Chitin. What is chitin, application, interesting facts. Chitin and chitosan. What it is? Products containing chitin
As well as many other nutritional components. But what is especially interesting about the composition of mushrooms is their unique texture, which has no analogues among other representatives of nature. And the substance chitin is responsible for the “fleshy” structure of mushrooms. Yes, that same chitin, known from biology lessons, which is found in the shells of crustaceans and insects. It is thanks to their unique chemical structure that mushrooms are classified as a separate kingdom. But what role does nature assign to chitin, other than creating shells and giving mushrooms uniqueness?
What is chitin
Chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer on the planet.
According to some estimates, nature produces exactly the same amount of this substance as cellulose every year. It, from a chemical point of view, is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide with a straight chain. Under natural conditions, it is part of complex organic and inorganic compounds.
Chitin as a natural biopolymer is found mainly in the exoskeleton (outer part of the skeleton) of shrimp, crabs, lobsters, and crayfish. Also found in mushrooms, yeast, some bacteria and butterfly wings. In the human body it is necessary for the formation of hair and nails, and in birds - plumage. Pure chitin is more fragile than when combined with other substances. Insect exoskeletons are a combination of chitin and. Crustacean shells are typically composed of chitin and calcium carbonate.
Chitin has many commercial analogues, including food and pharmaceutical products. They are commonly used as food thickeners and stabilizers and also help create an edible film on foods.
In food products, chitin is presented in a modified and more bioavailable form of chitosan. Chitosan is a derivative of chitin, formed as a result of exposure of the substance to temperature and alkali. As scientists say, this substance is similar in composition to the tissues of the human body. For industrial purposes, it is obtained from crustacean shells.
History of discovery
The discovery of chitin dates back to 1811, when Professor Henry Braconneau first discovered it in mushrooms. The scientist began to study with particular interest an unknown substance that was not susceptible to the influence of sulfuric acid. Then (in 1823) this substance was discovered in the wings of cockchafers and called it “chitin”, which in Greek means “clothing, shell”. This material was structurally similar to cellulose, but was much stronger. The structure of chitin was first determined by the Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann. And in 1859, the scientific world learned about chitosan. After chemists “purified” chitin from calcium and proteins. This substance, as it turns out, has a beneficial effect on almost all organs and systems of the human body.
Over the next century, interest in chitin faded a little, and only in the 1930s it grew with renewed vigor. And in the 1970s, the production of a substance from mollusk shells began.
Chitin in nature
As already noted, chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton (outer part of the skeleton) of many arthropods, such as insects, spiders, and crustaceans. Exoskeletons made of this strong and hard substance protect the sensitive and soft tissues of animals lacking internal skeletons.
Chitin is similar in structure to cellulose. And the functions of these two substances are also similar. Just as cellulose gives strength to plants, chitin strengthens animal tissue. However, it does not perform this function independently. Proteins come to his aid, including elastic resilin. The strength of the exoskeleton depends on the concentration of certain proteins: whether it will be hard, like a beetle’s shell, or soft and flexible, like the joints of a crab. Chitin can also be combined with non-protein substances such as calcium carbonate. In this case, crustacean shells are formed.
Animals that wear a "skeleton" on the outside are relatively inflexible due to the rigidity of the armor. Arthropods can bend limbs or segments of their body only at the joints where the exoskeleton is thinner. Therefore, it is important for them that the exoskeleton matches the anatomy. In addition to its role as a hard shell, chitin prevents the bodies of insects and arthropods from drying out and dehydrating.
But animals grow, which means that from time to time they need to adjust the “size” of the armor. But since the chitinous structure cannot grow with the animals, they shed the old shell and begin to secrete a new exoskeleton with the glands of the epidermis. And while the new armor hardens (and this will take a little time), the animals become extremely vulnerable.
Meanwhile, nature has endowed only small animals with shells made of chitin; such armor would not have protected larger specimens of fauna. It would not be suitable for terrestrial invertebrates either, since chitin becomes thicker and heavier over time, which means that animals would not be able to move under the weight of this protective armor.
Biological role in the body
Once in the human body, chitin, which has the ability to bind dietary lipids, reduces the activity of fat absorption in the intestine. As a result, the level of triglycerides in the body decreases. On the other hand, chitosan can influence calcium metabolism and accelerate its excretion in urine. Also, this substance can significantly reduce the level, but have a positive effect on the mineral composition of bone tissue.
In the body, chitin-chitosan plays the role of an antibacterial substance.
For this reason, it is included in some wound care products. Meanwhile, long-term use of chitin can disrupt the healthy microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and activate the growth of pathogenic microflora.  Functions of chitin and chitosan:
Functions of chitin and chitosan:
- baby food component;
- useful food supplement;
- reduces cholesterol;
- source of fiber;
- promotes the proliferation of bifidobacteria;
- helps with lactose intolerance;
- important for losing excess weight;
- antiulcer component;
- necessary for bone strength;
- has a beneficial effect on eye health;
- relieves gum disease;
- antitumor agent;
- component of cosmetics;
- component of many medical products;
- flavoring, preservative;
- used for the production of textiles and paper;
- seed treatment agent;
- important for cleansing.
