Diarrhea after antibiotics: how to treat? We select medications and diet. How to treat diarrhea after taking antibiotics for adults and children Abnormal stool after taking antibiotics
Drug-induced diarrhea is an adverse reaction of the body that occurs as a result of taking certain groups of medications. If you continue to take medications, the patient experiences loose, frequent stools, sometimes accompanied by unpleasant pain and vomiting. In most cases, this condition is caused by antibiotics. In medicine, this type of diarrhea is called antibiotic-associated. In addition to antibiotics, laxatives containing magnesium, antacid medications, medications for arrhythmia and blood pressure, contraceptives, antifungals and others can lead to diarrhea. In childhood, diarrhea occurs due to taking medications with bacteria, enzymes, and intestinal antiseptics.
Causes of diarrhea
Can I have diarrhea after taking antibiotics? Unfortunately, diarrhea after antibiotics is a fairly common occurrence that many patients have experienced. In many instructions for the use of antibiotics, possible adverse reactions include a mandatory item - diarrhea.
This reaction of the body can be explained by the fact that when antibiotics are taken orally in the form of a capsule or tablet, not only pathogenic bacteria are suppressed, but also beneficial ones, on which the quality of intestinal function directly depends. As a result of this negative effect, the intestinal microflora changes rapidly, new strains of bacteria arise, leading to bouts of diarrhea.
In medical language, this side effect of medications is called antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Can I have diarrhea after taking antibiotics? The risk of an adverse reaction in the form of diarrhea increases significantly with:
- use of antibiotics by older people;
- taking antibiotics in the presence of acute and chronic diseases of the digestive system, as well as other somatic pathologies that affect the state of the immune system;
- abuse of antibiotics and exceeding the prescribed dose;
- if you do not comply with the terms of taking the antibiotic or changing it without the doctor’s permission.
Diarrhea may occur on the first day of taking medication. If you find stool of altered consistency, you don’t need to worry right away, since you can restore the normal functioning of the digestive system and get rid of unpleasant symptoms in different ways.
How to help the patient?
What to do - diarrhea after taking an antibiotic? The human intestinal microflora returns to normal over time on its own. But as many people know, during diarrhea, beneficial substances that are responsible for the accelerated restoration of intestinal flora are washed out of the patient’s body along with the liquid. As a result of the described processes, the microflora cannot return to normal for a long time.

Treatment of diarrhea after taking antibiotics in adults and children should be comprehensive. This is the only way to achieve a quick recovery without consequences for the body.
Proper nutrition and special diet
You can eliminate watery diarrhea after taking antibiotics in an adult and restore intestinal function in the first days of diarrhea progression using various porridges of liquid consistency. Semolina, grated buckwheat porridge, rice-based soups and steam omelettes are good for this. Sweet berries and fruits with an astringent effect will bring benefits.
Nutritionists recommend including bananas, baked apples and boiled eggs in your daily diet, which contain a huge amount of useful pectin. It is recommended to replace bread with unsweetened crackers prepared at home.

How to stop diarrhea after taking antibiotics? Experts advise completely eliminating from the diet foods containing fiber, baked goods, milk and its analogues. They can severely irritate the intestines and make diarrhea worse.
Over time, the diet can be expanded by adding steamed meat or fish cutlets, soups with vegetables, crumbly porridges, excluding pearl barley and millet. The intestinal microflora will benefit from yoghurts with a balanced composition, which are consumed every day from the first days of diarrhea.

