cariogenic bacteria.
Streptococcus mutans is the main cariogenic bacterium.
Mutans Streptococci are bacteria that adhere to enamel and produce acid by converting sucrose to lactic acid. Therefore, the acid produced by these bacteria lowers oral pH and promotes demineralization tooth structures.
Long-term decrease in pH levels causes demineralization, which ultimately leads to the formation of cavities. Although Streptococcus mutans is commonly found on enamel surfaces, these bacteria have the ability to colonize the oral cavity, and earlier acquisition of SM is associated with increased caries.
In infants, SM is usually acquired from the primary caregiver, most often from the mother, through contaminated saliva. Although the mechanism of transmission is unclear, contributing factors may include close contact, sharing of utensils or food, and poor oral hygiene and/or open carious lesions in the primary caregiver.

Streptococcus mutans is strongly associated with dental caries. Its proportion in the plaque associated with early childhood caries can range from 30% to 50% of the total viable bacteria. In contrast, S. mutans typically constitutes less than 1% of plaque flora in children not associated with caries.
The earlier a child's mouth is infected with mutan streptococci, the greater the risk of developing caries in the future.
Bad eating habits
Frequent use carbohydrate-rich or sugary foods allows cariogenic bacteria to maintain a low pH level on the surface of the teeth.
Late night bottle feeding or prolonged use of a sippy cup can lead to early childhood tooth decay. Saliva flow decreases during sleep, so clearing sugary fluid from the mouth is slower.
Poor oral hygiene
Low fluoride levels on the surface of the teeth reduces the process of remineralization and increases the risk of developing caries. Children who already have one or more cavities have a higher risk of developing caries in their primary teeth.
When saliva flow is less than 0.7 ml/min, saliva cannot wash away carbohydrates from the surface of teeth. In addition, low salivary flow, low levels of IgA (secretory IgA or immunoglobulin A) in saliva, and low levels of calcium and phosphate in saliva reduce the likelihood of neutralizing acids in plaque.
Finally, low socioeconomic status may reduce interest in oral hygiene and healthy eating.

At what age can it appear
Tooth decay is common in very young children and adolescents.
There is a tendency to increase the incidence of caries in primary teeth in children. Very often it is found in children 2-3 years old or in children under 2 years old.
Teenagers are also exposed higher risk. Over time, teeth can wear down and gums can recede, making them more vulnerable to decay. Adults may also use more medications that reduce saliva flow, increasing the risk of tooth decay.
Kinds
The different types of dental caries are enamel caries, dentin caries, reversible caries, irreversible caries, pits and cracks, smooth surface, acute caries, early childhood caries, primary and secondary caries.
Caries of primary teeth begins with the fact that surface layers are destroyed, after which it penetrates deep into the dentin.
Circular caries is a special type of tooth decay that is characterized by destruction of bone tissue on the cervical edge of the tooth.
This disease very quickly penetrates the dental tissue and affects the nerve canals. It is very difficult to detect this type of caries in the early stages and difficult to manage in later and advanced stages. Circular caries often affects people over 30 years of age, but is often observed in children.

Caries that begins in a crack on the occlusal surfaces of the back teeth. Fissure caries is the name for carious lesions in the field of fissures(cracks). Such caries is usually caused by abnormal fissure anatomy. The teeth usually have an underlying crack that runs longitudinally.
Likewise, many small cracks that protrude from the side are called lateral cracks.

Retrograde
Development of carious lesions starts from the pulp side. First the dentin is damaged, then the enamel. Such caries can develop with purulent pulpitis, when the pathogen enters the pulp hematogenously, with injuries and anomalies of odontogenesis.
Other types
Stages of tooth decay
The morphology of caries in various hard tissues of the tooth has its own characteristics. There are five key stages of tooth decay.
White spots
The first stage of tooth decay is associated with the appearance yellowish spots or chalky white area on the tooth surface due to loss of calcium. This type of tooth decay is still reversible with proper treatment.

Enamel decay
At this stage, tooth enamel begins to be damaged below the surface layer, while the surface is not damaged. If decay persists, the surface of the tooth will be broken and the damage will be irreversible.
At this stage, the tooth must be cleaned and filled by the dentist.
In the third stage, decay progresses beyond the enamel into dentin. At this point, the dentist can restore the damaged tooth using a filling. The level of pain also begins to increase, as with many stages of tooth decay.
Any toothache should be noted immediately so that the problem can be resolved.

