How to cure herpes forever. Herpes: types, symptoms, treatment What is herpes and how
As a rule, herpes is popularly referred to as rashes on the lips, the so-called “cold.” But in fact, there are 8 types of herpes, which have their own characteristics of the course, distinctive clinical signs and treatment methods.
The cause of herpes is a highly contagious virus that is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. Regardless of what type of herpes is present in the human body, this disease is characterized by a period of latent course - the symptoms of the disease in question appear only at a time when the person’s immunity is sufficiently weakened.
Herpes viruses are common not only among people, but also in nature. This is due to the high level of survival of the virus outside mucous membranes or biomaterial - even indoors at room temperature, the herpes virus lives for another 24 hours.
Table of contents:Herpes type 1 (simple)
In the specialized literature, this type of disease in question is referred to as HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus type 1) and may be called oral or labial herpes. The typical location for this type of herpes is the lips and nasolabial triangle, and infection can occur in the first years of a child’s life.

If a person is diagnosed, then the herpes virus affects:
- the skin of the fingers on the upper and lower extremities - more often doctors observe damage to the nail fold;
- mucous membrane of the oral cavity, internal organs, eyes and nasal cavity;
- tissues of the nervous system.
The characteristic features of herpes simplex virus type 1 are:
- development of diseases of the nervous system;
- suppression;
- damage to cells of the nervous system.
Symptoms of herpes simplex type 1

The most characteristic sign of this type of herpes is a rash on the lips - small bubbles with liquid contents appear inside, they grow and eventually either “fade out” on their own or burst. In addition to this sign, doctors note general signs of intoxication:
- pain in muscle tissue;
- general weakness and drowsiness;
- of a short-term nature.
Note:if infection with herpes simplex type 1 occurred through oral-genital contact, then the rash, as the most pronounced symptom, will be noted on the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Diagnostic measures
The type of herpes in question is diagnosed either by patient complaints and a characteristic symptom (rash on the lips or mucous membranes of the genital organs), or by examining the body for some other reason. As part of diagnostic procedures, the doctor is obliged to:
- determine the type of pathogen that provoked the development of herpes simplex type 1;
- differentiate the pathogen;
- determine at what stage of the disease the patient sought medical help.
Treatment of herpes simplex type 1
We recommend reading:In general, therapy against herpes viruses has some features:
- There are no preventive medications;
- herpes viruses are absolutely not sensitive to antibacterial drugs (antibiotics);
- complete destruction of the virus is impossible;
- If the course of the herpes simplex virus type 1 is short-lived, then the use of any medications is inappropriate.
 One of the medicines that can have a truly therapeutic effect is Acyclovir. It is sold in pharmacies in various pharmacological forms - tablets, ointments, solutions. If you use this drug strictly according to the instructions, this will reduce the number of relapses of herpes simplex type 1 and shorten the treatment time for already visible signs.
One of the medicines that can have a truly therapeutic effect is Acyclovir. It is sold in pharmacies in various pharmacological forms - tablets, ointments, solutions. If you use this drug strictly according to the instructions, this will reduce the number of relapses of herpes simplex type 1 and shorten the treatment time for already visible signs.
Note:if a person has characteristic rashes on the lips, then it is necessary to exclude close contacts with other people - we are talking about kissing. Otherwise, the herpes simplex virus type 1 will certainly be transmitted to the body of a healthy person.
Herpes virus type 2
In the specialized literature, this type of disease in question is classified as genital herpes. Both men and women suffer from it, the cause of infection is unprotected sexual contact, however, the herpes virus type 2 can “settle” in the human body even with full caution during sex.
We recommend reading:
Treatment of this type of herpes should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor and after a full examination by specialists. In addition to Acyclovir, for patients diagnosed with type 2 herpes, doctors prescribe a whole range of therapeutic measures - independent choice of drugs is inappropriate.
Herpes type 3 (varicella zoster virus)
The same disease in medicine is called both the chickenpox virus and the herpes zoster virus. It enters the human body through airborne droplets, and if it is a child, then he will develop chickenpox. A person who has recovered from the disease remains a carrier of the virus for life, with its localization in the cells of the nervous tissue.
We recommend reading:
In some cases, the “quiescent” herpes virus type 3 in a child may reappear at an older age, and the clinical picture in this case will be of the nature of herpes zoster.
If a child’s body is infected with the type of herpes in question, then the following symptoms will be identified:
- high body temperature, chills;
- rashes on the skin in the form of vesicles;
- severe, unbearable itching of the skin.
As a rule, in childhood, type 3 herpes virus quickly becomes inactive and is localized in the cells of nerve tissue. Usually the virus in question does not manifest itself in any way, but in some cases (decreased immunity, too long a course of chronic diseases, and so on) the herpes virus type 3 manifests itself herpes zoster. And in this case, the following symptoms will occur:

As a rule, after 2-3 weeks, all signs of shingles disappear, and small scars remain at the site of the rash - depressions/pits with smoothed edges.
Treatment of herpes virus type 3
There is no specific treatment for the type 3 disease in question - doctors examine the patient and prescribe symptomatic therapy. In childhood, these are antipyretics and drugs that reduce itching of the skin. For herpes zoster - painkillers, antipyretics, and if concomitant inflammatory diseases are detected - antibacterial drugs.
Herpes type 4 (Epstein-Barr virus)
We recommend reading:This type of herpes is referred to in medical literature as the Epstein-Barr virus. It provokes the development of infectious disease, which is typical for people with diagnosed immunodeficiencies.

Symptoms of herpes virus type 4 and treatment
Infectious mononucleosis is a lesion of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and lymph nodes, most often characteristic of young people. The main signs of this disease are high body temperature, morphological changes in the structure of the blood, pathological changes in the spleen, liver and other internal organs.
The most common symptoms of herpes type 4:
- body temperature rises suddenly, without any apparent reason and immediately to critical levels;
- there are complaints of pain in muscles, joints, throat and head;
- the oral mucosa swells and swells - doctors can differentially diagnose pharyngitis and/or;
- a feeling of constant fatigue, rapid fatigue, drowsiness - these symptoms may persist even after treatment for the disease for several months;
- small papular-type rashes appear on the skin and mucous surface, which disappear without a trace after 3 days;
- lymph nodes increase significantly in size.
Diagnostic measures consist of conducting a full examination of the patient and laboratory testing of his biomaterial - specialists identify the DNA of the Epstein-Barr virus.
Note:It is this virus that can provoke the development of cancer - Burkitt's lymphoma. Therefore, treatment should only take place in a medical institution, under constant supervision by medical workers .
Herpes type 5 (cytomegalovirus)
Herpes virus type 5 causes the disease cytomegalovirus. It is noteworthy that the symptoms of this disease are vague, the pathology occurs in a latent form, and the clinical picture begins to develop only when the immune system is weakened.
Symptoms of herpes virus type 5 and treatment
The manifestation of cytomegalovirus is identical to the course of a cold:
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness and drowsiness;
- when swallowing, talking and at rest.
Cytomegalovirus can manifest as damage to the central nervous system, eyes, spleen and pancreas.
Herpes virus type 5 is especially dangerous during pregnancy - it has an active negative effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus. This may cause:

Note:Treatment of herpes virus type 5 is considered only during pregnancy. The feasibility of preserving the fetus is determined by the doctor - if the infection occurred after conception, then this is an absolute medical indication for artificial termination of pregnancy. In case of infection with herpes virus type 5, long before pregnancy, doctors prescribe antiviral, symptomatic therapy and a course of treatment with immunomodulators.
Herpes virus type 6
This type of disease in question is present in the etiopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. The disease manifests itself in people aged 20 years and older; multiple sclerosis has not been diagnosed at an earlier age.
Symptoms
Signs of multiple sclerosis include:
- constant fatigue;
- often recurrent;
- disturbance of sensitivity in various manifestations - tactile, temperature and others.