You can return baked goods only 7 days after your condition improves. Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regime throughout the entire treatment. At this time, you should increase the amount of fluid you drink per day to three liters. Both drinking purified water and sweetened compote with natural juice are suitable for this.
Folk remedies for treatment
How to treat diarrhea after taking antibiotics? A good effect in the treatment of diarrhea can be achieved from traditional medicine. Infusions and products made from medicinal herbs produce a sorbing and astringent effect, thereby restoring the balance of the intestines. The most effective recipes for decoctions and herbal infusions:
- Rice water. To prepare the broth, place the rice in a saucepan, add four glasses of clean water and cook until fully cooked. At the end, the product is filtered, and the finished liquid is consumed every three hours, 150 grams.
- Oak bark, dry calamus leaves. To prepare the product, take 250 milliliters of boiling water and add equal amounts of oak bark and dry calamus leaves. Leave for 45 minutes. The finished infusion is drunk three times a day, 100 ml per day before meals.
- Pomegranate peels. Boil a teaspoon of crushed dry pomegranate peels in a glass of water over low heat. Boil for five minutes. Take 150 ml 15 minutes before meals.
- Herbal infusion. Take 4 tablespoons of plantain, lingonberry leaf, rowan berries, mint, eucalyptus leaves. The mixture is boiled in a liter of water for one minute, filtered, and left for 60 minutes. Take 30 ml seven times a day.
You can restore the body's immune system with infusions of yarrow, nettle, mint, St. John's wort, and cinquefoil. To prepare the healing properties, simply pour a small amount of the selected herb into a glass of hot water, cool to room temperature and use the finished product throughout the day.
If diarrhea goes away without inflammation and does not provoke an increase in body temperature, then folk remedies will help quickly restore intestinal function, returning it to its previous state.
Treatment with medications
If diarrhea begins after taking antibiotics, then medications will help restore the body’s condition. Their use must be accompanied by the supervision of a treating specialist. When seeking help at a clinic, it is important to inform the specialist about taking antibiotics. Only after this will the doctor be able to understand how to further treat diarrhea and how to get rid of acute symptoms.
It is forbidden to start using medications on your own without visiting a doctor and making an accurate diagnosis. Only a specialist will be able to select effective medications to treat the ailment and prevent various complications.
Enterosorbents and probiotics
In pharmacies you can find a huge number of medications that effectively fight diarrhea. According to their composition and principle of action, all drugs can be classified into:
- enterosorbents - products characterized by a sorbing effect;
- probiotics - they contain beneficial bacteria that are so important for the normal functioning of the intestines.
Medicines from the group of enterosorbents retain and remove waste products of bacteria and toxins from the human body. These include activated carbon, Polysorb, Smecta, and Enterosgel suspension. All the drugs described absorb decay products and toxins, quickly cleanse the intestinal microflora and prevent the spread of the infectious process throughout the body.
From the group of antibiotics we can distinguish "Linex", a well-known and frequently taken medication for many patients. It helps to quickly restore the body and eliminate the infection. Particular attention should be paid to the new generation medicine "Rioflora Balance Neo". Unlike Linex, it contains 9 strains of living beneficial bacteria. In addition, it has a healing effect and helps eliminate wounds and ulcers from the intestinal walls that occur during diarrhea.
Without a prescription, each patient can purchase the following medications at the pharmacy to combat diarrhea: “Hilak Forte”, probiotics “Bifiform”, “Bifidumbacterin”.

Loperamide is often prescribed to patients with diarrhea. But a good effect from it can be achieved only for diseases of mild to moderate severity. The drug will not be able to cope with serious disorders. The effect of the medication will be much stronger if you use it together with probiotics.
If an adult has severe diarrhea as a result of taking the antibiotic Loperamide, the pathology can only worsen, since the drug leads to a reduction in intestinal motility and slows down the process of removing toxins from the body, which is dangerous due to serious intoxication.
The course of treatment with probiotics continues for 14 days after the antibiotics have ended.
How to prevent diarrhea?
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of diarrhea when taking antibiotics, so as not to have to treat it in the future? You can take care of the normal functioning of the intestines and stable bowel movements even at the beginning of taking antibacterial agents.
It is important to remember that diarrhea in most cases begins after taking antibiotics such as aminoglycosides and tetracyclines. The wider the spectrum of antibiotic exposure, the higher the risk of developing diarrhea.

In order to significantly reduce the risk of diarrhea, it is important to start using probiotics from the group of synbiotics (for example, Laminolact) together with antibiotics. The bacteria found in such products help microorganisms to normally tolerate the negative effects of antibiotics on the intestinal microflora. At this time, it is recommended to add natural yogurt and low-fat kefir to the daily menu, but get rid of all fried, spicy, salty, smoked foods.
Only comprehensive treatment of diarrhea after taking antibiotics in a child and an adult will help maintain the condition of the intestinal microflora and prevent problems with stool. It is equally important to strictly adhere to the dose of the antibiotic used. If you follow the regimen of taking the drug, you can easily prevent an overdose and reduce the risk of negative consequences.
Is it important to treat diarrhea?
Any diarrhea, regardless of the cause of its occurrence, is dangerous mainly because it leads to dehydration and leaching of beneficial minerals from the body. If treatment is not started in a modern manner, the consequences will be irreversible.
Pseudomembranous colitis
Pseudomembranous colitis is a severe form of intestinal disorder that is associated with long-term use of antibiotics. This type of disease is fatal to humans and occurs as a result of the proliferation of microbes of the species Clostridium difficile.