Cellulose involvement
The cellulose of the tooth is involved and contaminated due to the action of bacteria. The result is the formation of pus, causing the blood vessels and nerves in the pulp to die.
At this stage, root canal therapy is the only treatment option.
Abscess formation
Infection reaches the root end of the tooth. The bones surrounding the tooth also become infected, causing severe pain.
This is the final stage of infection. You may have visible swelling on your cheeks along the affected side.
The dentist will prescribe antibiotics and painkillers. He may perform root canal therapy or remove the infected tooth at this stage.

Stages by degree of destruction
Based on the degree of destruction, caries of primary teeth is classified into 4 stages.
Elementary
Appears in place of the enamel white opaque spot, which resembles lime (chalk stain). The pathological process triggers dismineralization and demineralization of enamel in the subsurface layer. The content of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and other minerals decreases in the area of the stain.
The enamel at the site of the stain loses its uniformity and shine, becomes soft and more penetrating. The small spot may become pigmented (yellow to dark brown). Caries may go away slowly, accompanied by remineralization. Then the spot acquires clear contours.
Surface
Shows demineralization and destruction of enamel within the dentinal-enamel junction. This is the first stage of dental disease, in which only the outer tooth enamel is destroyed. If left untreated, superficial caries will penetrate deeper into the tooth, affecting the dentin (and leading to moderate to deep caries).

Independently identifying superficial caries can be difficult: at this stage, pain from hot and cold foods may be mild and temporary, and patients are usually blamed for their tooth sensitivity.
If the decay is closest to the neck of the tooth, occasional pain may occur when brushing your teeth. Some try to see changes in the teeth in a mirror, but then suspected tooth decay is only possible on the outside of the front teeth.
Explicit caries can be considered as dark gray or brown spots. The only way to accurately identify and evaluate superficial caries is through regular oral examinations by your dentist. To assess the depth of dental damage, the doctor uses a dental probe or a diagnostic method. Initial and superficial caries should be distinguished from other pathologies of tooth enamel - fluorosis, hypoplasia and enamel erosion.
Moderate
With average caries, the destruction process affects not only the enamel, but also on the dentin layer of the tooth crown. Because there is a sufficient layer of dentin, caries can affect the dental pulp (the neurovascular bundle in the coronal cavity).
Deep
Large cavities appear in softened dentin - carious cavity. Between the bottom of the carious cavity and the pulp, only a skin (a very thin layer) of dentin remains, or the carious cavity extends into the pulp.
Signs
Early childhood caries develops over time and can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages.

Tooth decay can manifest itself as:
- Toothache, spontaneous pain, or pain that occurs without any apparent reason
- Tooth sensitivity
- Mild and sharp pain when eating or when the child drinks something sweet, hot or cold
- Visible holes or pits in the teeth
- Brown, black or white coloring on any tooth surface. This may be a dull white line on the surface of the tooth closest to the gum line. This is the first sign and usually goes unnoticed by parents or it may be a yellow, brown or black stripe on the surface of the tooth closest to the gum line which indicates progression of caries decay
- Pain when bitten
- Teeth that look like brownish-black tree stumps indicate that the child has developed tooth decay.
Methods of treatment and restoration
Treatment in most cases requires removal of decayed part of the tooth and replacing it with filling.
Fillings (also called restorations) are materials placed in teeth to repair damage caused by tooth decay (or cavities). Advances in dental materials and restorative and dental treatment techniques are providing new and effective ways to restore teeth.
There are several different types of restorations.
Direct restorations
They demand one-time filling directly into the prepared cavity or hole. Materials used for this include dental amalgams, also known as silver fillings; Glass ionomers; Polymer ionomers; And some composite (resin) fillers.

