Local methods to stop bleeding after tooth extraction. Bleeding after tooth extraction. Why does the socket sometimes bleed for a long time after a tooth is removed?
With the modern level of dentistry, tooth extraction (extirpation) is indicated in extreme cases, if it is impossible to save them. This is a surgical procedure performed under sterile conditions in a dental clinic. Bleeding after it is mandatory, since during the procedure the periosteum tissue is injured and the blood vessels are damaged.Normally, after extirpation, the bleeding stops within 10 minutes.
However, it happens that the gums become swollen, bleeding continues or resumes when the patient returns home. This symptom cannot be ignored, and it is important to see a doctor immediately. He knows how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction, determine why it is bleeding, and take the necessary therapeutic measures.
Why is it sometimes difficult to stop bleeding after a tooth has been pulled out?
Severe and prolonged bleeding after extirpation is quite rare. It is noted when wisdom teeth, premolars or molars (chewing teeth) have been pulled out. Dentists know this and take all possible measures to prevent complications. Other common causes of prolonged bleeding include:
- injury to large vessels;
- bone damage during manipulation;
- large wound;
- unprofessionalism of the surgeon;
- inflammatory process in neighboring tissues;
- problems with blood clotting;
- non-compliance with doctor's recommendations after removal.
How long can blood flow from the hole?
Heavy bleeding after a tooth extraction procedure is usually associated with a large number of blood vessels that are injured during manipulation. It is important to remember that even with complex interventions, the bleeding should stop within half an hour. Light bleeding continues for a longer time for the following reasons:

Sometimes blood can flow continuously during tooth extraction surgery and the wound does not heal at all. The dentist immediately takes measures to stop it. In some cases, bleeding occurs after a period of time and is considered secondary. It happens that ichor, a yellowish liquid, oozes from the wound. Normally, its release should end within 4 hours.
It happens that the blood flows for a long time (about a day), periodically stopping. In this case, its taste is constantly felt in the mouth. This situation indicates damage to soft tissues and gums and requires a visit to the dentist.
Sometimes children's baby teeth bleed, which is typical when they fall out. To stop the bleeding, the baby should bite on a sterile bandage or napkin. Improvement usually occurs within 5 minutes. If bleeding continues for more than 10 minutes, you should definitely tell your pediatrician about it. You may need to have a blood test.
Ways to stop bleeding
At the site where the tooth was removed, a hole forms and the alveoli are naturally filled with a blood clot (we recommend reading: what to do if a tooth is removed and the bleeding does not stop?). The clot is the result of rupture of blood vessels, dental artery and capillaries. The bleeding that occurs after the procedure is temporary and goes away within 20 minutes. The doctor speeds up this process by covering the wound with a cotton swab, which applies gentle pressure. He releases the patient after making sure there is no more bleeding.
If the bleeding cannot be stopped immediately, or the patient seeks help with secondary bleeding, the dentist uses tamponade of the hole with iodoform gauze. To do this, the oral cavity is cleared of blood clots, the wound is dried with a gauze swab, and the location of the bleeding is determined (from the gums or alveoli):

For bleeding from small vessels, electrocoagulation and the application of hemostatic sponges are often used. It is also useful to apply cold to the socket area. Rinsing is prohibited during the first day after dental surgery.
With the help of medications
Common methods of stopping bleeding involve the use of hemostatic drugs. Local anesthesia is also administered using medications that contain adrenaline. After its introduction, the blood stops oozing. If a tooth is pulled out, the doctor may prescribe the following to the patient:
- tablets or 1% solution of Vikasol intramuscularly;
- 10% solution of calcium chloride in combination with calcium gluconate intravenously;
- for hypertensive patients - “Captopril”, “Clonidine”, “Nifedipine”;
- intravenous or intramuscular injections of "Dicynon".