During normal intestinal function, microorganisms of this type cannot multiply, as they are blocked by the moving beneficial bacteria. When problems arise with the microflora of an organ under the influence of antibiotics, beneficial bacteria quickly die, which leads to the growth of a pathogenic environment.
As a result, Clostridium bacteria reach a critical point in the body, and their waste products begin to poison the intestines.
Colitis of the pseudomembranous type can be identified if the patient has the following symptoms of malaise:
- diarrhea that is thin in consistency and frequent (sometimes the urge to defecate appears 20 times a day);
- over time, the stool becomes watery with inclusions of thick mucus, sometimes blood, changes its color, and begins to emit an unpleasant odor;
- body temperature rises for no reason;
- cutting pains appear in the abdomen;
- attacks of vomiting and nausea occur;
- characteristic weakness of the body.
Diagnosis of the described disease is carried out through biochemical analysis. If the presence of the disease is confirmed, the doctor prescribes antibiotics that are aimed at eliminating pathogenic bacteria.
Who is at risk?
Negative consequences are typical for the following groups of people:
- elderly age;
- chronic and acute diseases leading to decreased immune defense;
- if while taking antibiotics you were also taking laxatives;
- a person cannot eat food on his own and is fed through a tube;
- when using antibiotics while bearing a child or breastfeeding;
- taking antibiotics together with anti-cancer medications;
- if the patient has HIV infection.
When does a doctor's help become mandatory?
And although diarrhea often goes away on its own and does not lead to any special complications, in some cases its appearance requires mandatory assistance from a doctor. If diarrhea appears as a result of taking antibiotics, then every patient needs to consult a doctor, especially pregnant women with kidney disease, heart disease, cancer patients and HIV-infected people.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- intestinal upset only gets worse over time;
- cramps and pain appear in the abdomen;
- increased body temperature, general weakness of the body;
- green impurities in the stool with traces of blood and mucus.
Self-treatment of diarrhea after taking antibiotics in all the cases described above is considered dangerous. If you do not provide the patient with qualified assistance, the result may be irreversible. When the first symptoms of illness appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
The discovery of antibacterial agents back in the last century opened up new horizons in the treatment of a large number of diseases that were previously resistant to therapy. Therefore, great hopes were placed on this group of medications. However, as is known, the bacterial flora has powerful adaptive mechanisms that allow them to survive such external influences. That is, not all antibiotics can help treat the disease. Moreover, there is a possibility of the emergence of a new pathological condition associated precisely with taking drugs from this group. Diarrhea after antibiotics, in other words, called antibiotic-associated diarrhea, brings a lot of trouble and is dangerous in its consequences. This article is devoted to this topic.
When taking an antibiotic, the active substance is designed to act on certain pathogenic pathogens. But this is not always the case in practice. When taking antibiotics, the so-called endosymbiont microflora is also damaged. That is, the effect of antibacterial drugs is not selective. Medicines “indiscriminately” kill both pathogenic and beneficial (resistant) microorganisms.
What is fraught with the emerging situation? Own symbiont bacteria perform a number of functions in the human body.
- Detoxification (neutralization of various toxins);
- Digestive (participation in the digestion of fat-soluble vitamins and other important nutrients);
- Protective (protection against bacteria, fungi, which have a detrimental effect on the human body);
- Synthetic (associated with the formation of complex compounds from simpler ones).
When pathogenic and beneficial bacteria needed by the body die while taking antibiotics, conditions arise for colonization of the intestines by pathogenic microorganisms. Those bacteria that are considered opportunistic under normal conditions acquire virulent properties. This leads to the development of severe dysbiosis with bacterial overgrowth syndrome. One of the manifestations is diarrhea. It occurs when taking antibiotics.
Diarrhea after antibiotics is one of the possible consequences of using medications. After all, such antimicrobial drugs kill not only pathogenic bacteria, but also beneficial ones. With disorders, the stool becomes watery. The frequency of bowel movements increases up to 10 times per day. Diarrhea after taking medications is observed in those whose body is often overloaded with medications. This situation requires a competent approach and treatment.
Mechanism of development of diarrhea
Loose stools after taking medication can be explained by various mechanisms.
- The most common reason is taking macrolide antibiotics. Such drugs are considered the safest, since their action is aimed at preventing bacteria from multiplying (bacteriostatic). However, doctors believe that taking them increases gastrointestinal motility and provokes diarrhea.
- Broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs, for example, cephalosporins, help destroy good bacteria and disrupt intestinal microflora (have a bactericidal effect).
- After potent antibacterial agents, the rate of development of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract slows down.
- With a weakened immune system and long-term use of antibiotics, favorable conditions are created for re-infection. Its consequence will be diarrhea. Characteristic clinical signs of this condition are pain, the presence of bloody impurities in the stool, and high temperature.
When infected with the pathogenic microorganism Clostridium difficile, a number of complications are possible. Doctors explain this by the high degree of resistance of bacteria to most antimicrobial drugs. The main clinical sign is considered to be sharp pain and body temperature around 38 degrees Celsius.
Doctors assess the condition as stable when the patient manages to restrain the urge for 1 - 1.5 hours. If there are no blood cells or purulent impurities in the stool, the patient does not have a fever, the situation is also considered stable.
Only a medical institution can tell you how to treat correctly. The medication should be prescribed by a doctor after diagnostic procedures and tests. The doctor needs to choose the optimal treatment method for diarrhea after antibacterial medications. To do this, it is necessary to establish the type of pathogen and determine a technique for how to cope with it with minimal likelihood of complications.
Who is more susceptible