What is it needed for
There is a number of scientific evidence that indicate the effect of chitin in lowering cholesterol concentrations. This property is especially noticeable in the combination of chitosan and chromium. This effect was first proven in rats by Japanese scientists in 1980. Researchers then discovered that the cholesterol reduction was due to chitin's ability to bind lipids to cells, preventing them from being absorbed by the body. Then Norwegian scientists announced the results of their experience: in order to reduce cholesterol levels by almost 25 percent, you need to take chitosan in addition to your diet for 8 weeks.
 The positive effects of chitin are also felt by the kidneys. This substance is especially important for maintaining optimal well-being in people undergoing hemodialysis procedures.
The positive effects of chitin are also felt by the kidneys. This substance is especially important for maintaining optimal well-being in people undergoing hemodialysis procedures.
The effect on the skin is to activate the ability to quickly heal wounds.
It affects the body according to the principle of soluble fiber. This means it improves the functioning of the digestive organs, speeds up the passage of food through the intestinal tract, and improves intestinal motility.
Improves the structure of hair, nails and skin.
Beneficial features
Numerous studies have shown that chitin and its derivatives are non-toxic, which means they can be safely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. According to some data, about 2 million people take chitin-based dietary supplements in the USA and Japan alone. And their number is only growing. By the way, Japanese doctors recommend that patients take chitin as a remedy against allergies, high blood pressure, and arthritis.
In addition, it is known that chitin completely decomposes under the influence of microorganisms, and therefore is an environmentally friendly substance.
Chitin and...
…digestion
Introducing chitin into a regular diet is the best thing a person can do for their health. That's what some researchers say, at least. After all, consuming this substance will not only help you lose excess weight, but will also lower blood pressure, prevent the occurrence of ulcers in the digestive system, and facilitate the digestion of food.
 Several studies conducted in Japan and Europe have shown that chitin and its derivatives promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines. Scientists also have reason to believe that chitin not only improves the functioning of the colon (eliminating irritable bowel syndrome), but also prevents the formation of malignant tumors and polyps in the tissues.
Several studies conducted in Japan and Europe have shown that chitin and its derivatives promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines. Scientists also have reason to believe that chitin not only improves the functioning of the colon (eliminating irritable bowel syndrome), but also prevents the formation of malignant tumors and polyps in the tissues.
It has been proven that this unique substance protects against gastritis, stops diarrhea, relieves constipation, and removes toxins.
…lactose
This may be surprising, but the research results convince us of the truth of this assumption. Chitin alleviates lactose intolerance. The results of the experiments surprised even scientists. It turned out that against the background of chitin, even food consisting of 70 percent does not cause symptoms of indigestion.
…excess weight
Today there is some evidence that chitin is a fat blocker. When a person consumes this, it binds to lipids that enter the body with food. And being an insoluble (non-digestible) component, the associated component is automatically endowed with the same ability. As a result, it turns out that this strange “duet” is passing through in transit. Fat absorption does not occur. It has been experimentally established that for weight loss it is necessary to consume 2.4 g of chitosan per day.
...wound healing
Chitin is one of the most important substances for patients with burn wounds. It has remarkable compatibility with living tissue. Scientists have noticed that thanks to this substance, wounds heal faster. It turned out that the acidic mixture of chitin accelerates the healing of injuries after burns of varying degrees. But the study of this ability of chitin continues.
…mineralization
This polysaccharide plays a crucial role in the mineralization of various tissues. And the main example of this is mollusk shells. Researchers, having studied this ability of chitin, have high hopes for this substance as a component for the restoration of bone tissue.
“Did you order locusts for lunch?”
 Chitosan burst into the food industry in the 1990s. When advertising a new dietary supplement, manufacturers repeated that it helps reduce weight and cholesterol, prevents osteoporosis, hypertension, and stomach ulcers.
Chitosan burst into the food industry in the 1990s. When advertising a new dietary supplement, manufacturers repeated that it helps reduce weight and cholesterol, prevents osteoporosis, hypertension, and stomach ulcers.
But, of course, the use of chitin in food did not begin at the end of the last century. This tradition is at least several thousand years old. Residents of the Middle East and Africa have consumed locusts since time immemorial as a healthy and nutritious dish. There are references to insects as food on the pages of the Old Testament, in the records of the ancient Greek historian Herodotus, in the ancient Roman annals, in the books of Islamists and in the legends of the Aztecs.
Among some African peoples, dried locusts with milk were considered a traditional dish. In the East there was a tradition of presenting insects to the husband as the highest gift. In Sudan, termites were considered a delicacy, and boiled ants were the highlight of Aztec dinner parties.
There are now different opinions regarding such gastronomic tastes. But in many Eastern countries they still sell fried locusts, in Mexico they cook grasshoppers and bedbugs, Filipinos enjoy various dishes made from crickets, and in Thailand tourists are willing to be offered specific delicacies made from beetle larvae, crickets, caterpillars and dragonfly dishes.