These are the early symptoms of multiple sclerosis caused by herpes virus type 6, but as the disease develops, more serious signs of pathological damage to the patient’s organs and systems appear. These include:
- rapid changes in mood, disturbances in the psycho-emotional background;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision of any object;
- slow-witted;
- complete absence of pain reaction;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- muscle spasms, cramps;
- unusual pronunciation of words;
- violation of the swallowing instinct.
Note:The clinical picture of herpes virus type 6 can be variable - it all depends on which parts of the central nervous system are affected by the virus. This process is unpredictable, so doctors are careful in determining the symptoms of the type of herpes in question.
Treatment of herpes type 6
In the process of carrying out therapeutic measures, doctors use a whole range of medications:
- antioxidants;
- angioprotectors;
- corticosteroids;
- drugs with immunomodulatory effects;
- production stimulating agents;
- immunoglobulins.
But this list is far from complete - medications are selected on a strictly individual basis and only by specialists.
Herpes virus type 7
Most often, this herpes virus is combined with herpes type 6. This combination provokes the development of chronic fatigue syndrome, which is actually not a dangerous disease, and cancer of the lymphoid tissue.
This type of disease in question is characterized by the following manifestations:

Diagnostic measures and treatment
Diagnosis of herpes virus type 7 is carried out only in laboratory conditions - the patient’s blood is examined. The following methods are used:
- immunogram.
Treatment of this type of herpes consists of antiviral therapy, which is aimed at strengthening the immune system.
Note:preventive measures have not yet been developed.
Herpes type 8
Herpes virus type 8 affects lymphocytes, but can remain in the body of absolutely healthy people for a long time. Routes of transmission of herpes virus type 8: through the placenta from mother to child during pregnancy, during organ transplantation, and can be activated during radiation therapy.
Symptoms and treatment
Herpes virus type 8 causes several cancers:
- Kaposi's sarcoma– formation of multiple malignant neoplasms;
- primary– oncology with damage to the serous membranes;
- Castleman disease.
Treatment of such serious cancers is carried out through the use of radiation therapy or surgery.
All types of herpes virus must be treated - the general state of human health will depend on this. There are no safe diseases, especially those of viral etiology - the lack of therapy can lead to irreversible pathological processes in organs and systems.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of herpes
Important:You cannot rely solely on traditional medicine - remedies from this category can only strengthen the immune system, but cannot in any way get rid of the virus. Even completely official medications cannot cope with this task! But you shouldn’t give up traditional medicine either - some remedies will actually effectively curb the appearance of signs of various diseases caused by herpes viruses.
 Pour 3 tablespoons of dried chamomile flowers into 500 ml of boiling water and leave for 6-8 hours (it is better to prepare the product overnight). The resulting infusion can be taken orally, 1 tablespoon immediately after meals - this will help quickly relieve inflammation in the upper respiratory tract and restore immunity during a cold.
Pour 3 tablespoons of dried chamomile flowers into 500 ml of boiling water and leave for 6-8 hours (it is better to prepare the product overnight). The resulting infusion can be taken orally, 1 tablespoon immediately after meals - this will help quickly relieve inflammation in the upper respiratory tract and restore immunity during a cold.
If symptoms of herpes simplex type 1 appear, namely a rash on the lips, then you need to moisten a gauze pad in the resulting infusion of chamomile and make lotions. This will speed up the healing process of a “cold” on the lips, and if there is purulent inflammation, then chamomile will “draw out” all the liquid.

This plant is brewed in the same proportions as chamomile. But both traditional healers and trained doctors warn: you should not drink too much of this tea. The maximum permissible dosage is 500 ml per day, and not in one gulp, but in several doses.
Note:Licorice root can cause severe poisoning, therefore, it is strictly forbidden to use a medicine based on it during pregnancy, with diagnosed hypertension and renal failure.
 This plant acts on the herpes virus from the inside, so the effect is quite impressive. Some healers recommend eating 2 flowers of this plant every day and treating in this way for 2 weeks, and then taking a break for 10-15 days.
This plant acts on the herpes virus from the inside, so the effect is quite impressive. Some healers recommend eating 2 flowers of this plant every day and treating in this way for 2 weeks, and then taking a break for 10-15 days.
You can prepare a decoction from the stems and leaves of tansy - 1 tablespoon of dry raw materials per glass of boiling water, cook the decoction for 10 minutes at low boil. Take 1 teaspoon of tansy decoction once a day after meals.
You can use the same decoction for external use - lubricate the affected areas of the skin, make lotions.
Oils in the treatment of herpes