There are several groups of people who have an increased tendency to develop diarrhea after taking an antibiotic drug.
- Elderly people.
- Patients suffering from pathological gastrointestinal syndromes, both acute and chronic.
- In the presence of concomitant somatic diseases.
Diarrhea after antibiotics develops against the background of a violation of the course of administration, an overdose, or non-compliance with the instructions for using the drug.
Treatment methods

Diarrhea is accompanied not only by discomfort, but also by pain in the intestines and stomach. Frequent visits to the toilet over a long period lead to weight loss, provoke a lack of vitamins in the body, weaken the immune system and increase the process of dehydration.
This situation is extremely dangerous for pediatric patients from birth to 5 years, since a fluid loss of 10% or more poses a threat to the child’s life. Due to the fact that it is sometimes difficult for parents to force their child to drink fluid in the right amount, the only way to eliminate dehydration is a dropper. If diarrhea progresses in an infant, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Emergency help
What to do in a critical situation, if diarrhea leads to dehydration while taking antibiotics? The child's condition must be assessed by external signs. These include lethargy, dry skin, periodic fainting, and lack of urination for more than 3 hours. In this situation, hospitalization and treatment in a hospital are indicated. If the loss of fluid in the body is insignificant, you should consult a doctor to adjust and replace medications.
What to do if diarrhea does not stop after antibiotics in an adult? You need to take first aid measures and then consult a doctor for consultation and a course of treatment. For mild diarrhea as a result of using antimicrobial drugs, taking probiotics will help restore the microflora.
If the frequency of trips to the toilet exceeds 6 times a day, this may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process in the large intestine or pseudomembranous colitis. In this situation, you need to consult a doctor.
If your doctor suspects such a serious illness, you should stop taking antibiotics. The patient is admitted to the hospital for examination. Colitis, together with taking antibacterial medications, threatens the patient’s life. The frequency of bowel movements in the intestinal tract can reach 21 times a day, which provokes a severe stage of dehydration. Intoxication develops.

Treatment without consulting a medical specialist is prohibited. The use of Loperamide and other similar drugs in case of progression of diarrhea after antibiotics enhances the process of poisoning and provokes the development of megacolon or deformation of the large intestine.
Nutrition adjustments
Any pathological syndromes of the stomach and intestines are treated with diet. If dysbiosis increases, doctors advise reducing the load on the gastrointestinal tract. You should adhere to a fractional nutrition method. The number of meals needs to be increased, but the portions should be small. Sweets and fried foods increase fermentation processes in the intestines and complicate digestion, so they should be excluded from the diet. During the first 1-2 days you should adhere to a strict diet.
- Porridges and cereals are allowed. Rice has a positive effect on irritated mucous membranes. Rice porridge is recommended to relieve diarrhea after antibiotics in children.
- Kissels based on berries or fruits restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract; vitamin complexes are necessary as preventive measures for vitamin deficiency. Many people prefer blueberry compote; this berry has an antidiarrheal effect.
- It is recommended to add crackers to the menu. It’s better to cook them yourself, without adding sugar.
2–3 days after stabilization of the intestinal tract, it is allowed to diversify the diet with vegetable-based soups and add fermented milk products. Baked meat and omelet are acceptable. Recommendations for dietary adjustments for adults and children are the same.
Medications