Are grasshoppers an alternative to meat?
In the modern world, beetle eating is treated differently. Some people get hot just from the thought that someone somewhere is clicking cockroaches instead of seeds. Others decide to taste gastronomic exoticism while traveling around the world. And for still others, grasshoppers and all the chitinous brethren serve as ordinary food, which remains held in high esteem for hundreds of years.
This fact could not but interest researchers. They began to study what benefits a person can get from consuming insects. As one might expect, scientists have determined that all this “buzzing exotica” supplies humans with chitin, which is undoubtedly a plus.
In addition, during studies of the chemical composition of insects, it turned out that some contain almost as much protein as beef meat. For example, 100 g of grasshoppers contain 20.5 g of protein, which is only 2 g less than beef. Dung beetles have about 17 grams of protein, termites have 14 grams, and bees have about 13 grams of protein. And everything would be fine, but collecting 100 grams of insects is much harder than buying a 100 gram piece of meat.
Be that as it may, at the end of the 19th century, the British Vincent Holt founded a new movement for gourmets and called it entomophagy. Adherents of this movement, instead of meat-eating or vegetarianism, “professed” eating insects. Proponents of this diet considered their chitin-rich diet almost medicinal. And the dishes from their menu are healthier and cleaner than animal products.
How to get the most chitin from food
Shrimp belongs to the list of foods with the maximum chitin content. But if you really want to get the maximum substance from this product, then preference should be given not to the royal ones, but to smaller specimens. Their shells are easier to chew, and the chitin from them is more easily absorbed by the body. If you take fish as a source of chitin, then it must be cooked exclusively with scales. Well, don’t forget about mushrooms, from which you can prepare dozens of dishes. And the best part is that you don’t have to chew on anyone’s shells or scales.
Pharmaceutical analogue
 Fried grasshoppers, cockroaches or dung beetles are, of course, not a unique source of chitin. A modern person can easily replenish the body’s reserves of the substance by avoiding such exotic cuisine. It’s not for nothing that researchers have been learning to isolate this useful component from natural sources for decades.
Fried grasshoppers, cockroaches or dung beetles are, of course, not a unique source of chitin. A modern person can easily replenish the body’s reserves of the substance by avoiding such exotic cuisine. It’s not for nothing that researchers have been learning to isolate this useful component from natural sources for decades.
In the Soviet Union, for example, a medicine containing chitin appeared in the second half of the twentieth century. True, at that time this development was kept classified as “Secret”. Soviet scientists, after a series of experiments on mice, dogs and monkeys, proved the effectiveness of chitin in treating radiation. A few years later, the effectiveness of the drug was tested in humans.
Then it turned out that, in addition to protection from radio radiation, this substance is effective against allergies, cancer, intestinal dysfunction and hypertension. Today, research continues. And not so long ago, scientists were able to obtain chitosan from bees. This event served as a new impetus for the development of the science of chitinology.
Consumption standards
A safe dose of chitin is considered to be a daily portion not exceeding 3 g. Otherwise, instead of improving motility, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract may be impaired.
Meanwhile, more active consumption of this polysaccharide is allowed for people with excess weight and high cholesterol. It is also worth paying attention to the maximum allowed daily allowances of chitin for fatty liver degeneration, impaired metabolism, diabetes mellitus and allergic conditions. In addition, people with diabetes, frequent constipation, intoxication, and also after skin transplantation feel an increased need for chitin.
On the contrary, it is not advisable for people with dysbacteriosis, flatulence, gastritis, pancreatitis, or inflammation in the digestive organs to become overly fond of mushrooms and crustaceans.
Side effects
Research confirms that chitin has an extremely low level of toxicity. Side effects may occur in people with shellfish allergies. This usually manifests itself in the form of constipation and flatulence. Excessive consumption of chitosan complicates the functioning of the digestive system, even to the point of complete blockage.
How to recognize a deficiency
 Elevated cholesterol levels are one of the symptoms of chitin deficiency. Impaired kidney function may also indicate a lack of substances from mollusk shells. And even pediculosis (lice), as some researchers say, also appears when the body lacks chitin.
Elevated cholesterol levels are one of the symptoms of chitin deficiency. Impaired kidney function may also indicate a lack of substances from mollusk shells. And even pediculosis (lice), as some researchers say, also appears when the body lacks chitin.
Other symptoms include:
- physical weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- obesity;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent allergies;
- intestinal disorders;
- joint pain;
- excess waste.
What are the benefits of old crabs?
Plants serve as a source of cellulose for humans, which is, so to speak, a natural analogue of plastic. Many years ago, scientists learned to make many things from this material, including plastic and viscose.
But some animals can also produce natural “plastic.” And in the world of fauna it is chitin. For many years, crab meat was used in the food industry, and the shells of these crustaceans were thrown away. Several thousand tons annually. And all because scientists could not figure out how to extract chitin from these shells. It was only in 1975 that chemists were able for the first time to isolate the necessary substance from the armor and process it into the desired form. This is how a surgical thread appeared, which does not cause allergies, promotes rapid healing of wounds, and then dissolves in the body. This discovery served as an incredible impetus in the development of medicine. It's hard to believe, but all this is thanks to crab shells, which until recently were thrown away as garbage.