Amalgam fillers have been used for decades and have been tested for safety and durability. Dentists have found amalgams to be safe, reliable and effective for restorations.
Glass Ionomers are tooth-colored materials made from fine glass powders and acrylic acids. They are used in small fillings that cannot withstand heavy chewing pressure. Resinous Ionomers are made from glass with acrylic acids and acrylic resin.
Indirect
They require two or more visits and include inlays, onlays, veneers, crowns and bridges. They are made of gold, metal alloys, ceramics or composites.
At your first visit, the dentist will prepare the tooth and examine the area that will be restored. During the second visit, the dentist will place the new restoration in the prepared area.
Some offices use newer CAD/CAM (computer-aided design or computer-aided manufacturing) technology, which allows them to perform indirect restorations in the office in 1 visit, eliminating the need for the patient to return again.
For indirect restoration, the dentist may use porcelain or ceramic materials.
- The first material looks like natural tooth enamel in color and translucency.
- Another type of indirect restoration may use porcelain fused to metal, which provides additional strength.
- Gold alloys are often used for crowns, inlays or onlays.
- Less expensive alternatives to gold are metal-based alloys that can be used in crowns and are resistant to corrosion and decay.
- Indirect composites are similar to those used for fillers and are tooth-colored, but they are not as strong as ceramic or metal restorations.

Prevention of caries in children
Preventing tooth decay involves these simple steps:
- Start brushing your child's teeth as soon as their first tooth appears. Brush your teeth, tongue, and gums twice a day with fluoridated toothpaste or supervise your brushing.
- For children under 3 years of age, use only a small amount of toothpaste, about the size of a grain of rice.
- Starting at age 3, use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste
- Brush your child's teeth daily with a toothpick after age 2.
- Make sure your child eats well-balanced foods and limits or eliminates sweets
- Check with your dentist about using supplemental fluoride if you live in an area without fluoridated water.
- Also ask about dental sealants and fluoride varnish. Both are applied to teeth.
- Schedule (every 6 months) - dental cleanings and exams for your child.
By following preventative measures and not forgetting about regular dental examinations of baby teeth, you can easily protect your child's baby teeth from caries. The main thing is monitor his oral cavity and do not trigger the first signs and symptoms of caries.
Dental problems can occur in patients of any age, including very young children. Unfortunately, parents do not always pay enough attention to the health of their child’s teeth and are in no hurry to visit the dentist for a preventive examination. This approach can lead to serious problems in the future. Caries of primary teeth in children can progress at a much faster rate than in adults, quickly affecting the teeth and having a negative impact on the rudiments of permanent teeth. Bite pathologies can lead to changes in the correct structure of the jaws and disruption of the harmony of a person’s appearance.
Caries diagnosed in a child requires immediate treatment. To avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to carefully monitor regular hygiene procedures and control the child’s diet. If, despite preventive measures, caries does occur, treatment must be carried out immediately, otherwise the infection may spread deeper, affecting future permanent teeth.
Important! If you independently detect signs of caries in a child, you should immediately seek help from a pediatric dentist. The doctor will be able to adequately assess the extent of tooth damage and prescribe the necessary treatment.
In rare cases, therapeutic measures are not required. This usually happens when the initial stage of caries is detected on a baby tooth, which within a few months should fall out and be replaced by a permanent one. In other situations, caries must be treated.
Caries of primary teeth is the development of a pathological process in the hard tissues of a child’s teeth, leading to the gradual destruction of tooth enamel and internal tooth tissues.
Features of childhood caries
The child’s immune system is not yet strong enough to fully resist the influence of pathogenic bacteria on dental tissue. The process of enamel mineralization continues after teething, so the disease progresses faster on weak teeth.
Attention! According to pediatric dentists, caries on a baby tooth can go through all stages from the formation of a stain on the enamel to the complete destruction of deep tissues in just one month. The rapid development of the disease is facilitated by general malaise. In children who are often sick, caries can progress faster.
Newly erupted baby teeth also sometimes develop caries. It is called bottle or nursery. This variety is characterized by carious spots on the upper incisors and canines. The affected tissues are located in a circle in the area of the tooth neck. The development of the disease begins with the leaching of mineral salts from the enamel and the formation of stains, quickly spreading deep into the dentin and tooth root.
This type of caries usually occurs in children under 2-3 years of age who drink formula or other drinks containing sugar at night.