Diet helps normalize stool, but a complex treatment method is required. It is very difficult to correct the situation without taking medications. Medicines are used strictly as prescribed by the doctor in compliance with all dosages. More often than not, several medications are used simultaneously.
- Antibacterial agents are used when diagnosing colitis to suppress resistant bacteria, for example, Metronidazole.
- Probiotics are prescribed in the form of a dry medicinal preparation of lactobacilli. The healing effect is achieved by normalizing the microflora of the intestinal tract. Medicines in this group include Linex.
- Prebiotics are made on the basis of carbohydrate components. The therapeutic effect is to stimulate the development of beneficial microorganisms. They allow you to normalize the microflora and eliminate the unpleasant clinical manifestations of the syndrome. Lactusan is effective in this regard.
- Enterosorbent-type medications are created on the basis of charcoal. Used to remove and destroy pathogenic microorganisms from the gastrointestinal tract. Eliminates toxins, helps normalize motor skills. Allows you to get rid of the clinical signs of diarrhea. Activated carbon is an effective and affordable enterosorbent.
- Another type of medication for diarrhea after using antibacterial agents is rehydrants. Available in the form of powders that need to be diluted with water. In addition to active substances, the composition contains vitamins of various groups and glucose. Participate in normalizing water balance in the body. The most common of them is Regidron. It is commonly prescribed to treat diarrhea in children.
It is required to take medications in accordance with the dosage. For the treatment of diarrhea after antibacterial agents in children, the help of a doctor is required.
Traditional methods
Before using natural methods, you must agree with your doctor. If you have an individual intolerance to some components of plant origin, their use is not recommended.
Diarrhea from antibiotics can be overcome by using the following folk recipes in addition to diet and medications.
- A decoction based on oak bark promotes stool consolidation and has an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect. It is able to relieve the patient from discomfort and pain in the gastrointestinal tract in a short period of time. You will need to dilute 10 grams of crushed oak bark in 500 milliliters of water. The resulting liquid must be boiled for 15 minutes, then strain. Take 20 grams 3 times a day.
- Dried blueberries are highly effective against diarrhea. Kissel or a decoction with 20 grams of berries per 250 milliliters will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
- Pomegranate peels help stop frequent urges to go to the toilet. It is allowed to use both fresh and dried bark. For 250 milliliters of water you will need 20 grams of raw materials. The broth needs to be boiled for 20–30 minutes. It is correct to consume 2 teaspoons 30 minutes before meals.
- To prepare the next decoction you will need to take crushed mint leaves and rowan berries in equal proportions of 10 grams. The resulting mixture is poured with a liter of boiling water and then filtered. You should take half a glass 10–15 minutes before meals.
If you don’t have the ingredients described above at home, strong black tea will help alleviate the condition. Adding sugar is not recommended.
Hospital treatment
The fight against diarrhea after taking antibacterial medications in adults is carried out at home. Hospitalization is necessary if the frequency of visits to the toilet is more than 10 times a day or if there are clinical signs of dehydration. Symptoms are characteristic of colitis and other pathological syndromes of the inflammatory type of the gastrointestinal tract.
For young patients, hospitalization is a mandatory measure for recovery. Intravenous infusion of drugs is required. Self-medication has a high risk of death.
Danger of dysbacteriosis
If dysbiosis with diarrhea is not treated after taking antibacterial medications, dehydration of the body develops. Frequent bowel movements remove beneficial bacteria and vitamins.
In the absence of treatment, irreversible complications for the stomach are possible. In the worst case, the patient begins to develop pseudomembranous colitis. Pathological syndrome occurs with an advanced form of gastrointestinal disorder after taking an antibiotic. The balance of bacteria in the stomach and intestines is disturbed, and the active proliferation of C. Difficile bacteria begins.
During the progression of pseudomembranous colitis, the following clinical signs occur.
- Frequency of bowel movements more than 10 times a day.
- The pathology is accompanied by severe pain.
- The stool contains admixtures of mucus and blood cells.
- Nausea occurs.
- Body temperature rises.
- The stool takes on a greenish tint and is characterized by a persistent unpleasant odor.
To make a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a biochemical type of blood cell analysis. The course of treatment is based on the use of special medications that eliminate pathogenic flora of the gastrointestinal tract.
Preventive actions