Areas of use of chitin
 Man has found many ways to use chitin for his own benefit. So in medicine, durable chitin is used to create surgical threads. Because of its ability to quickly absorb water, it has become a part of tampons and sponges. Chitin has strong antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties. For this reason, it often serves as an additional component of medical bandages and dressings.
Man has found many ways to use chitin for his own benefit. So in medicine, durable chitin is used to create surgical threads. Because of its ability to quickly absorb water, it has become a part of tampons and sponges. Chitin has strong antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties. For this reason, it often serves as an additional component of medical bandages and dressings.
In the digestive industry, chitin is included in many products as a thickening component. In addition, the substance is used to purify water from fats, heavy metal salts, toxins, and as a component of pet food. It is also included in many cosmetics and even serves as a component for making underwear. Chitin is used in biomedicine, microbiology, and agriculture. To combat mites, beekeepers use apizan, a product created on the basis of low molecular weight chitosan.
Chitin in cosmetology
Recently, chitin-based preparations have been gaining popularity among the range of cosmetic products. Modern shampoos, conditioners and hair styling products, toothpastes, creams and gels quite often contain this useful polysaccharide. The extract obtained from crustacean shells restores elasticity to the skin, strengthens nails, and covers hair with a protective film. If we talk about hair, then thanks to the chitin “coating” it is easier to comb, acquires a healthy shine, does not become electrified, and looks more voluminous. And yet they retain the ability to breathe.
New generation anti-aging cosmetics contain a chitin derivative – chitosan. It smooths out wrinkles, refreshes skin color, and improves blood circulation. The same substance is included in anti-obesity drugs, as it helps remove excess fluid, fats and toxins from body tissues.
Chitin recipes
 Traditional healers also never ignored chitin. In particular, bees and their metabolic products have always been valued in Rus'. But now - about bees, as a source of useful chitin. The preparation of many medicinal products is based on dead bees (dead insects). They serve as a source of chitin. Most often, water and alcohol tinctures are prepared from dead bees. These remedies in folk medicine were used to quickly heal wounds, prevent the formation of scars, and also as a hemostatic, analgesic and general strengthening agent.
Traditional healers also never ignored chitin. In particular, bees and their metabolic products have always been valued in Rus'. But now - about bees, as a source of useful chitin. The preparation of many medicinal products is based on dead bees (dead insects). They serve as a source of chitin. Most often, water and alcohol tinctures are prepared from dead bees. These remedies in folk medicine were used to quickly heal wounds, prevent the formation of scars, and also as a hemostatic, analgesic and general strengthening agent.
Alcohol tincture to strengthen the body
Ingredients:
- dead bees – 1 tablespoon;
- alcohol 40 percent.
How to cook
Grind the dead bees (you can use a coffee grinder) and add alcohol. Leave the mixture for 21 days in a dark place. During this time, shake the mixture regularly (at least once a day). Store in a tightly closed container in a dark place.
The product is taken to strengthen the immune system and cleanse the body.
Water infusion for weight loss
Ingredients:
- dead bees – 2 tablespoons;
- boiling water – 500 ml.
How to cook
Pour boiling water over the dead meat, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 2 hours. Strain, cool. Take 1 tablespoon three times a day before meals (half an hour before).
The product regulates hormonal balance, accelerates fat burning, and promotes weight loss.
Powder against tuberculosis (from mole cricket)
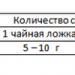
Two days before preparing the recipe, they stop feeding the mole cricket. This technique allows you to cleanse the insect's digestive tract. Then disinfect with alcohol. And only after that they start drying. It is best to dry it in the oven at low temperature. Grind dried insects in a coffee grinder. Take, mixed with honey, 2-3 times a day. Single dosage – 1 teaspoon.
Chitin has remained an unsolved substance for researchers for a long time. But every year scientists are learning more and more about this unique polysaccharide. And the more discoveries they make, the more they admire the properties of chitin. And not so long ago, in scientific circles they started talking about the potential possibility of creating even more products from chitin. How realistic these ideas are remains to be seen.
Sources
If you think that locusts are eaten only in some countries in Africa and the Middle East, then you are deeply mistaken. In fact, you and I regularly consume insect dishes. And it's very useful. For several decades now, chitin and its derivatives have been added to food, medicine, cosmetics, and even bandages and surgical threads (suture material). The Japanese were the first to do this, followed by Europeans and Americans. Now we have also become familiar with chitin.
Anyone who didn’t skip biology classes at school remembers that chitin is the substance from which the shell of cancer is made. However, chitin is not only found in crayfish. It is part of the exoskeleton of all arthropods: crustaceans (crabs, shrimp, lobsters) and insects (beetles, butterflies). In addition, chitin is found in the cell wall of yeast, algae and fungi.