Home methods
If secondary bleeding is detected from the hole after extirpation or the gums are bleeding, it is important to seek medical help. It is unacceptable to rinse your mouth or heat the sore area. At home, to alleviate the condition, you should do the following:

Features of bleeding after wisdom tooth removal
Wisdom teeth are the 8th molars in the jaw row. They erupt by the age of 18-25 and later, and may be absent throughout life (remain in the gums). Wisdom teeth have lost their physiological necessity and erupt with pain and discomfort. The reasons for their removal are:
- longitudinal tooth fracture;
- development of periostitis, periodontitis, ostiomyelitis of the jaw due to the fault of the wisdom tooth;
- fracture of the molar crown, which cannot be restored with filling;
- extension, increased mobility of the figure eight;
- the tooth does not want to “come out”, causing discomfort and periodontitis;
- incorrect figure eight position, which damages the gum tissue.
After removing the 8th molar, it is very important for the surgeon to stop the blood flowing from the gum pocket. Sometimes the bleeding is very strong and prolonged (up to 40-60 minutes), especially in transverse position, deformed roots (blood clots do not form due to the large edges of the wound). In this case, the doctor applies self-absorbing sutures.
When blood continues to ooze from the hole, apply a compress or hemostatic sponge. They are removed in the doctor’s office after 4-7 days, based on the condition of the wound and the rate of its healing. Self-removal is unacceptable, as it can cause infection and cause re-bleeding.
When should you see a doctor?
Tooth extraction leads to injury and swelling of the surrounding soft tissue. It goes away on its own within 2 days. An ice compress on the cheek and taking antihistamines (if an allergic reaction to anesthesia is detected) will speed up the process. If swelling persists for more than 2 days, you should visit a doctor.


Tooth extraction often leads to an increase in body temperature. Low-grade fever (up to 38 degrees) can be observed two days after the intervention. If you exceed 38.5 degrees, feel pain, twitching and swelling in the area of the hole, you should not delay a visit to the doctor. Suppuration is possible, caused by a tooth fragment in the wound or ignoring the dentist’s recommendations.
If you follow the recommendations of specialists, discomfort after surgical procedures goes away within 7-10 days. The main thing is to avoid self-medication and try not to further injure the affected area of the gum. You should immediately consult a doctor in the following cases:
- severe swelling in the area of the extracted tooth;
- weakness and fever;
- unpleasant odor from the hole;
- pain intensifies and spreads wider;
- I have to spit out blood every few seconds.
Rules of conduct after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a trauma for the body, and it reacts to it with post-traumatic inflammation. The course of the postoperative period is difficult to predict, but following the dentist’s recommendations significantly reduces the risk of complications:

You should not donate blood immediately after tooth extraction, since even slight blood loss after surgery reduces hemoglobin levels and weakens the body. You should wait a couple of weeks and then plan the procedure. Additionally, it is important to give up alcohol, smoking, and other bad habits. It is necessary to maintain careful oral hygiene. Teeth should be brushed regularly, avoiding the post-operative area. It is prohibited to use a waterpik. Timely dental examinations will allow you to avoid removal.
From this article you will learn:
- why does bleeding occur after tooth extraction,
- If a tooth is pulled out, the blood won't stop - quick help at home.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
Situations where blood bleeds after tooth extraction most often occur when the patient has high blood pressure (due to hypertension or severe stress), as well as if a large vessel was damaged during surgery.
Most often, bleeding develops while still in the dentist’s chair (immediately after tooth extraction), but sometimes bleeding can be delayed, i.e. develops only a few hours or overnight after removal. In the latter case, patients often passively wait for the bleeding to stop on its own, and this can sometimes lead to significant blood loss and weakness.
Bleeding after tooth extraction: before and after photos
How long does blood bleed after tooth extraction (normal) –
Normally, bleeding should stop within the first minute after removal, as soon as the hole fills with blood. However, during the first time, ichor may be released from the wound (do not confuse it with blood), and do not be alarmed if the saliva turns reddish at first - this is normal.
Why doesn't the bleeding stop after tooth extraction?
To know how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction, you need to understand the reasons for the development of bleeding in a particular patient. We will talk specifically about secondary bleeding that occurs after the patient comes home. They usually appear within 8-12 hours (from the moment of removal). There are the following 3 groups of reasons...