Nursery caries is a disease that occurs as a result of night feeding of children without subsequent oral hygiene procedures.
The main causes of caries in primary teeth
The main risk factors for developing the disease are two reasons:
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Improper brushing techniques or irregular procedures lead to the accumulation of microbes and the formation of plaque on the enamel surface. The nutrient medium is an excellent condition for the development of caries infection.
- Wrong diet. The child must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals from the food they eat, which is the key to strong teeth. Excessive consumption of sweets is undesirable, since carbohydrates are an excellent food for bacteria, which multiply at a high speed on the surface of the teeth after eating candy.
These are the main reasons that lead to disruption of the protective functions of enamel. The protective layer of the tooth can no longer resist infection, and caries penetrates inside, affecting dentin and deeper tissues.

Children should be given sweets only after meals. It is best to teach your child to eat not sweets and cakes, but fruits, dried apricots, raisins or, in extreme cases, marmalade or marshmallows.
Conditions for the development of childhood caries
There are a number of factors that create conditions conducive to the formation of pathology in children. These include:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the dentition;
- hereditary factor of predisposition to carious infections;
- weak immune system;
- individual characteristics of saliva (composition and amount released);
- poor diet (eating only soft foods, excess sweets);
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- excess fluoride in drinking water, causing fluorosis;
- infections suffered during the prenatal period.
The greater the number of factors that are relevant in each specific case, the higher the likelihood of developing caries and the rate of spread of infection.
The connection between tooth decay and breastfeeding

One of the ways to naturally prevent caries is to breastfeed a child up to one and a half years old; mother's milk has a protein component that has an antimicrobial effect in the oral cavity.
The disease is caused by a large number of streptococcal bacteria that multiply in dental plaque. Low levels of acidity provide conditions favorable for these microbes.
Attention! Mother's milk does not change the acidity of the baby's mouth. This product contains maternal immune cells, which, on the contrary, help fight streptococci. Breastfeeding until a child is one and a half years old and longer helps to increase the level of lactoferrin in the child. This is a protein component that has an antimicrobial effect.
Through breast milk, the baby receives various vitamins and minerals that may not be enough in regular foods. The phosphorus and calcium contained in milk help strengthen dental tissues and accelerate the process of enamel mineralization.
Symptoms of the initial stage of bottle and cervical caries
Before the age of three years, caries most often develops in the cervical area of the front teeth. The disease mainly affects the upper jaw, since the lower teeth are better cleaned by saliva and the tongue after bottle feeding. Caries located in this part of the tooth can be bottle and cervical.
Symptoms of cervical caries
This variety is characterized by the following characteristics:
- location of carious tissue in the gum area;
- the initial stage of caries (in the form of a spot) is visible only to a qualified dentist;
- There is no increased sensitivity of the tooth;
- after the top protective layer thins, the enamel often changes color;
- over time, the carious spot becomes larger and a depression appears in it;
- With the development of a carious cavity, the child experiences pain.
The deep stage of cervical caries can lead to damage to the roots and result in tooth loss.
Signs of bottle caries
Nursery caries manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- plaque formation on the front teeth;
- the appearance of multiple spots of white and yellowish tint;
- several teeth are involved in the process at once;
- spots are located in a circle closer to the neck of the tooth;
- there is an increase in sensitivity;
- over time, the color of the spots changes to dark shades of brown;
- the baby begins to complain of pain when eating hot or cold food, eating sweet and sour foods.
If left untreated, bottle caries spoils the appearance of a child's smile and quickly progresses to complications such as pulpitis.

This image shows two types of carious lesions in children's teeth: bottle caries - visible to the naked eye, because the color of the enamel changes, as well as cervical caries - the initial stage can be determined by a dentist, it becomes noticeable at a more advanced stage.
Treatment of caries in children should not be delayed, regardless of age. The earlier measures are taken, the less invasive they are. The development of caries, regardless of the child’s age, includes four main stages:
- Formation of light spots. As a rule, there are no obvious symptoms, but sometimes a child may complain of increased tooth sensitivity. It is very difficult to detect spots on the enamel on your own, however, an experienced dentist is able to diagnose them. This stage of caries can last from several weeks to several months, depending on a combination of different factors (age, nutrition, oral hygiene, etc.).
- Superficial caries. The spots become darker, and the boundaries of the affected tissue become obvious. The child may notice discomfort when the teeth are exposed to thermal (hot, cold) and chemical (sour, spicy, sweet) irritants. After eliminating the irritant, the symptoms quickly disappear.
- Average caries. The enamel structure is destroyed and caries penetrates into the deeper tissues of the tooth. Carious cavities are clearly visible to the naked eye. Painful sensations become more intense and last longer. Bad breath often occurs due to the proliferation of microorganisms and tissue decomposition.
- Deep stage. Carious lesions affect the deepest tissues, noticeable destruction and deep dark cavities appear on the tooth. The unpleasant odor intensifies, and the pain in the tooth practically does not subside. The child often complains, is capricious and suffers from unpleasant sensations.