From all diseases
Chitin additives are added to food to improve its appearance, enhance taste and aroma, or as a preservative. Some people prefer insects in the form of dietary supplements.
Benefits of such a diet:
- protects the body from radioactive radiation;
- suppresses the growth of cancer cells;
- prevents the development of heart attacks and strokes (enhances the effect of blood thinning drugs);
- increases immunity ;
- regulates blood cholesterol levels (helps with atherosclerosis and obesity);
- improves digestion (reduces the acidity of gastric juice, stimulates the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria);
- fights inflammatory processes;
- accelerates tissue regeneration (restoration) processes.
In living nature, chitin is found so often that in terms of prevalence it occupies an honorable second place among organic substances (after cellulose). Some scientists even believe that in the very near future humanity will completely switch to a chitin diet. Thus, North Carolina polymer chemistry professor Sam Hudson recently said that modern researchers “stand on the threshold of a brave new world, as infinite as the number of products that can be obtained from chitin.”
From the history
And it all started with the fact that back in 1811, the director of the Botanical Garden in Nancy (France), Professor Henry Braconneau, began studying the chemical composition of mushrooms. His attention was drawn to a strange substance that sulfuric acid could not dissolve. This was real chitin. It soon became clear that the biopolymer isolated by the French scientist was found not only in mushrooms, but also in the elytra of insects. And in 1823 the substance was given an official name. “Chitin” - from the Greek “chiton” - clothing. In 1859, chemists, having gotten rid of calcium and proteins, obtained a new substance from chitin - chitosan - even more interesting than its predecessor. However, after all the discoveries, no one except narrow specialists was interested in chitin for 100 years.
It was only discovered at the end of the 20th century how beneficial chitin with chitosan is for health. However, people began to eat arthropods along with their chitinous cover a long time ago. Even in the Bible, in the book of Leviticus, “clean” and “unclean” insects are mentioned, that is, those that can or cannot be eaten. For example, locusts and grasshoppers are considered “clean”. John the Baptist ate locusts and wild honey in the desert. The ancient Greek historian Herodotus mentioned Africans who caught locusts, dried them in the sun, doused them with milk and ate them. It is believed that even the ancient Romans did not disdain locusts in honey, and the wives of the founder of Islam Mohammed sent entire trays of locusts as gifts to their spouses.
Boiled ants were served at dinner parties at the court of the Indian ruler Montezuma. The famous zoologist and traveler Alfred Brehm in his book “The Life of Animals” described how the inhabitants of Sudan catch and happily eat termites. Many nations have a gastronomic love for spider bugs that has survived to this day. In some countries in Africa and the Middle East, locusts are sold in shops and bazaars, and dishes made from them are included in the menus of expensive restaurants. There are many ways to prepare crickets in the Philippines. In Thailand, crickets, caterpillars, dragonflies, and beetle larvae are eaten. In Mexico they eat stink bugs and grasshoppers.
Chitin diet
It is curious that the insect diet was invented at the end of the 19th century. In 1885, the English traveler and naturalist Vincent Holt, as a counterweight to vegetarianism and meat-eating, began to call for entomophagy - feeding on insects. Unaware of the healing effects of chitin and chitosan, Holt nevertheless wrote: “Insects as a source of nutrients are much healthier and cleaner, since they themselves feed exclusively on plant foods.”
Although it is difficult to get enough of insects, it is possible. The main thing is to calculate (at least roughly): how many grasshoppers, termites, bees and dung beetles need to be caught so that they weigh 100 grams in total.
Comparative nutritional value in grams per 100 g of product:
- Grasshoppers: proteins - 20.6; fat - 6.1
- Dung beetles: proteins - 17.2; fat - 3.8
- Termites: proteins - 14.2; fat - 2.2
- Bees: proteins - 13.4; fat - 1.4
- Beef: proteins - 23.5; fat - 21.2
Entomophagy is, after all, exotic. Today, in order to experience the healing effect of chitin (chitosan), it is not at all necessary to overcome the disgust of chewing cockroaches and scarabs. You can just go to the store and buy something dietary.
Chitin in our country
The very first drug based on chitin was created in the 1960s in the Soviet Union. It was supposed to protect people from ionizing radiation. All research on the new drug was strictly classified by the military, and its composition was hidden even from doctors. After a series of experiments on mice, dogs and monkeys, it was proven that the drug helps animals survive after a lethal dose of radiation. A little later, scientists found out that chitin drugs also help humans, and also that their properties are not limited only to the radioprotective effect.
Chitin and its derivatives help fight cancer, allergies, hypertension, intestinal diseases, etc. In addition, chitinous inclusions contribute to a longer action of other drugs.
Research on chitin and chitosan continues today. In Russia, this is done by members of the Russian Chitin Society, created in 2000. It included not only scientists involved in the research of chitin and chitosan, but also specialists from other fields of science, representatives of industry, medicine, and agriculture. In the West, the best chitinologists are awarded the Braconno Prize, named after the discoverer of chitin, Braconno. In Russia, a similar award is named after an enthusiast of chitin research, Academician Pavel Shorygin.