- Systemic reasons
–
First, bleeding may be caused by taking aspirin during the week before the extraction, or when the patient took it for pain relief immediately after the extraction. You cannot take it, because... it reduces blood clotting. Secondly, bleeding can be caused by taking anticoagulants, or if you have a blood disease (associated with a defect in the blood cells “platelets”).Women often do not stop bleeding after tooth extraction due to increased concentrations of estrogen in the blood. This can be either due to menstrual periods, or due to taking contraceptives. An increased concentration of estrogen leads to degradation (this process of clot degradation is called fibrinolysis).
In addition, high blood pressure, which is always present against the background of hypertension, or appears briefly against the background of stress, can also be causes of bleeding.
- Not following doctor's recommendations
–
if the patient does not refuse heavy physical activity in the first days after removal, this can lead to bleeding. If the patient rinses the mouth too intensively and rinses out the blood clot, this can lead to bleeding, as well as after picking at the wound with the tongue or foreign objects, etc. To avoid this, read.
- Local factors –
bleeding may develop due to severe trauma to the blood vessels during the removal process (especially if it was complex and was accompanied by a cut in the gum). Thus, if the doctor severely injured the bone and gums, bleeding can be expected.Often a predisposing factor to bleeding is a purulent infection in the socket of an extracted tooth - when the tooth is removed due to inflammation. Pathogenic bacteria release toxins, which (like estrogens in women) lead to fibrinolysis of the blood clot, i.e. to its destruction.
Bleeding after tooth extraction: video
The video below shows a young man who developed bleeding 6 hours after a tooth extraction. As you will see, a massive blood clot formed above the hole of the extracted tooth, which was removed by hand. If such a clot has formed, it really needs to be removed, but it is better to do this with a sterile gauze swab. After this, you need to make another tight swab from a sterile bandage, place it on the hole and bite firmly.
How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction -
If you have a tooth pulled out, the bleeding does not stop: what to do will depend on how much bleeding there is. Those. The first thing you must do is assess the severity of the situation. If the bleeding is really severe, then it is best not to wait until it stops on its own (this may not happen), but to contact a dental surgeon to apply sutures to the socket of the extracted tooth.
You can go to any 24-hour private dentistry, or to the emergency room of an Emergency Hospital or Regional Clinical Hospital (the latter always have a doctor on duty). When contacting government agencies, do not forget to take your medical insurance and passport with you. If you don’t have a policy with you, then you are required to provide emergency assistance without it (and free of charge), but, as a rule, difficulties arise with this.
Important : if bleeding is associated with the presence of systemic factors, then any local means to stop bleeding (which we will discuss below) will not be effective enough in this group of patients. For example, this applies to women (while menstruating or taking contraceptive medications), patients with bleeding disorders, blood disorders, and patients who have recently taken aspirin or anticoagulants.
And this also applies to patients with high blood pressure. So, all these groups of patients need professional help from a dental surgeon (socket tamponade and/or suturing of the extracted tooth socket).
How to stop bleeding from a socket at home -
How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction, if it is not very strong: first, you need to remove thick blood clots from the oral cavity using the desired sterile gauze swab (it can be made from a sterile bandage). After that, the following remedies can help you...
- Tamponade of the socket –
also make a very tight gauze swab from a sterile bandage, place it over the socket of the extracted tooth and bite firmly. You need to clench your teeth so tightly that you feel that the tampon fits tightly to the wound surface (but without causing pain).

- Take your blood pressure –
if your blood pressure is high, take a blood pressure lowering medication. If you don’t have a blood pressure measuring device, most likely your elderly neighbor does. In addition, almost any pharmacy will measure your blood pressure completely free of charge, and will also recommend a drug to lower your blood pressure.
- Hemostatic sponge after tooth extraction –
if tamponade of the socket does not help, then you can buy a hemostatic sponge at the pharmacy and place it in the upper part of the socket, then immediately place a gauze swab on top of the socket and bite it firmly. If the sponge is actually placed inside the hole, then the bleeding decreases/stops almost instantly.How to do this - first remove the blood clots on top of the hole, cut off a fairly large fragment of the sponge (2x2 cm), and try to push the sponge into the hole with clean tweezers. A large fragment of a sponge is taken because when soaked in blood, the sponge immediately becomes several times smaller. After this, bite the tampon tightly and press the ice to your cheek for 5-10 minutes.