To treat herpes rashes, it will be effective to use various oils - tea tree, fir, camphor. During the period when such manifestations of herpes of any type appear, simply lubricate the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day.
 Note:Any remedies prepared according to prescriptions from the category of traditional medicine cannot be used in the treatment of herpes without first consulting a doctor. Firstly, it is necessary to exclude banal hypersensitivity and/or individual intolerance. Secondly, the above medicinal plants have quite a powerful healing effect and in some cases can provoke a deterioration in health. Thirdly, it is necessary to exclude/confirm the presence of diseases concomitant with herpes in order to outline the direction of the therapeutic course.
Note:Any remedies prepared according to prescriptions from the category of traditional medicine cannot be used in the treatment of herpes without first consulting a doctor. Firstly, it is necessary to exclude banal hypersensitivity and/or individual intolerance. Secondly, the above medicinal plants have quite a powerful healing effect and in some cases can provoke a deterioration in health. Thirdly, it is necessary to exclude/confirm the presence of diseases concomitant with herpes in order to outline the direction of the therapeutic course.
Herpes is often an almost harmless disease, but there are types of this virus that can become really dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. Only a doctor’s consultation and competent, timely medical care will help patients.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Introduction
Herpes, or herpes infection, is one of the most common human viral infections, characterized by rashes on the affected area in the form of blisters.The virus can be transmitted through household items (towels, dishes, toys, bed linen).
If there are rashes, a sick person can spread the infection with his hands to other organs (from the lips to the genitals or to the eyes).
Therefore, if you have a rash, you should use an individual towel, dishes, and avoid kissing and oral sex. The ointment should be applied to the rash with a special glass rod purchased at the pharmacy. You should wash your hands thoroughly even after accidentally touching the rash. It is not recommended to squeeze out the bubbles and tear off the crusts, because... this also promotes infection.
Incubation period(the time from the moment of infection to the onset of the disease) can last from 1 to 26 days.
The herpes simplex virus, having entered the body through the skin and mucous membranes, can cause diseases in the following organs and systems:
- mucous membranes and skin (herpes of the wings of the nose, lips, genitals; stomatitis, gingivitis - damage to the gums);
- organs of vision (inflammation of the cornea, iris and retina, optic neuritis);
- ENT organs (herpetic sore throat, inflammation of the larynx and pharynx, herpes of the outer ear, sudden deafness);
- Cardiovascular system (myocarditis or damage to the cardiac muscle of the heart; aggravates atherosclerosis);
- respiratory organs (inflammation of the bronchi and lungs);
- gastrointestinal tract (liver damage - hepatitis - and intestines - proctitis, colitis);
- central nervous system (inflammation of the substance of the brain and meninges, i.e. encephalitis and meningitis; damage to nerve plexuses and nodes; aggravating effect on schizophrenia and senile dementia);
- female genital organs (inflammation of the cervix, inner lining of the uterine cavity, membranes of the fertilized egg, infertility);
- male genital organs (damage to sperm, urethra, prostate gland);
- lymphatic system (lymphadenopathy).
Provoking factors for relapse herpes can be:
- infections (bacterial or viral);
- weakened immunity;
- stressful situations;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- lack of vitamins in the body, “strict” diets and exhaustion;
- overwork and heavy physical activity;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
Symptoms of herpes simplex
 Type 1 virus can infect mucous membranes or skin anywhere. But most often, characteristic rashes are localized on the lips or wings of the nose, on the oral mucosa. Less commonly, the skin on the cheeks, forehead, ears and other places is affected.
Type 1 virus can infect mucous membranes or skin anywhere. But most often, characteristic rashes are localized on the lips or wings of the nose, on the oral mucosa. Less commonly, the skin on the cheeks, forehead, ears and other places is affected. 1-2 days before the appearance of the rash, itching, burning, and sometimes weakness and general malaise may be noted. Then bubbles up to 3 mm in diameter with transparent contents appear. The appearance of bubbles is accompanied by severe pain and unpleasant tingling. Bubbles can merge with each other. There is slight swelling and redness of the tissue in this area. The rash may be accompanied by fever and headache.
Then the contents of the bubbles become cloudy, swelling and redness disappear. After 3-5 days, the blisters burst, and the ulcer at the site of the bubble becomes covered with a crust. On days 7-9, the crust is torn off, leaving no trace. The process can last up to 2 weeks.
In 30% of women and 10% of men, primary herpes leads to complications, the most severe of which is herpetic meningitis (damage to the meninges).
Relapses of herpes occur with similar manifestations. A milder course of the disease and faster healing of ulcers may be observed. Relapses (in the presence of provoking factors) can occur up to 6 times per year.
Symptoms of genital herpes
 Genital herpes is a lesion of the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia. It can be caused by viruses of types 1 and 2.
Genital herpes is a lesion of the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia. It can be caused by viruses of types 1 and 2. Infection occurs through sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal) or when the infection is transferred by hand from a different location. The source of infection can also be a sexual partner without acute manifestations of the disease, i.e. carrier of the virus.
There are primary and recurrent genital herpes. Recurrent herpes can occur in typical, atypical and asymptomatic (viral shedding) forms.
An atypical course of the disease occurs in 65% of cases. The viral nature of the chronic inflammatory process in the genital organs in such cases is confirmed by laboratory examination, because There are no rashes typical for herpes blisters.
In a typical course, the initial concern is itching and burning in the area of the subsequent appearance of vesicular rashes, and general malaise. Chills and fever, headache may occur. Pain during urination and purulent vaginal discharge may occur. Nearby lymph nodes become enlarged.
Then bubbles (single or confluent) appear on the head of the penis, the foreskin in men, and in the area of the labia majora and minora in women. The transparent contents of the vial become cloudy. After 4-5 days, the blisters open and the ulcers become crusty. With confluent rashes, the size of the ulcerative surface can be significant. The process lasts about 3 weeks.
Herpes can “spread” to the mucous membrane of the vagina, urethra, cervix, skin of the buttocks, thighs in women; and in men - on the urethra, testicles and prostate gland.
Genital herpes in women can lead to the following consequences:
- constant itching in the perineum and vagina;
- infection of the fetus in the early stages and miscarriage;
- infection of the fetus in late pregnancy can manifest itself as damage to the eyes, skin, nervous system and developmental delay. Primary infection of a woman in the last trimester of pregnancy is especially dangerous.
Genital herpes in men can cause prostate cancer.
Relapses of genital herpes are easier than the episode of primary infection, without fever and malaise. There are fewer rashes during relapses.
Symptoms of herpes zoster
 A third type of herpes virus causes herpes zoster (or shingles) and chickenpox. Activation of the virus in persons who had chickenpox in childhood occurs in the presence of provoking factors (decreased immunity, stress, severe illness, etc.).
A third type of herpes virus causes herpes zoster (or shingles) and chickenpox. Activation of the virus in persons who had chickenpox in childhood occurs in the presence of provoking factors (decreased immunity, stress, severe illness, etc.). Initially, severe pain appears along the nerve (usually along the intercostal nerves), malaise, and headache. A few days later, along the course of the nerve, a group of vesicles with transparent, and subsequently with purulent or bloody contents, appears on swollen, slightly reddened skin. The rash resembles the chickenpox rash. Bubbles can be arranged in the form of a ribbon or in the form of a ring. After opening the blisters, ulcers form and become crusty.
In weakened individuals, the rashes can occupy a significant area, and the blisters tend to merge (bullous form). Such patients (patients with malignant neoplasms, blood diseases, diabetes mellitus, receiving corticosteroid hormonal drugs, chemotherapy or radiation therapy) may develop other severe forms of herpes zoster:
- hemorrhagic (bubbles with bloody contents);
- gangrenous (with gangrenous ulcers);
- generalized (with damage to internal organs and systems).
When the virus affects the nerve ganglion (geniculate ganglion), the following triad of symptoms is observed: neuritis of the auricular and facial nerves, skin rashes in the area of the auricle and sharp pain in the ear.
When the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves are damaged, sharply painful unilateral rashes appear on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, tongue, hard and soft palate. The blisters quickly open, forming ulcers and erosions.
In all severe forms of herpes zoster, herpetic meningoencephalitis (damage to the brain and meninges) can develop.
The rash can be localized in the inguinal-femoral region, on the neck, scalp, on the face (along the branches of the trigeminal nerve). The lesion is characteristically unilateral.
When contracting herpes zoster, the pain syndrome is pronounced. The pain can be aching, dull, shooting, or pulling. Pain can be observed only at the affected area or radiate (simulate cholecystitis, angina).
Severe pain is explained by damage to the nerve ganglia and plexuses by the virus. Therefore, pain can persist for a very long time even after the rash disappears (up to several months). This also explains impaired skin sensitivity, impaired salivation or sweating for a long time.
Herpes in children
 Usually, the first “encounter” with the herpes virus occurs in early childhood, when children become infected from adults through kissing or violating hygiene rules (licking a spoon, pacifier, etc.). Infection can also occur through airborne droplets - when a patient sneezes or coughs.
Usually, the first “encounter” with the herpes virus occurs in early childhood, when children become infected from adults through kissing or violating hygiene rules (licking a spoon, pacifier, etc.). Infection can also occur through airborne droplets - when a patient sneezes or coughs. The external manifestations of herpes in children are the same as in adults: small blisters appear in the area of redness of the skin, and after they open, ulcers form. The child's general condition suffers little; a slight increase in temperature may be noted.
With facial herpes, rashes often appear not only on the lips, but also on the skin of the nasolabial triangle and in the nasal passages.
More often in children at an early age, herpes simplex manifests itself in the form of acute herpetic stomatitis or herpetic sore throat.
In a child with eczema or neurodermatitis, if infected with the herpes virus, multiple rashes appear not only on the face, but also on the hands, forearms, and sometimes on the torso. The rash resembles the chickenpox rash. The child's condition is serious, the temperature rises to 39-40 o C. Manifestations of stomatitis, conjunctivitis, pneumonia, and meningitis may occur. The addition of a secondary infection can even lead to death.
Recurrent herpes simplex occurs in children several times a year.
The occurrence of herpes zoster is possible only in children over 10 years of age; This disease does not occur at an early age.
Herpes: types, symptoms and causes - video
Herpes on the lips is a viral disease caused by type I herpes virus. This pathogen can infect the skin, mucous membranes, and nervous system.
Statistical studies have been carried out, during which it was found that approximately 65 - 90% of the world's population is infected with the herpes virus. Some of these people have an infection caused by the herpes virus type I.
There is no structure in the CIS that would register cases of herpes. It is believed that there are currently about 290 million infected people living in the post-Soviet space.
Herpes on the lips is a seemingly “harmless” disease that affects the skin and leads to the appearance of blisters and unpleasant itching.
In fact, the herpes virus may pose a more significant danger to humans. It is capable of affecting nervous tissue, blood cells, leading to a decrease in immunity, the growth of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels, and is capable of activating the HIV virus and the process of growth of malignant tumors.
The causative agent of herpes on the lips
The causative agent of herpes on the lips is the herpes virus type I (other names: Herpes simplex virus 1, Human herpesvirus 1, HSV-1, HSV-1), which contains DNA. The size of the virus is from 150 to 200 nanometers. The shape resembles a cubic one.Herpes virus type I is persistent in the environment, and most people are highly susceptible to it. Therefore, infection occurs relatively easily.
In total, there are 6 species in the herpesvirus family.
Types of herpes viruses:
- Herpes virus type I mainly causes skin lesions above the waist. The most common location is on the lips, in the mouth area.
- Herpes virus type II predominantly affects the skin below the waist. It most often causes sexually transmitted infections.
- Herpes virus type III causes shingles and varicella (chickenpox).
- Herpes virus type IV The Epstein-Barr virus is the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis.
- Herpes virus type V– cytomegalovirus, causes cytomegalovirus infection.
- Herpes viruses types VI, VII and VIII have not yet been studied enough. Modern researchers believe that these pathogens are important in the development of various types of rashes and chronic fatigue syndrome.
- herpes on the lips;
- herpes of the skin of the upper half of the body;
- herpes of mucous membranes(most often the oral cavity);
- ophthalmoherpes– herpetic eye lesions;
- genital herpes– rare, more often caused by herpes virus type II;
- herpetic encephalitis– brain damage;
- pneumonitis– inflammation of the lungs of herpetic nature.
Causes of infection with herpes simplex virus type I. Ways of transmission of herpes on the lips.
 Infection with the herpes virus can occur from a sick person or a virus carrier. After recovery, the pathogen can persist in the body for a long time, and sometimes for a lifetime.
Infection with the herpes virus can occur from a sick person or a virus carrier. After recovery, the pathogen can persist in the body for a long time, and sometimes for a lifetime. Ways of infection with herpes virus type I:
- contact: through handkerchiefs, during kissing, during close contact;
- airborne: during close proximity to a person with a herpes virus infection;
- sexual route: infection during sexual intercourse occurs relatively rarely, this is more typical for herpes type II;
- during blood and plasma transfusion, infection of the fetus from a sick mother.
How does the herpes virus become infected?
The first contact with the herpes virus occurs very early, most often in infancy. The infection is asymptomatic, but the virus accumulates in the body in nerve cells. It penetrates the skin or mucous membranes, then into the nerve endings, migrates along the nerves and accumulates in the roots of the spinal cord. Once the virus has become integrated into the genetic apparatus of nerve cells, its removal from the body becomes impossible. In the future, when the body is weakened and appropriate conditions are present, herpes develops on the lips or other areas of the skin.What conditions are necessary for the disease to develop?
- poisoning, living in unfavorable environmental conditions, occupational hazards;
- frequent, chronic and severe infectious diseases;
- diseases and pathological conditions of the skin;
- AIDS and malignant tumors;
- endocrine diseases: adrenal dysfunction, diabetes, etc.
After suffering from herpes on the lips, immunity is formed. But it is unstable - immune mechanisms are active only as long as the virus is in the body.
Options for the outcome of the disease:
- the virus remains in the body for life without causing further disease;
- herpes acquires a recurrent course: after recovery, the infection develops again.
Symptoms of herpes on the lips
The incubation period for this disease lasts from 2 to 8 days. After this, characteristic symptoms appear.Variants of the course of herpes on the lips:
- spicy;
- chronic.
| Signs of acute herpes on the lips |
Appearance of bubbles: |
| Signs of chronic herpes on the lips | Most often, chronic herpesvirus infection has a relapsing course. Stages of chronic herpes on the lips:
|
 Diagnosis and treatment of herpes on the lips is carried out by a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist. The manifestations of herpes on the lips are quite typical, so the disease is almost impossible to confuse with any other. Sometimes it is necessary to distinguish herpes on the lips from diseases such as herpes zoster, herpangina caused by enteroviruses (damage to the tonsils).
Diagnosis and treatment of herpes on the lips is carried out by a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist. The manifestations of herpes on the lips are quite typical, so the disease is almost impossible to confuse with any other. Sometimes it is necessary to distinguish herpes on the lips from diseases such as herpes zoster, herpangina caused by enteroviruses (damage to the tonsils). Complications of herpes on the lips:

- Infection and suppuration. Most often it occurs if the patient scratches the lesions, independently opens the blisters, and introduces bacteria (staphylococci and other pyogenic microorganisms) into them. At the same time, swelling and redness increase, severe pain occurs, body temperature rises even more, and general well-being is disturbed. A boil or cellulitis may develop.
- Spread of rashes. Occurs due to improper self-medication and non-compliance with hygiene rules. Herpetic blisters spread throughout the face, appearing in the shoulder girdle and on the arms.
- Spread of the process to internal organs. The risk of this complication is highest in people with reduced immunity. Herpes of the esophagus, cornea, trachea and lungs, bronchi, and brain may develop (the most severe complication).
- Decreased immunity. The herpes virus contributes to a decrease in immune strength, as a result of which acute infectious diseases develop and chronic ones worsen.
Diagnosis of herpes on the lips
The lesions have a characteristic appearance, so the diagnosis is easily established after examination. Errors are practically eliminated.If the doctor has doubts, he prescribes laboratory tests:
| Study title | What does it reveal? | How is it carried out? |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | Detection of antibodies to the herpes virus in the patient’s blood. If antibodies are produced and present in the blood in sufficiently large quantities, then this is confirmation that the pathogen is present in the body. With herpes virus infection, the level of antibodies in the blood increases over time. This can be revealed by conducting two studies at a certain interval. | For research, blood is taken from a vein.
|
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Detection of viral DNA in the material. A study aimed at directly detecting the pathogen. | Blood and the contents of vesicles may be taken for examination.  |
| Immunofluorescence | Detection of virus antigens in the material. If the pathogen is present, then as a result of the chemical reactions carried out, a glow becomes visible. | The contents of the bubbles are taken for examination.
|
| Complete blood count and urinalysis | General clinical studies that are performed on all patients if any disease is suspected. With herpes virus infection, all indicators are normal. |
Treatment of herpes on the lips
Typically, herpes on the lips is treated on an outpatient basis. Sometimes, with a severe course of the disease and the development of complications, hospitalization in a hospital is indicated.In most cases, ointments and gels with antiviral drugs are used to treat herpes on the lips.
| Name medicine* | Description | Directions for use and doses** |
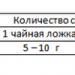
| Acyclovir (syn.: Zovirax, Gerpevir) | Acyclovir is an antiherpetic drug. It interacts with the DNA molecule of the pathogen, breaks it and blocks the reproduction of the pathogen.  | For herpes on the lips, Acyclovir is used externally as an ointment or cream. Mode of application: apply an antiviral agent to the affected area 5 times a day. Treatment usually lasts, depending on the doctor’s prescription, for 5–10 days. |
| Valaciclovir (syn.: Valtrex) | Valaciclovir is a precursor drug. Once in the body, it turns into acyclovir.  | Valaciclovir is available in 250 and 500 mg tablets. It is able to convert into Acyclovir only after it enters the bloodstream, under the action of liver enzymes. Mode of application: |
| Allomedine | The main active ingredient in the drug is Allostatin. It belongs to alloferons - new antiviral agents of plant origin. Effects of the drug:

| The gel is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day for 2-3 days. |
| Infagel | A gel containing an antiviral and immunostimulating drug – interferon. It is most effective in the initial stages, when the patient is just beginning to be bothered by itching.  | Apply the gel to the affected area 2 times a day, every 12 hours. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. |
| Oxolinic ointment | An ointment that has an antiviral effect and destroys almost all types of viruses, except HIV.  | Apply 3% oxolinic ointment to the affected area 2 – 3 times a day. Continue treatment from 2 weeks to 2 months. |
| Viru-Merz serol | Gel with antiviral effect. Effective against herpes viruses types I and II. The active substance included in the drug blocks the attachment of the virus to the cell and penetration inside.  | Apply the gel to the affected area 3 to 5 times a day. Treatment usually lasts 5 days. If there is no improvement within 2 days, you should consult a doctor to prescribe another drug. |
| Remantadine (syn.: Rimantadine, Flumadin, Algirem, Polyrem). | Antiviral drug. Mainly used to treat influenza in the early stages. But it is also effective for herpes on the lips.  | Release form: In the form of tablets of 0.05 and 0.1 g. Directions for use:
|
| Famciclovir (syn.: Minaker, Famvir) | An antiviral drug effective against herpes infections caused by herpes viruses type I and II, herpes zoster.  | Release form: Tablets of 0.25 and 0.125 g. Directions for use (adults):
|
| If a herpes virus infection is accompanied by a decrease in immunity, then immunostimulating drugs are prescribed: Timalin, Timogen, Immunofan, Ribomunil etc. They must be taken strictly as prescribed by an immunologist. |
||
**Information about medications is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute a guide for self-treatment. We are not responsible for harm to health or any other harm resulting from the patient’s self-administration of the described medications. Self-medication without the participation of a medical specialist is unacceptable, as it can lead to negative consequences.
How to treat herpes on the lips during pregnancy?
 Herpes on the lips of a pregnant woman does not pose such a danger to the fetus as genital herpes (on the genitals, caused by the herpes virus type II). The mother's body produces antibodies that protect the fetus.
Herpes on the lips of a pregnant woman does not pose such a danger to the fetus as genital herpes (on the genitals, caused by the herpes virus type II). The mother's body produces antibodies that protect the fetus. If symptoms of the disease appear, you should visit a doctor. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe treatment, guided by:
- the degree of danger of herpes virus infection for the fetus;
- the feasibility of using antiviral drugs and their danger to the fetus.
- Acyclovir ointment;
- Zovirax ointment.
Precautions to take after giving birth if the mother has herpes on the lips:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before any contact with the child;
- Wear a gauze mask while feeding and caring for the baby;
- do not allow the lesions to come into contact with the child’s skin: do not touch him with your lips, do not kiss him until complete recovery.
How does herpes on the lips in men affect the conception of a child?
Men are often interested in the question: is it possible to plan to conceive a child if there is herpes on the lips? The disease does not affect the quality of sperm in any way; the virus does not infect it. Therefore, if a man has a disease, it is quite possible to plan a pregnancy.How to treat herpes on the lips with folk remedies?
| Folk remedy | Description | Mode of application |
Adaptogens:
| Adaptogens are herbal products that activate the body’s internal resources, tone, and increase immune strength. The body fights the herpes virus more successfully, and recovery occurs faster. | Adaptogens are taken in accordance with the instructions included in the package with the drug. |
| Treatment with aloe and Kalanchoe | Aloe and Kalanchoe are home potted plants; their juice contains adaptogens. They are used topically to treat many diseases, including herpes on the lips.
| Cut an aloe or kalanchoe leaf. Apply a fresh cut to the affected area for 2–3 minutes. Then update the slice and repeat. |
| Peppermint | Peppermint contains substances that have a soothing effect on the skin, reduce inflammation, irritation, and itching.  | Cooking method:
Apply the decoction to the affected areas several times a day. |
| Garlic | Garlic cloves contain phytoncides - substances that can destroy various types of bacteria and viruses, including type I herpes virus.
| Cooking method:
Apply the paste wrapped in gauze to the affected area for a while. Precautionary measures:
|
| Propolis tincture | Propolis tincture destroys pathogens and improves the functioning of protective mechanisms in tissues. It has cauterizing properties.  | Propolis tincture is used to cauterize ulcers remaining in place of herpetic blisters. To do this, use a cotton or gauze swab or a cotton swab. Some time after cauterization, you can apply an emollient cream to the lesion. For example, from chamomile or calendula. |
| Fir oil | Fir oil contains phytoncides - substances that destroy pathogens.
| Directions for use: apply fir oil in a small amount to affected areas of the skin every 2 hours. It is worth remembering that fir oil can irritate the skin, increase burning and other unpleasant sensations. |
| Foods that should not be consumed if you have herpes on the lips | Products recommended for herpes on the lips |
If you have the disease, products containing the amino acid arginine, which is necessary for the reproduction and functioning of the virus, are not recommended:
| For herpes virus infection, products containing the amino acid lysine are recommended - it is believed that it inhibits the reproduction of the pathogen. Foods containing large amounts of lysine:
Products containing zinc:
|
Activities aimed at increasing immunity:
- treatment of all existing chronic diseases;
- proper sleep, rest;
- good nutrition;
- taking vitamins, minerals (various vitamin and mineral complexes that are sold in pharmacies);
- hardening;
- proper work and rest schedule, avoiding stress;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- playing sports.
Measures aimed at preventing the spread of infection and infection of other people
 Herpes virus type I is very highly contagious. Therefore, sick people and those around them must take certain precautions.
Herpes virus type I is very highly contagious. Therefore, sick people and those around them must take certain precautions. Necessary measures:
- Do not touch the area where the rash is located with your hands. If you touch the fireplace, you should immediately wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- Do not apply antiviral agents to the skin of the lips with your hands. Use cotton swabs and swabs for this.
- Do not comb or squeeze, or open the bubbles yourself. This will lead to the spread of infection to adjacent areas of the skin.
- The patient should have his own separate dishes, towel, and other objects that come into contact with the lips.
- During illness, you should refrain from kissing and oral sex.
- Do not wet contact lenses or other objects with saliva.
Vaccinations against herpes on the lips
Currently, there is no vaccination against herpes viruses. This is due to the fact that immunity is strong only as long as the virus is actively present in the body. In the absence of the virus, immunity is lost and new conditions for infection are created.There are 8 types of herpes virus that affect the human body. The symptoms of some of them are similar, for others they vary greatly - the diseases manifest themselves as skin rashes, fevers, sore throat, mental damage and even oncology.
Treatment of herpes in most cases is monotonous: it is aimed at suppressing viral activity with certain drugs and increasing immunity. For different types of infection, complex therapy requires additional medications to combat specific symptoms.
What drugs are used in therapy against herpes infection?
To treat the herpes virus in modern domestic medicine, the following drugs are usually used:
For different types of disease and affected areas, different forms of drugs are prescribed. So, for labial (simple) herpes, external agents are usually used, for extensive rashes - tablets and injections. In case of genital infection, suppositories also come into play. Low-dose injections are recommended for newborns because they cannot take other forms of medication.
Attention! If a herpetic infection is complicated by additional fungal or bacterial diseases, antibiotics are additionally prescribed. In other cases, these drugs are dangerous to take; they can only worsen the patient’s condition. When prescribing, they try to limit themselves only to forms for local/external use; oral medications are prescribed only for particularly extensive internal bacterial damage.
How to treat herpes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, primary infection with herpes is most dangerous. If a woman has already encountered this disease, her body produces antibodies that are transferred to the embryo, thereby protecting it (albeit not 100%) from infection. Recurrences of herpes infection are also not so scary; with adequate treatment, the risk of infecting a child is minimal.
First of all, therapy is aimed at suppressing the activity of the virus and reducing the duration of the acute period of the disease.
In the first 24 hours after the onset of herpes symptoms, you should start taking antiviral drugs:
- Acyclovir;
- Valaciclovir;
- Penciclovir;
- Famciclovir.
You can take any analogues of these drugs. Safer and more effective than others for treatment are acyclovir medications, which include Zovirax, Gerpevir, Supraviran, Acigerpin. These substances are active against herpes viruses types 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
Typically, the prescription of antiviral drugs in pregnant women is limited to local administration - in the form of ointments, gels, creams. This is justified by the low percentage of penetration of the active substance into the mother’s body, since at the same time it passes through the placental barrier (enters the child’s body). Antibacterial ointments are also recommended for external use - oxolinic, tetracycline, erythromycin and tebrofen, Neosporin, Vidarabine, Riodoxol.
It is important to know! In case of significant damage to the body by herpes, in case of primary infection or a particularly acute relapse, drugs are prescribed in tablets: 500 mg of Valaciclovir twice a day for 10 days or 200 mg of Acyclovir three times a day for 5 days.
For severe pain, women are advised to lubricate their skin with Xylocaine 2%. To speed up the regeneration of affected areas, you can take sitz herbal baths with chamomile or string, and then apply drying ointments, such as zinc, to the damaged areas.
Features of treatment of newborns and children up to one year
If the mother has a herpes infection, the newborn must be isolated during the incubation period of the virus. It does not matter whether the child has clinical symptoms or not. However, if the mother was healthy, the baby is isolated only if characteristic signs are present.
Traditionally, herpes treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- If symptoms of herpes occur, 30 mg of Acyclovir per kilogram of body weight is prescribed intravenously daily for 10 days.
- Generalized infection is treated with increased doses of Acyclovir - up to 60-90 mg - for 2-3 weeks.
- Human immunoglobulin is also used at 4-6 mg per kilogram intravenously through a dropper in the first 3 days. The drug can be replaced with Viferon, Roncoleukin or Reaferon.
If the organs of vision are damaged or there are skin rashes on the newborn’s body, in addition to intravenous therapy, local antiviral agents are used - Acyclovir ophthalmic ointment and interferon-based gels. Herpetic rashes on the gums () and the inner sides of the lips are treated with hydrogen peroxide 3%. To anesthetize feeding, anesthesin or lidocaine is used before feeding.
Treatment of labial and genital herpes (types 1 and 2) in men and women (on the butt)
Labial herpes simplex usually “spreads” over the skin of the face, neck, mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, and touches the eyes. Scratching and frequently touching affected areas can spread the infection throughout the body.
Mainly located in the groin area: on the external genitalia, inner thighs, butt. The disease can spread to the vagina in women or to the urethra and testicles in men. Touching also transfers the infection to any other parts of the body - to the stomach, armpits, face.