Few people remember information about this element from biology lessons. Where is it found in nature? Why does the body need it? The answers to these questions are presented in the article.
Description of the substance
Chitin is a natural compound of nitrogen-containing polysaccharides. In nature, it is found in the skeletons of crustaceans, the wings of insects, the tissues of fungi, as well as in the stems and leaves of plants.
Until recently, chitin was considered a waste material, because it cannot dissolve in various alkalis and in water. However, this element is of great importance for many living beings. It is worth considering that chitin is a substance that is part of the human body. Thanks to it, we develop very strong nails and hair.
Meaning in wildlife
Chitin is the main part of the exoskeleton in many arthropods. This includes crustaceans, spiders and some insects. Since the bodies of such inhabitants of our planet are devoid of internal skeletons, something must protect their internal organs from damage. Therefore, we can say with confidence that chitin performs a protective function.
However, this element does not exist on its own. It is combined with other substances, such as proteins, and this allows it to be either harder or, conversely, more flexible. First of all, the chitinous cover is intended to protect internal organs. But besides this, it also protects the body from drying out and dehydration.
The disadvantage of such a shell is that it cannot increase in size. Therefore, the animal is forced to shed it and wait until a new protective shell is formed. This does not take much time, but the fauna representative at this time becomes defenseless.

Chitin is a substance found in the shells of small animals only. Such a shell will not be able to protect large individuals. It is not suitable for terrestrial invertebrate inhabitants either. Over time, it begins to become heavy and rough, which means it becomes more and more difficult to move in it.
Role in the human body
Chitin is responsible for binding lipids in the human body. This means that the intestines become easier to work with, and the level of cholesterol and other harmful lipids in the body decreases. Digestion is normalized and stomach function improves. This element also stimulates bone mineralization in the human body. However, it should not be taken for a long time, as this can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system and lead to the proliferation of pathogenic and opportunistic flora in the body.
Chitin is a source of fiber and also helps fight excess weight. With its help, you can strengthen the bones of the skeleton, as well as increase the number of bifidobacteria in the body. When exposed to the skin, chitin has an antimicrobial effect and promotes rapid healing of wounds, abrasions and cuts. The element also has a positive effect on nails, skin and hair. Therefore, it is included in many cosmetics and vitamin supplements.
Chitin in mushrooms
Mushrooms are a valuable product for the human body. They contain a lot of useful substances, such as selenium, potassium, zinc, copper, as well as a large amount of B vitamins. However, that’s not all. These products also contain chitin. Mushrooms are considered a unique variety of organisms due to their special fleshy tissue called mycelium. This structure is given to it by chitin, which is part of the mycelium. It is not surprising that mushrooms occupy a special place between animals and plants and fulfill their unique role for the human body.
The chitin in mushrooms will only benefit the body if you consume a moderate amount of this product.

Do not forget that this element is not digested and absorbed in the intestines, although it improves digestion. Chitin in the cell wall of the fungus is fiber for the human body. However, scientists do not recommend eating mushrooms very often. They can be included in the diet only occasionally, no more than once a week. It is not recommended to eat mushrooms for children under 7 years of age.
Role in digestion
Scientists have proven that animal chitin introduced into the diet has a positive effect on the digestive system. This substance can fight excess weight and also reduce blood pressure. When used correctly, it will relieve stomach and intestinal ulcers and ensure easy digestion of food. Eating chitin will relieve constipation, diarrhea, and also remove toxins from the body.
Scientists have proven that eating a moderate amount of chitin will provide an increase in certain groups of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines. By taking this dietary supplement, you reduce the risk of developing malignant tumors and polyps.
Eating insects
As mentioned above, chitin consists of nitrogen-containing polysaccharides. Since ancient times, residents of Africa and the Middle East have eaten large quantities of insects. Moreover, such a dish was not considered a dessert, but was a full meal. This is evidenced by ancient records. For example, some peoples ate locusts with milk. For other peoples, termites or boiled ants were a real delicacy.

However, today you can taste dishes made from insects. Of course, scientists were interested in the eating of insects by the aborigines, so various scientific studies were carried out. Eating insects has been found to be very beneficial for human health. Firstly, the composition of insect cell walls includes chitin, which is already a definite plus. However, this is not all. For example, the body of a grasshopper contains almost the same amount of protein as beef meat. This is why insects are considered complete nutritious foods.
Chitin deficiency
Cellulose and chitin are substances similar in composition and functions. However, the first of them is part of plant cells, and the second is part of the cell wall of arthropods.

The first thing you should pay attention to is the increased level of cholesterol in the body. Another symptom indicating chitin deficiency is improper functioning of the kidneys. However, these are not all the signs. Very often, people who are deficient in this element suffer from decreased appetite, weakness, improper bowel function, sludge in the body, frequent allergic reactions, joint pain and obesity.
If you notice the symptoms listed above, be sure to consult a doctor. If the doctor determines a chitin deficiency, he will select the right diet for you, and also include multivitamin complexes in it.