It’s more convenient when you don’t put the sponge on yourself, but on your relative (or a nurse you know at the entrance). Keep in mind that when the sponge gets wet with blood, it immediately becomes soft and can be difficult to insert into the hole. In this case, you can cut off a new piece of sponge and try to insert it into the hole again.
- Taking the drug "Ditsinon" (analogue - Etamzilat) –
This is a hemostatic drug in 250 mg tablets. The drug begins to act approximately 30 minutes after administration, but a pronounced hemostatic effect develops after approximately 2-3 hours. A single dose for adults should be no more than 250-500 mg. The drug should not be used in people with a tendency to thrombosis, thromboembolism, or thrombophlebitis (read the instructions for use carefully).
If none of the above helps -
If nothing helps, and if you feel weak and dizzy, then you shouldn’t wait any longer. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
- The best option in the conditions of Russian free medicine –
take a taxi to the nearest 24-hour private dental clinic, where you will get stitches. If you feel weak, then do not drive yourself unless you want to get into an accident. For anesthesia, 2 stitches and a hemostatic sponge you will have to pay approximately 750-1000 rubles.
- Feel free to call an ambulance –
when talking to the ambulance dispatcher, complain not only about bleeding, but also about severe dizziness and weakness. With such symptoms, an ambulance will definitely arrive. Usually they will first try to stop the bleeding using tampons with peroxide (which a priori cannot help in this situation). Seeing the failure of such therapy, they will be forced to take you to the hospital, where they will put stitches on your wound and send you home.
Prevention of bleeding after removal -
First of all, before removing a tooth, you must inform the doctor that you have taken aspirin, coagulants, are on your period, or are taking birth control pills. You should also be warned if you have reduced blood clotting, blood diseases, or high blood pressure. In these cases, the doctor will place a hemostatic sponge in the hole in advance and apply sutures.
In addition, we recommend that you definitely ask your doctor (even before the extraction begins) to put 1-2 stitches on the hole of the extracted tooth, even if you are asked to pay another 300-500 rubles for this pleasure. This applies not only to large multi-rooted teeth, but even to single-rooted teeth. The fact is that stitches will not only prevent possible bleeding...
Studies have shown that using sutures to reduce the size of the wound can reduce pain after removal by approximately 30-50%, eliminate the loss of a blood clot from the socket, and also reduce the risk of development after removal. And also do not forget to follow your doctor's recommendations. We hope that our article on the topic: Pulled out a tooth, how to stop the bleeding - turned out to be useful to you!
Bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth occurs, most often, under the influence of adrenaline, used together with an anesthetic for pain relief. At the beginning, adrenaline causes contraction of the walls of arterioles (small vessels) in the wound, but after 1-2 hours the second phase of its action begins - vasodilation - bleeding may occur. This type of bleeding is called early secondary bleeding.
Late secondary bleeding from the socket can be observed several days after tooth extraction. It is associated with the development of the inflammatory process in the wound and purulent melting of the organizing blood clots in the vessels damaged during surgery.
Other causes of bleeding from a tooth socket
Local causes: In most cases, primary bleeding occurs from the vessels of soft tissues and bone as a result of a traumatic operation with rupture or crushing of the oral mucosa, fracture of part of the alveolus, interradicular or interalveolar septum.
Bleeding from the depths of the socket is usually associated with damage to the dental branch of the artery. Heavy bleeding may accompany tooth extraction during an acute inflammatory process, since the vessels are dilated and do not collapse.
Common causes: Prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction occurs in diseases characterized by impaired blood clotting or disorders of the vascular system. These include hemorrhagic diathesis: hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemorrhagic vasculitis, hemorrhagic angiomatosis, angiohemophilia, C-vitaminosis. Diseases accompanied by hemorrhagic symptoms: acute leukemia, infectious hepatitis, septic endocarditis, scarlet fever, etc.