Treatment for both of these types of herpes is similar. Therapy is usually carried out in three stages:
- Taking antiviral drugs for 5-10 days: Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Cytarabine, Famciclovir, Ribavirin, Trifluorothymidine, Bofanton, Tromandathrin, Oxolin, Tebrofen, Amiksin in the form of injections, ointments or tablets.
- Raising immunity during a period of remission of 30-60 days: human immunoglobulin, Pentaglobin, Cytotect, Vesikbulin, Camedon, Kagocel, Viferon, Cycloferon, Ridostin, Leukinferon, Neovir, etc.
- Prevention of relapse of the disease once every 6 months: Amiksin + polyvalent vaccine against herpes is prescribed (a total of 5 subcutaneous injections of 0.2 ml every other day).
With labial herpes, it is often enough to carry out the first stage of treatment, while the genital form is treated with a full course. Often, only boosting immunity (simplified second stage of treatment) without vaccination is used to prevent relapses.
How to treat herpes zoster (type 3)?
Shingles often goes away on its own, but treatment against the zoster virus is still used to improve the immune system, relieve uncomfortable symptoms, and reduce the risk of relapses. Therapy is especially necessary for elderly people (over 50) and with severe immunodeficiency. In this case the following is prescribed:
- Antiviral drugs. Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Valacyclovir, Penciclovir. It is advisable to start treatment in the first 3 days.
- Painkillers. To alleviate the physical and psychological condition of the patient, narcotic analgesics (for example, Oxycodone) are prescribed in the United States; in Russia, non-narcotic analgesics are prescribed: Ketoprofen, Ketorolac, Ibuprofen, Naproxen.
- Anticonvulsants. Sometimes, for severe neuropathic pain, patients are recommended to take Gabapentin or Pregabalin.
Several drugs should be noted separately, since their use is most effective and is often prescribed by doctors: deoxyribonuclease, Isoprinosine, acyclovir drugs, ganglion blockers (Gangleron). Additionally, patients are recommended to take vitamin B complexes and interferon ointments/aerosols (Eridin, Alpizarin, Florenal, Helepin). If herpes reaches a gangrenous form, antibiotics and Solcoseryl are added to therapy.
Recovery from shingles is usually incomplete - neuralgic symptoms of the disease remain (postherpetic neuralgia). Treatment continues with the same anticonvulsants and analgesics, opioid drugs are added, but antiviral drugs are no longer required. Neurological therapy is aimed primarily at eliminating the pain syndrome.
Antiviral therapy for ophthalmoherpes (in the eyes)
In the treatment of herpetic eye lesions, the same antiviral drugs are used, but in the forms of eye ointments, drops, or for internal use. The clinic actively uses drugs based on 5-iodo-2-deoxyuridine: 
- Keretsid;
- Stoxyl;
- Idukollal;
- Herplex;
- Dendryl;
- Oftan-I'm coming.
Patients are also prescribed other compounds of this group- acyclovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir, sorivudine, vidarabine, TFT, brivudine and foscarnet. Florenal, Riodoxol, Tebrofen can be added to the list of antiviral drugs against eye herpes. Interferon-type drugs include leukocyte interferon, Poludan, Cycloferon, Timalin, Taktivin and Amiksin.
Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus (herpes type 4) and herpetic sore throat
There is no specific treatment regimen for patients with EBV infection; the therapeutic complex is determined according to the individual indications of the patient’s condition. Persons with high fever, severe tonsillitis/sore throat, jaundice, anemia and airway obstruction should be hospitalized. In other cases, treatment can be done at home.
Patients need maintenance therapy with rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (for severe pain, 2% lidocaine or xylocaine is added to the solution). It is important to ensure you drink plenty of fluids.
First of all, the prescription of antiviral drugs is required: 
- Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Valaciclovir and other acyclic nucleoside analogues;
- Cidofovir, Adefovir and other acyclic nucleotide analogues;
- Foscavir, Foscarnet, phosphonoacetylic acid and other pyrophosphate analogues.
Additionally, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Tylenol, acetaminophen, paracetamol;
- antibacterial(in the presence of concomitant infections): selected depending on the sensitivity of the microflora, mainly cephalosporins, macrolides, lincosamides;
- antifungal: fluconazole, metronidazole;
- glucocorticosteroids(for severe disease): orazone, dexamethasone, prednisolone, deltazone, hydrocortisone;
- immunoglobulins and immunomodulators: Alphaglobin, Gammar-P, Sandoglobulin, Intron A, Reaferon, Cycloferon, Viferon.
Cytomegalovirus infection (herpes 5): treatment for adults and children
There is also no correct separate treatment regimen for CMV. Symptoms of the acute phase of the disease are treated with the same antiviral drugs as other herpes viruses. More often, however, Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir are used.
Additionally, immunomodulatory therapy is required, including vitamin support and stimulation of the immune system with interferons and globulins. Cycloferon, Viferon and other similar drugs are prescribed, the course of treatment is several weeks. The patient also needs to improve their lifestyle: change their diet, exercise, take enough fluids, and walk in the fresh air.
Often the acute form “attaches” other diseases that require adequate treatment with antibiotics. This therapy is concomitant and does not reduce the severity of the symptoms of the herpes virus itself, so it is used only as an addition to the complex of antiviral and immunomodulatory agents.
Features of herpes treatment 6
When a child or adult exhibits symptoms of this form of herpes, a typical antiviral therapy regimen is prescribed. Comprehensive treatment usually includes Ganciclovir, the most effective drug against HHV-6 from the group of acyclic nucleoside analogues, as well as Foscarnet and Cidofovir. For children under 12 years of age, only the latter is allowed to be used.
Acyclovir is ineffective against herpes type 6. Adefovir and Lubocavir are sometimes used, and experimental vaccines are being developed. To relieve the symptoms of infection, use antipyretics (Paracetamol or Ibuprofen), drink a lot of water and diuretic herbal teas.
Herpetic rashes in children practically do not itch, so external antibacterial ointments are not required to prevent additional infection. However, care should be taken to take vitamin complexes in order to strengthen the body’s natural defenses and accelerate the production of a sufficient amount of antibodies against HHV-6.
In adulthood, the infection manifests itself with severe immunodeficiency, so suppression of symptoms should be carried out primarily with interferon immunomodulators. However, such treatment is prohibited if the disease manifests itself after an organ transplant, since during this period a weak immune system is necessary to prevent tissue rejection.
How are herpes types 7 and 8 treated?
These two types of herpes have been studied so little that there are no definite treatment regimens. In individual therapeutic complexes, classical antiherpetic drugs are used in combination with medications aimed at eliminating the symptoms of concomitant diseases.
Thus, in the presence of oncological diseases from herpes type 8, treatment with interferons is contraindicated, however, chemotherapeutic antitumor drugs can be added to the complex. Surgery and radiation therapy may be required. If the mental state of a patient is affected by herpesvirus-7, adequate psychotherapy is necessary with the possible use of antidepressants and psychoanalysis sessions.
Treatment of herpes of internal organs
Herpes on internal organs is treated according to the classical scheme, but the drugs are prescribed orally - there is no place to use them locally.
The most commonly prescribed antiviral drugs are:
- Acyclovir;
- Famvir;
- Valtrex;
- Ganciclovir;
- Cytarabine et al.
They are used in the form of suppositories, tablets and injections. Immunomodulators are also used in the same forms:
- Viferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Isoprinosine;
- Lycopid.
Attention! It is highly not recommended to self-prescribe medications that affect the immune system. This should be done by the attending physician or immunologist.
In addition to classical therapy, auxiliary drugs are prescribed: for the liver - hepetoprotectors, for severe inflammatory processes - anti-inflammatory drugs, for those with concomitant fungal or bacterial diseases - antimycotics and antibiotics.
Folk remedies for the treatment of herpes
Every year they deserve more and more popularity in medical circles. In case of minor damage, treatment with natural herbal preparations can give an excellent result; in case of extensive spread of the disease, it is recommended to combine them with drug treatment.
Domestic doctor L.V. Pogorelskaya offers the following treatment regimen for recurrent herpes:
- Decoction from a collection of herbs. Mix lemon balm, thyme, raspberry leaves, wormwood, juniper and oregano in a ratio of 4:3:4:2:3:3. Brew 1 tsp daily for an hour. in a glass of boiling water and drink in two doses for 14-28 days.
- Alpizarin in the amount of 0.1 g three times a day for 21 days.
- Twice before lunch, 40 drops of Eleutherococcus extract before meals.
- Alpizarin or helepin ointment for rashes three times a day for 14-28 days.
Infusions, decoctions and compresses from the following plants also help against herpes: Amur velvet, pinnate Kalanchoe, Canadian desmodium, medicinal calendula, warty birch, yellowing kopek, common juniper and pine, kopek lespesda, buckthorn, cotton, twig-shaped eucalyptus and western thuja
In total, there are 8 types of herpes infection in humans, and the symptoms of different viruses are for the most part not similar to each other. The range of symptoms of herpes varies from simple - so-called. “colds” - to psychiatric and oncological diseases.
Symptoms of herpes type 1 - the virus that causes the “cold”
Herpes type 1 is the simplest and most quickly suppressed virus. Basically, the infection is stored in the nerve endings of the cervical spine in a dormant state, but with a decrease in immunity or under the influence of stress, it becomes more active and manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- First, the skin turns red and there is a burning sensation and itching.
- After 6-48 hours, one or more vesicles - bubbles containing a clear liquid inside - form on the inflamed area.
- If left untreated or scratched, the vesicles burst, spreading infected fluid around and causing the affected area of skin to enlarge.
- In place of the burst bubbles, a wound appears, which over time becomes covered with a crust.
- With the support of the immune system, the disease gradually “falls asleep” again - goes into a latent state. Without support, large areas are damaged and wounds do not heal normally.
If a person has symptoms, they can infect others through contact. Most often, herpes 1 is localized on the face and mucous membranes of the mouth. It can affect the lips, cheeks, chin, mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, mouth or larynx. Sometimes the infection gets to the skin of the torso, causing the disease to spread to the body.
Symptoms of herpes type 2 - the genital form of the virus