Scope of use
Chitin is very actively used in many areas of human life. For example, it is used to make strong and reliable ones. It is also capable of quickly absorbing liquids, which is why it is used to make various sponges and tampons. Do not forget that chitin has antibacterial properties. Therefore, it can be used for the manufacture of various dressings.

In addition, chitin has found its use in cosmetology, in the production of animal feed, as well as in agriculture and microbiology.
Chitin is the main structural substance of the cell walls of fungi, as well as the integument of arthropods. It has good waterproof properties and is also an excellent structural component. Man was able to use chitin for his own purposes. What is it and why has it become so popular today?
Molecule structure
Because it is a polymer, it is made up of many individual molecules of glucose isomers. These isomers are called N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine, and due to the unusual beta bond in the composition, they are able to form branched polymer chains.
Chitin is sometimes called chitosan. Its main difference is that it is very similar in structure to the well-known cellulose, which is part of the cell walls of plants. If the latter takes first place in production and isolation from plant tissues, then chitin, in turn, comes second in this ranking. This once again proves the popularity of the substance in industry and cosmetology.
In nature
Plants do not have chitin, since their cell walls already contain another biopolymer - cellulose. On this basis, true plants and algae are distinguished, and the presence of one of the biopolymers is a comparative characteristic of different kingdoms of organisms.

Chitin release
On an industrial scale, chitosan is isolated from crustaceans, although this is a rather expensive business. Therefore, the method for isolating this polymer is constantly being modernized, and as a result, new sources of natural chitin have been found.
Thus, the high reproduction rate of insects has become the main reason why chitin is extracted from bees or house flies. What are these flies of yours, you ask. However, if you look at an industrial scale, the production of chitin from insects has gained momentum, and the output is a sufficient amount. Thus, in Russia, some points for raising bees for the purpose of extracting chitin have already been developed.
Don’t forget about mushrooms, as well as some seaweeds, since the cell walls of these organisms contain chitin, which is isolated in the same way as cellulose in plants. Although the efficiency of such a business leaves much to be desired, it cannot be excluded from the list of possible sources of chitosan.

The value of chitin for humans
What is chitin in biology? This is not only a structural component that prevents water loss, but also a biopolymer with bactericidal properties. This makes it possible to use chitin in the production of bandages, gauze and special bath sponges.
Chitin binds well to fats. If a person takes special medications that contain a certain proportion of chitosan, fats in the intestines bind to the biopolymer and are excreted from the body along with it. As a result, the amount of digestible fat decreases, which reduces the amount of cholesterol in the body. However, chitin can also play a cruel joke on a person if used in excess; it also reduces the content of vitamin E and leads to other unpleasant consequences.
Chitosan has recently been added to cosmetic products as a natural component. Such cosmetics make the skin elastic, nails healthy, and after using shampoos with chitin, hair becomes shiny and healthy.
In Asian countries, as well as in the West, fried grasshoppers, locusts and other arthropods are sold in many markets. Entomophagy has recently become a popular trend among gourmets, thanks to the content of such useful chitin in the integument of small insects and crustaceans.

Doctors have found that chitin helps with wound healing due to its high compatibility with animal tissue. This makes it possible to use the biopolymer in the manufacture of special healing ointments, but the study of such properties of chitosan is still ongoing.
There is a very high nutritional value of such a biopolymer as chitin. What can a handful of small insects provide that is even difficult to chew? The answer will amaze you: 100 g of grasshoppers can provide the body with 20.5 g of protein, when the nutritional value of the usual beef is not much different and is 22.5 g. The only problem is that collecting 100 grams of small grasshoppers is much harder than cutting 100 g of meat cattle
Chitin - what is it? It is a chemical compound belonging to polysaccharides that contains nitrogen. Its full chemical name is poly-N-acetyl-D-glucose-2-amine. But to pronounce it this way is long and cumbersome, so scientists came up with a simple and interesting word - chitin, meaning “shell” or “clothing” in Greek.
Definition
Everyone knows that the shells of crustaceans and insects contain chitin. Why is this biopolymer so popular? In nature, a huge amount of cellulose is produced every year, which is part of almost all plants and, oddly enough, chitin. In addition to marine animals and beetles and moths, this substance is found in the cells of fungi and bacteria. Chitin ensures the growth of hair and nails in humans.
Chitin - what is it? It is a rather fragile substance, so in nature it is found in the form of compounds with proteins and other chemical elements. This polymer has many analogues in the food and pharmaceutical industries. It is used as stabilizers and thickeners. In products, chitin takes the form of chitosan, a substance that is formed under the influence of high temperature and alkali.
History of discovery
How did this polymer come into the human field of vision? Chitin - what is it? People learned about it in 1811 thanks to the work of Professor Henry Braconneau. He was the first to decide on a chemical study of mushrooms. He was intrigued by a substance that did not respond to the rather aggressive effects of strong acids.