Stages of development of childhood caries: spots appear on the teeth - spots darken, pain appears - the enamel structure of the tooth is destroyed - deep dentin tissues are affected - tooth destruction.
Diagnostic measures
There are plenty of methods for diagnosing caries in modern dentistry. The methods used depend on the qualifications of the doctor, as well as on the capabilities of the particular dental clinic. The most common research methods are:
- Visual examination by a doctor using dental instruments (probe, mirror).
- Transillumination. The teeth are illuminated with rays of a special spectrum, which makes it possible to detect darkening and changes in the structure of the tooth.
- Radiography. An X-ray allows you to identify caries in hidden areas and assess its extent and depth. In this way, you can examine 1-2 teeth or take a panoramic picture of the entire jaw.
- Laser methods. The direction of special rays onto the tooth, which, reflecting from the surface with certain deviations, makes it possible to judge the presence of pathology.
- Caries markers. A common technique involves applying special indicators to the teeth that color the affected tissues in a bright color. The most commonly used dye is methylene dye, which imparts a blue color to areas affected by caries.
- Luminescent study. In a specially darkened room, the oral cavity is illuminated using UV rays, assessing color changes in different areas. Damaged areas of the tooth appear darker than healthy ones.
- Drying. A stream of air is directed onto the surface of the tooth. The healthy surface of the tooth remains smooth and shiny, while areas with initial signs of caries are dull.
- Electroodonometry. A study involving the use of a weak electric current to determine the degree of tooth sensitivity.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes several research methods at once to obtain a complete picture and correctly prescribe treatment for caries in children.

Transillumination is a method of examining teeth based on passing a cold beam of light through the tooth, which is harmless to the body. At the same time, signs of caries damage are detected in the form of specks of various sizes.
The initial stages of caries are often similar to the symptoms of fluorosis and hypoplasia of tooth enamel. To avoid mistakes in determining the disease, the dentist conducts differential diagnostics.
Features of caries treatment in children of different ages
The treatment method and its duration are mainly determined by the stage at which the disease is detected:
- Stage of formation of a carious spot. In such a situation, conservative treatment is possible, which consists in restoring the properties of the enamel and saturating it with minerals. For the remineralization procedure, a solution of sodium fluoride (2-4%) and calcium gluconate (10%), as well as the drug Remodent, is used.
- The superficial stage and all subsequent ones require the use of a drill. The tissues affected by caries are completely removed, the cavity is disinfected with an antiseptic, and then a filling based on a composite or other modern material is installed.
Before starting treatment, the doctor assesses the likelihood of pain during treatment and the need for anesthesia. Anesthesia is performed by injection or by applying an anesthetic superficially (in the form of an aerosol or gel). After filling, the dentist performs finishing and polishing of the tooth.
Attention! If caries has reached the deepest stage, tooth depulpation may be required. In this case, the doctor removes the nerve and fills the root canals.
Treatment of caries in children can be complicated due to the fear of young patients before the doctor. Therefore, an important point is to meet the doctor, have a calm conversation and explain the need for a procedure that you should not be afraid of at all.