The symptoms of herpes type 2 are similar to type 1, but the localization of the blisters is different. In a dormant state, this virus is located in the nerve endings of the sacral clutch. Vesicles are formed mainly in the groin area, on the thighs, buttocks, anus and genitals.
In addition to the usual symptoms, deterioration in mood and mental state, loss of appetite, and signs of intoxication are observed. Possible enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin area. In women, vesicles can appear inside the vagina and on the cervix, in men - in the urethra.
Attention! Most often, relapses of the second occur in autumn or winter, when the prevalence of other viral diseases is high. On average, with the support of the immune system, symptoms disappear within 2-3 weeks.
Symptoms of herpes type 3 - the Zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles
The herpes zoster virus is usually infected in childhood, and it manifests itself in the form of ordinary chickenpox. When a child recovers, an infection remains in the endings of his trigeminal nerve forever, although it does not manifest itself under normal living conditions.
When immunity falls, a person gets sick with an acute respiratory infection or simply lives unhealthy, the symptoms of the disease appear again. Most often, the lesion occurs in people over 50 years of age, while recurrence of this type of herpes is the rarest (observed in only 5% of patients).
Repeated disease is called herpes zoster and has the following symptoms:

As a rule, the disease goes away after 1-3 weeks. After the rash appears, the pain is replaced by itching. In rare cases, the pain does not go away, it subsides, but appears throughout life.
Symptoms of herpes type 4 - mononucleosis from the Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr virus causes a disease called infectious mononucleosis. The disease is quite dangerous and requires treatment to prevent undesirable consequences - deep genital ulcers in women, destruction of blood cells, oncological pathologies (types of lymphomas), autoimmune diseases and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Typically, when infected with herpes virus type 4, the following symptoms are observed after 7-14 days:

The patient is often thirsty and has a fever for about a week. Lymph nodes shrink within a month, blood changes can last up to 6 months. Correct treatment leads to recovery and lifelong immunity; its absence leads to a chronic form of the disease:
- Erased– muscle pain, joint aches, frequent low-grade fever, fatigue.
- Atypical– frequent relapses of infectious diseases (acute respiratory infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary system).
- Active– ordinary mononucleosis symptoms are complicated by herpetic rashes, fungal or bacterial infections. Possible damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, dyspepsia.
- Generalized– severe damage to the central nervous system, including meningitis, encephalitis, radiculoneuritis. Increased risk of myocarditis, hepatitis or pneumonitis.
Symptoms of chronic Epstein-Barr infection manifest themselves in waves - the number and intensity of symptoms gradually increase and also gradually decrease depending on the state of the immune system.
Symptoms of herpes type 5 - cytomegalovirus infection (CMV)
 Cytomegalovirus does not appear immediately after infection; the carrier of the infection often does not even know about his own situation. With a strong immune system, the disease may never enter the active phase, but simply “sleep” in the body asymptomatically until the end of life (in 90% of cases this happens). However, the person will continue to transmit the virus to other people.
Cytomegalovirus does not appear immediately after infection; the carrier of the infection often does not even know about his own situation. With a strong immune system, the disease may never enter the active phase, but simply “sleep” in the body asymptomatically until the end of life (in 90% of cases this happens). However, the person will continue to transmit the virus to other people.
Patients with symptoms of CMV most often complain of signs of acute respiratory infections and mononucleosis (fever, fatigue, headaches, chills) that occur 20-60 days after infection. The duration of the disease is generally 4-6 weeks. If the activity of the virus is caused by immunodeficiency, pleurisy, pneumonia, arthritis, encephalitis or myocarditis may occur. Autonomic disorders are observed.
In its generalized form, CMV causes damage to the entire body - inflammation of the tissues of internal organs, eyes, brain, as well as paralysis. In men, there may be damage to the tissues of the testicles and urethra; in women, there may be inflammation or erosion on the cervix, uterus, vagina or ovaries, and blue-white discharge.
Symptoms of poorly studied forms of herpes virus types 6, 7 and 8
 Herpes type 6 lives in microphages and lymphocytes. Among all adults, about 50% are carriers of this infection, infecting the rest through blood and saliva, as well as by airborne droplets.
Herpes type 6 lives in microphages and lymphocytes. Among all adults, about 50% are carriers of this infection, infecting the rest through blood and saliva, as well as by airborne droplets.
Symptoms of the disease are itching and mucous membranes, fever, ulcers or spots on the skin of the back, chest or abdomen (exanthema), mononucleosis syndrome, asthenia. With immunodeficiency, encephalitis is possible.
The infection often occurs in young children (3 months - 4 years). It is manifested by sudden exanthema and fever (up to 40° C), signs of intoxication. Symptoms last up to 4 days, then they are replaced by a rash that goes away within 3 days. Sometimes after a fever there is no rash, but there may be cramps due to too high a temperature. Upon reaching 5 years of age, most children develop immunity against herpes type 6; relapse can only be caused by particularly severe immunodeficiency.
Herpes type 7 promotes the activation of type 6 virus and increases the risk of developing chronic fatigue syndrome. This syndrome is the main manifestation of a viral infection.
It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- general loss of strength;
- constant fatigue and lack of tone;
- bad mood, anxiety and psycho-emotional overload;
- loss of ability to work and concentrate;
- lack of positive changes even after a long rest;
- memory disorders;
- headaches and tearfulness;
- sleep disturbances and lack of sleep even during prolonged sleep;
- signs of depression;
- slight increase in temperature for a long time (up to six months);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Worth noticing! When making a diagnosis based on these symptoms, a specialist must differentiate the disease from psychiatric/nervous pathologies, HIV infection, cancer, anemia and thyroid dysfunction.
Herpes type 8 least studied. Its symptoms include the development of other diseases - Kaposi's sarcoma, primary lymphomas, Castleman's disease and multiple myeloma. In this case, the patient develops malignant neoplasms on the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs and lymph nodes, which look like symmetrical plaques or dark red or purple spots. There may also be a bloody cough, severe dyspepsia, and pain when eating.
Symptoms of any type of ocular herpes
Ophthalmoherpes develops on the retina, eyelids or mucous membranes of the eyes. Relapses can occur 3-5 times a year - this is one of the most common forms of herpes infection, mainly caused by types 1 and 3 of the virus.
The symptoms of ocular herpes are similar to allergies or from a bacterial infection; herpetic vesicles appear on the eyes, and the following signs are also observed:
- the eyeballs and eyelids turn red;
- there is pain and a feeling as if there is a foreign body in the eye;
- in good lighting there is discomfort;
- visual acuity decreases and becomes “foggy”;
- sparks or flashes are visible before the eyes;
- the shape and size of objects seem incorrect or double;
- twilight vision is significantly reduced;
- blepharospasms - the eyelids contract convulsively.
Patients often complain of severe pain in the orbit and above the eyebrow. The field of view becomes narrower, and there may be a blind spot in the center. Moving your eyes is difficult and painful. All this may be accompanied by nausea, low-grade fever and headaches.
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat
Adults and children who have the herpes virus in their bodies often experience a sore throat caused by this infection. Its onset is usually abrupt and extremely acute:
- The temperature rises to 40-41° C, as with pneumonia.
- Severe pain occurs in the throat, it is very difficult to swallow, the discomfort lasts for at least 3 days.
- The mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes swollen, visible with white bubbles on the tonsils and palate.
- Over time, the vesicles merge with each other, forming a dense white “patina” covered with a film and surrounded by redness.
- Suppuration of the rash lasts up to 3 weeks, during which herpes can spread to the skin of the face.
The incubation period of herpetic sore throat lasts 1-2 weeks. Sometimes the patient recovers easily - intoxication goes away before the vesicles appear by 6 days, treatment is greatly simplified. Sometimes complications arise - herpetic rhinitis, chronic tonsillitis, otitis media, myocarditis, encephalitis, etc.
Symptoms of herpes on internal organs
Internal herpes manifests itself with the usual symptoms of other diseases, since it causes them. No visible signs of the herpes virus are usually observed; the type of infection can only be determined by clinical studies and laboratory tests.
As a rule, with ulcers in the esophagus due to herpes rashes, a person suffers from pain behind the sternum and when swallowing. A doctor can detect ulcers through an endoscopic examination. Pneumonia, bronchitis and tracheitis with characteristic symptoms (fever, cough, shortness of breath) are detected through special tests for type 1 herpes; often these diseases are accompanied by a fungal or bacterial infection.
If the patient has herpetic hepatitis, the symptoms will be similar to those usual for hepatitis B or C - jaundice, change in the color of urine and stool, fever. To identify the cause of the disease, the patient is prescribed a test for herpes viruses. AND So for any other damage to internal organs, this virus does not have any specific symptoms.
Symptoms of postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is an echo of the disease after recovery from type 3 herpes. After a relapse of the Zoster virus, the patient remains with a feeling of discomfort and symptoms of infection, although the disease has already “subsided.” Acute symptoms also disappear completely. So, with such neuralgia there are:
- residual drying and flaking crusts in places where there was;
- throbbing pain or tingling in this area, sometimes extremely strong;
- itching between painful attacks, causing irritation, which only intensifies subsequent pain;
- numbness of the skin areas at the site of the former lichen or an extremely strong reaction to external irritants;
- muscle weakness and paralytic conditions (more often in old age).
Typically, postherpetic neuralgia lasts 2-3 weeks, but sometimes it remains for 2 months or even a year. Some symptoms last even longer, such as muscle weakness or extreme skin reactions. All this interferes with the normal lifestyle of people who have experienced reactivation of the chickenpox virus.
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?