The blood clotting process is disrupted in patients taking indirect-acting anticoagulants (neodicoumarin, phenylin, syncumar) and direct-acting (heparin).
A tendency to bleeding is observed in patients suffering from hypertension.
Manifestation of bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth
The socket of the extracted tooth, the alveolar process and neighboring teeth are covered with a blood clot, from which blood flows.
Attention! The diagnosis is approximate and does not replace a consultation at the dentist's office.
How to treat Bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth
Stopping bleeding from the hole is carried out in a dental clinic. Under anesthesia, the blood clot is removed, the socket and surrounding areas of the alveolar process are dried. Then the cause of the bleeding is determined.
Arterial bleeding is stopped by suturing the wound and bringing its edges together, ligating the vessel or suturing the tissue. Bleeding from small vessels can be stopped by electrocoagulation of the bleeding tissue area or by applying a small crystal of KMnO4 with isolation of the surrounding tissue.
Bleeding from the walls of the socket, interradicular or interalveolar septum is stopped by squeezing areas of the bone with surgical forceps, a clamp or a needle holder. Cauterization of the bleeding area of the bone.
To stop bleeding from the depths of the hole, tamponade is performed using various means (iodoform turunda, turunda with dimexide, hemostatic sponge, kolapol, kolapan, catgut, tampon with caprofer or aminocaproic acid).
After removing the blood clot, the hole is washed with hydrogen peroxide, dried and the hole is tightly tamponed starting from its bottom. Prescribe cold (ice) to the soft tissues of the face. After 20-30 minutes, if there is no bleeding, the patient is released.
If bleeding continues, the hole is carefully packed again. Turunda is removed from the hole only on the 5-6th day, when granulation of its walls begins. Premature removal of the turunda can lead to re-bleeding.
At the same time as stopping bleeding, agents that increase blood clotting are used using local methods.
For bleeding associated with low levels of prothrombin as a result of a violation of its synthesis by the liver (hepatitis, cirrhosis), the vitamin K analogue vikasol is prescribed. You can also prescribe epsilonaminocaproic acid. Dicinone has a rapid hemostatic effect.
Patients suffering from hypertension are treated with antihypertensive therapy simultaneously with stopping bleeding using local agents. Once the blood pressure decreases, the bleeding stops.
In case of heavy and prolonged bleeding that does not stop despite general and local hemostatic treatment measures, urgent hospitalization of the patient is indicated.
Bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth
Bleeding from the socket can occur both immediately after tooth extraction and some time after the operation. In the latter case, the cause of bleeding may be the patient’s violation of the regimen (rinsing the mouth, eating hot food), the disintegration of a blood clot, or an increase in blood pressure. Usually, as a result of rupture of dental arterial branches, capillaries of the periodontium and gums during tooth extraction, moderate bleeding occurs, which, thanks to the pressure of a gauze ball placed on the wound, stops after 10-15 minutes. However, in some cases, more often as a result of rough intervention, bleeding continues. The cause of bleeding may also be dilatation of blood vessels as a result of paralysis of their walls after the spasmodic effect of adrenaline added to the anesthetic solution on them. In addition, the cause of bleeding (and very long-term bleeding) may be a violation of blood clotting ability. In cases of continued bleeding after tooth extraction, it is necessary to determine the location of the bleeding. If it comes from a wound of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to stitch the bleeding area of the mucous membrane with 1-2 catgut sutures, which leads to the cessation of bleeding.
If there is bleeding directly from the tooth socket, it is necessary to recurettage it with a sharp spoon to remove any remaining granulation tissue that may be the cause of the bleeding. If after curettage the bleeding does not stop, tight tamponade of the hole is indicated. To do this, use a narrow (preferably iodoform) gauze swab, which is placed tightly first on the bottom of the hole, and then filled with the entire hole (Fig. 90).