The most common method of treating cavities is surgery. It consists of excision of necrotic tooth tissue and restoration of the anatomical shape using filling materials.
Treatment of the youngest children
The patient's age does not play a decisive role in the choice of treatment method. Treatment procedures are determined depending on the stage of the disease and the degree of tooth damage. In any case, before visiting the doctor, adults should prepare the child by explaining what manipulations await him in the dentist’s office. Fortunately, it is now possible to painlessly treat any stage of caries, which is extremely important for pediatric patients.
Use of silver
The method involves applying silver nitrate to the surface of the tooth. Silver plating has a pronounced antimicrobial effect, causing the death of all pathogenic bacteria on the tooth surface. The protective properties of enamel are enhanced. After six months, as a rule, another procedure is prescribed.
Silvering has an unpleasant side effect - the child’s teeth acquire a dark gray tint, which does not disappear until the teeth are replaced with permanent ones.
Remineralization
This manipulation involves saturating tooth enamel with substances that it has lost due to the onset of the carious process. Preparations containing calcium, fluorine and phosphorus are applied to the cleaned tooth. They help restore the protective functions of the enamel.
The procedure is a good preventive measure. It can be done every six months to prevent the formation of caries. During remineralization, the child does not experience any unpleasant sensations, so the procedure is an excellent way to prevent and treat caries at the stage of stain formation. Unfortunately, it is not effective when a carious cavity has already appeared.
Tooth filling
This method is used in children over 1 year of age when other measures are no longer effective. When treating a child under 3 years of age, dentists try to avoid using a drill. If caries has not progressed to a deep stage, it is possible to treat the tooth with special acids that clean the cavity from tissues affected by infection. After this, the surface is disinfected and a filling is installed (usually light-curing).
Unfortunately, with deep caries you cannot do without drilling. The dentist administers anesthesia to the child and then carefully cleans the surface with a drill.

Remineralization of teeth is a preventive procedure that can significantly strengthen enamel, replenish the deficiency of mineral components, reduce tooth sensitivity and prevent the development of caries.
Treatment of children over 2-3 years old
Treatment of caries in patients of this age category requires the use of the following additional procedures:
- Ozone therapy (use of gas to treat the dental cavity).
- Preparation (opening a carious cavity with its cleaning, antiseptic treatment and filling).
- Depophoresis (a physiotherapeutic technique consisting in the introduction of calcium preparations into the tooth cavity through the action of an electric current).
- Phototherapy (use of a special medicinal paste applied to the tooth followed by laser treatment).

Ozone is one of the most powerful antiseptics. In this regard, ozone therapy is an effective way to combat bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa in the oral cavity.
Possible complications
When a child is diagnosed with caries, treatment should begin as early as possible. If the disease is ignored, the process can lead to consequences that can affect both the physiological and psychological health of the baby.
Important! Caries left without treatment will not go away on its own, but will almost certainly lead to the development of complications. Infected tissues are a source of spread of pathogenic microflora.
The most common consequences of advanced caries are:
- spread of the inflammatory process from the oral cavity to neighboring tissues;
- development of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- chronic allergic reactions;
- cardiovascular diseases.
Preventive measures
At any age, it is better to prevent caries than to deal with its treatment and consequences later. In the case of a child, prevention is especially important.
Dentists recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- Daily oral hygiene (in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed) under the supervision of adults. Dental care products should be selected in accordance with age and the dentist’s recommendations.
- Limit foods containing large amounts of sugar.
- A balanced diet rich in minerals and vitamins the child needs.
- Additional intake of vitamin D, in accordance with the recommendations of the pediatrician.
- Mandatory preventive examination by a pediatric dentist, recommended every six months.
- Spine on the leg: causes and treatment
- Features of testing for hidden infections in women
- Can spines form on the hands?
- Treatment of caries during pregnancy
- Caries during pregnancy: can it be treated and its effect on the fetus?
- How to properly treat caries of baby teeth in a child. Caries of baby front teeth is not dangerous.
- Smell from under the crown: what to do The tooth on the pin has come off, what to glue it with
- Tetracycline teeth: signs and treatment of the disease What are tetracycline teeth
- I pinched a nerve in my back - what should I do?
- How to treat intestinal dysbiosis: treatment with diet, medications
- Pinched nerve in the spine and its treatment
- Do papillomas need to be removed?
- If the tooth under the crown is sick, it can be cured without removing the structure
- What to do when water gets into your ear?
- Vitamins for joints and cartilage for athletes: ranking of the best Supplements for joints and ligaments
- Nettle for bleeding: properties and method of use Why nettle does not help with bleeding
- Vacuum massage: how to place cans correctly?
- How to make your voice go down
- Interesting facts you didn't know about teeth
- How to recognize implantation bleeding