Twelve years later, in 1823, a similar substance was discovered in the shells of cockchafers. It was at this point that the polymer got its name. The structure of the material was similar to cellulose, but much stronger. The spatial structure of chitin was discovered by chemist Albert Hofmann. Thirty-five years later, the scientific community learned about chitosan.
For more than half a century, talk about this substance stopped. It seemed that everything had already been clarified, there was nothing more to study on this issue, but in the thirties of the last century, interest in quinine arose again. This was due to the development of the cosmetics industry. Forty years later, science has come up with a way to produce this unique material on an industrial scale.
In nature

In the natural environment, chitin is found at almost every step. What is this valuable substance doing underfoot? The shell of an insect or arthropod, the cell of a fungus and lichen, the wings of butterflies and moths contain chitin. Chitin is part of the cell wall of fungi. It holds their specific shape, makes them soft and elastic.
Thanks to the known strength of this material, small creatures can exist freely, because their soft bodies do not have a skeleton, unlike fish and vertebrates. Chitin protects insects and arthropods from dehydration and drying out.
For greater strength, chitin is combined with proteins such as resilin. The physical properties of the material depend on its concentration: hardness, mobility, flexibility and others. In combination with calcium, chitin forms the shell of mollusks.
If an animal grows out of its “armor”, then the process of changing its shell is observed. For some time, the insect becomes defenseless against external factors. Fortunately, fresh chitin quickly hardens under the influence of air and heat.
Biological role

Chitin is part of the cells of animals and plants that humans eat. Once in the body, this substance binds fats and thus reduces cholesterol levels in the blood. In addition, it affects calcium metabolism and accelerates its excretion, reduces the level of fat-soluble vitamins, especially E.
It is known that chitin also exhibits antibacterial properties, so it is used in antiseptic preparations. This substance is added to baby food for newborns who are lactose intolerant.
Chitin can be used to prevent peptic ulcers, prevent tumors and osteoporosis.
Unfortunately, there are also negative sides. Long-term use of chitin suppresses the reproduction of normal intestinal microflora and stimulates the activity of opportunistic bacteria, causing dysbiosis.
Beneficial features

Chitin in mushrooms is a real gift from nature to man. Eating foods containing this substance helps maintain health. Due to its effect on cholesterol and other lipid fractions, chitin helps reduce weight and blood pressure, prevents the development of stomach ulcers and improves the digestion process. There are studies that say that chitin not only normalizes the functioning of the large intestine, but also has a preventive effect on cells, preventing the growth of tumors and polyps.
Another useful function of the biopolymer is facilitating the digestion of lactose. Even in people with dairy allergies, adding chitin has been proven to produce amazing results.
There is a hypothesis that chitin, in one form or another, binds fat molecules and prevents them from interacting with the cells of the body. All lipids consumed in food pass through the intestinal tube in transit, leaving no consequences. Eating 2.5 grams of chitin per day is known to help with weight loss.
Pharmaceutical analogue

Chitin in the cells of insects or fungi is an excellent cosmetic and medicinal product, but delving into exotic cooking or chewing someone’s shells or scales for the sake of losing weight is not very convenient. Therefore, the pharmaceutical industry is actively trying to establish affordable production of artificially synthesized chitin.
In the last century, the development of a similar medicine was carried out in the USSR, but the research was carried out in closed state laboratories and was not exposed to the general public. Scientists have proven that chitin copes well with radiation sickness. Experiments were carried out on animals, and after some time on humans.
Following radiation, allergies, oncology and hypertension conquered chitin. Research is still ongoing, since the “golden mean” between the cost of production and the quality of the resulting product has not yet been found. Recent discoveries in this area indicate that a method has been found for producing chitosan from bees. This gave a new round of development to cosmetology and medicine.
Norms and side effects

Maybe we should start eating chitin with spoons? The composition of shrimp shells and fish scales does not only have this component, so excessive enthusiasm for seafood will not lead to anything good. Ardent seafood fans forget about helminthiasis and toxin poisoning.
The safe amount of chitin per day should not exceed 3 g. Overweight people can afford to slightly exceed the indicated dosage.
Chronic liver disease, metabolic disorders, diabetes and allergies are successfully treated with chitin, so if you have been diagnosed with one of these, you should reconsider your attitude towards this substance, as it can help maintain health.
Areas of use

Chitin is a fairly popular concept. Man has learned to use any substance for his own benefit. Medicine decided to use it as a basis for surgical material and bandages, as an antiseptic, as an inducer of epithelialization (wound healing) and a means to combat fungal diseases. Chitin sponges and tampons absorb water well and do not deform.
The food industry uses it as a natural thickener. Water purification is not complete without chitin, as it binds fats, heavy metal salts and toxins. Elite pet food also contains this substance.
The cosmetics industry advertises chitin as a universal remedy for maintaining youth and slimness. These include hair care products (shampoos, balms, gels), toothpastes, and face and body creams. Anti-aging cosmetics based on chitosan miraculously transform women - smoothes wrinkles, improves skin color, stimulates blood circulation.
In addition, chitin is used in the production of fabrics for underwear.
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?