To maintain the pressure of the tampon in the socket, a gauze roller is placed on top of it, above the socket, which is pressed against the teeth of the opposite jaw while the jaws are clenched. In cases of bleeding after the removal of a multi-rooted tooth, the hole of each root is tamponed separately. After bleeding stops, the tampon is removed from the hole no earlier than after 4 days. Usually, for local causes of bleeding, these interventions are sufficient to stop the bleeding. However, if the blood clotting ability is impaired, in cases of a common cause of bleeding, even tight tamponade of the hole may not give the required effect.
Hemophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis, thrombopenia can be the causes of bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth, which, after a fairly short-term cessation, resumes and continues for 2-3 weeks.
If there is a suspicion of a blood disease, patients after tooth extraction must be urgently admitted to the hospital.
Against the background of general therapeutic measures (Vicasol, horse serum, gelatin, calcium chloride, fractional transfusion of small doses of blood, etc.), local therapy is carried out - tight tamponade of the hole with iodoform gauze, filling the hole with a hemostatic sponge. A good therapeutic effect is obtained by tamponing the hole with pieces of fresh placenta. For this purpose, a piece of the placenta is washed with a stream of isotonic sodium chloride solution, and then tightly inserted into the hole. A pressure gauze pad is placed over it. After the bleeding has stopped, a piece of the placenta is removed from the socket on the 3-4th day.
However, it should be remembered that in people suffering from a blood disease, tooth extraction may cause such prolonged bleeding that it threatens the patient’s life. Therefore, in such patients, tooth extraction should be considered an extremely dangerous intervention, requiring special vital indications and carried out after appropriate preparation only in a hospital setting.
In some cases, 1-2 days after tooth extraction, constant pain appears in the area of the extracted tooth socket and bad breath. The cause of this complication is usually an infection of the blood clot in the socket. Predisposing factors are the traumatic nature of the operation and the leaving of a bone fragment of the alveolar wall in the socket.
Often the pain factor in alveolitis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 38°C and above, the appearance of hyperemia of the mucous membrane and swelling of the soft tissues around the hole, and inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Treatment. Carefully remove the disintegrating blood clot with a sharp bone spoon, wash the hole with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide and insert a tampon moistened with 96% alcohol and sprinkled with anesthesin powder. Sometimes a single treatment of this type gives a significant effect. It is necessary to repeat changing the tampon daily or every other day until the pain disappears. Usually, in cases where the cause of inflammation is a foreign body - a bone fragment of the alveolar wall, its removal quickly leads to recovery. Sometimes inflammation in the socket of an extracted tooth spreads to the bone marrow surrounding the alveolus. In such cases, the course of the disease is significantly prolonged due to the development of limited osteomyelitis.
Recovery occurs after the rejection of small sequesters.
Modern methods of tooth extraction and the use of high-quality medications make it possible to remove a tooth with a minimum of pain and complications. But it happens that after tooth extraction the bleeding does not stop. The reasons can be very diverse, related to general or local problems caused by primary or secondary factors.
If the primary bleeding continues several hours after removal tooth, then there is no need to worry. This time is needed for the formation of a blood clot, which performs a protective function to prevent infection from entering the tissue.
If a tooth is pulled out and the bleeding does not stop, then you need to consult a doctor. He will figure out why this happened and take adequate measures.
Causes of bleeding after tooth extraction
To local reasons bleeding include:
Among the most common common causes are diseases of the cardiovascular system. Especially often the blood does not stop with high blood pressure.
Since tooth extraction is a surgery, bleeding is not unusual. And situations where a tooth was pulled out - the bleeding does not stop occur regularly. During the procedure tissues such as gums and periosteum suffer, sometimes bone tissue. The greatest impact is on the blood vessels.
It will be more difficult for a wound to heal if:
- there were granulomas or cysts;
- the crown was damaged;
- The tooth root is too large.
A tooth is pulled out, how can I stop the bleeding after a few days? There is no need to worry if blood continues to bleed for another 3 days after wisdom tooth removal; this is considered normal. A few drops of blood may appear on the 4th day.
Actions of the doctor and patient after tooth extraction
Immediately after tooth extraction, the dental surgeon applies it to the gums sterile swab. It is enough to hold it for 10-20 minutes for a clot to form. It is needed so that tissue grows on top, which will gradually fill the hole.
You must follow all the doctor’s recommendations to avoid damaging the clot. You can’t eat or drink for some time, you can’t rinse the hole with anything, so that the integrity of the clot is not damaged. A complication is indicated if blood continues to flow after 30 minutes.
Sometimes bleeding begins more than half an hour after tooth extraction. This is called secondary bleeding. You should not try to stop it yourself; you should immediately go to the hospital.
For two hours the patient should not:
- drink alcohol;
- smoke;
- eat;
- rinse the mouth;
- exercise;
- take a hot bath.
What you can do yourself
 Although it is not recommended to do any manipulations on your own, it is possible that the patient will not be able to get to the hospital for a short period of time. How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction at home? A sterile swab is placed on the hole that is located at the site of tooth extraction and clamped well with the teeth. You need to sit like this for at least half an hour.
Although it is not recommended to do any manipulations on your own, it is possible that the patient will not be able to get to the hospital for a short period of time. How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction at home? A sterile swab is placed on the hole that is located at the site of tooth extraction and clamped well with the teeth. You need to sit like this for at least half an hour.
In order for the wound to heal quickly, you need to rinse your mouth at least 3 times. saline solution. Rinsing should not be intense so as not to damage the clot. A tea bag placed on the wound will help stop the bleeding. It lasts for half an hour. Tannic acids constrict blood vessels.
If a regular tampon does not stop the bleeding, then it is removed and a new one is applied, soaked in a solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide.
You can also touch the cheek apply a cold object. It will narrow the blood vessels and stop the bleeding, or at least make it less profuse. It is strictly forbidden to apply cold to the wound itself, as this can cause complications.
If the wound is very painful and bleeding begins after the anesthetic wears off, then you can take any painkiller that does not contain aspirin; it thins the blood.
If, in addition to bleeding, you feel dizziness and weakness, then a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed for a minute.
What measures will the doctor take?
 After tooth extraction in the socket a clot forms. His education plays a big role. It is a barrier against infection entering the blood. And also tissue will form under it, which will fill the place where the roots of the tooth were previously.
After tooth extraction in the socket a clot forms. His education plays a big role. It is a barrier against infection entering the blood. And also tissue will form under it, which will fill the place where the roots of the tooth were previously.
To avoid complications, before removing a tooth, the doctor must be aware of existing chronic diseases. This will allow you to quickly take adequate measures if the bleeding does not stop.
The most common reasons why complications arise:
- damage to a large blood vessel;
- damage to the hole;
- gum damage;
- fracture of the interradicular septum;
- hemophilia;
- leukemia;
- other diseases affecting blood clotting;
- clot removal;
- inflammatory process;
- high pressure.
If the doctor is aware of the presence of diseases in advance, then it will be enough to take a medicine that solves this problem. The patient should also know and inform the doctor about the presence of an allergic reaction or individual intolerance to certain drugs.
How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction in the dental office? If the reason was disruption of the integrity of a blood vessel, then the doctor applies cold to the cheek. If the vessel is large, then it must be treated with a hemostatic agent and sutured. If the bleeding site is on the bone, then bone wax or absorbable hemostatic gauze is applied.
 Then the vessel is compressed and a tampon soaked in an agent to stop bleeding is placed in the hole. The tampon will remain in the hole for 3 to 5 days. The doctor must also remove it.
Then the vessel is compressed and a tampon soaked in an agent to stop bleeding is placed in the hole. The tampon will remain in the hole for 3 to 5 days. The doctor must also remove it.
If medications do not help, then the doctor sutures an open wound. This will stop the bleeding and speed up the healing process. In extreme cases, medications are administered that promote rapid blood clotting. If the cause of the complication is inflammation, then the wound is thoroughly disinfected, and the patient is prescribed antibiotics. If blood continues to flow for several days after a tooth has been pulled out, most likely an infection has entered the wound.
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
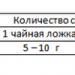
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?