Strengthening the immune system will significantly reduce the likelihood of diarrhea after taking antibacterial medications. It is necessary to follow the correct diet. Quit drugs, smoking, and alcohol abuse. A number of recommendations should be followed during therapy.
The main rule for a quick recovery from the syndrome described above is to never self-medicate. Without medical education, it is difficult to determine how to treat diarrhea. The doctor will find out the type of pathogen that caused the diarrhea and will formulate the optimal course of therapy.
Only a doctor can correctly determine the dosage and method of using the drug. Why can’t you choose a medication yourself? If the course of administration is violated, pathogenic microorganisms develop resistance to the drug, which leads to a chronic course of the pathology.
Recently, there has been a practice of replacing prescribed drugs with less expensive analogues. When treating diarrhea after taking antibacterial agents, this is unacceptable. If you lack money, it is better to ask your doctor to recommend another drug.
It is also necessary to take into account side effects and complications when using the tetracycline group of antibiotics and, when the first clinical signs of deterioration occur, seek help from a doctor.
Doctors recommend starting the use of probiotics from the beginning of the therapeutic course. You should not wait for clinical signs of gastrointestinal dysbiosis to appear. After completing the antimicrobial therapy, it is recommended to take probiotics for 2 weeks. The doctor will give the necessary instructions for the most effective fight against the disease.
The concept of recovery from antibiotics appeared when the era of widespread use of antibiotics began. Antibiotics not only saved the lives of millions of people, but also began to have unwanted side effects, such as diarrhea (diarrhea) and colitis (inflammation of the intestines), associated with changes in intestinal microflora.
Rice. 1. The total area of the intestine (its internal surface) in adults is approximately 200 m2.
Diarrhea and colitis after antibiotics
When treated with antibiotics, the number of microbes sensitive to them decreases and the growth of normal tissue is inhibited. The number of antibiotic-resistant strains is increasing. Opportunistic bacteria multiply rapidly and begin to acquire properties that damage the macroorganism.
Clostridia, staphylococci, Proteus, enterococci, Klebsiella and yeast-like fungi are the most well-known representatives of pathogenic intestinal flora. In most cases of diarrhea that occurs after antibiotics, the leading place is occupied by clostridia ( Clostridium difficile). The frequency of their damage is:
- from 15 to 30% of cases with antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD);
- from 50 to 75% of cases with antibiotic-associated colitis;
- up to 90% of cases with pseudomembranous colitis.

Rice. 2. Photo of Clostridium difficile under a microscope.

Rice. 3. The photo shows a colony of Clostridium difficile.
The cause of diarrhea (diarrhea) and colitis is a violation of the intestinal microbiocenosis (intestinal dysbiosis). The growth of pathogenic bacteria leads to damage to the intestinal wall and increased secretion of electrolytes and water.
Intestinal microflora is involved in the utilization of fiber. As a result of this process, short-chain fatty acids are formed - a source of energy for the intestinal mucosa.
With an insufficient amount of fiber in the human diet, the trophism (nutrition) of intestinal tissues is disrupted, which leads to increased permeability of the intestinal barrier to toxins and pathogenic microbial flora.
Enzymes produced by intestinal microflora take part in the process of breaking down bile acids. After being released into the gastrointestinal tract, secondary bile acids are reabsorbed, and a small amount of them (5 - 15%) is excreted in the feces, participating in the formation and movement of feces and preventing their dehydration.
If there are too many bacteria in the intestines, then bile acids begin to break down prematurely, which leads to secretory diarrhea (diarrhea) and steatorrhea (excretion of increased amounts of fat).
All of the above factors form:
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is the most common complication of antibacterial treatment in adults. The incidence of this complication ranges from 5 to 25% in people taking antibiotics;
- The development of colitis is somewhat less common;
- A rare but serious disease that develops after antibiotics is pseudomembranous colitis.

Rice. 4. The photo shows a normal intestinal wall (histological specimen).
Antibiotics that cause diarrhea
Penicillins
Penicillins of earlier generations (ampicillin, benzylpenicillin) more often affect the intestinal microflora. The use of modern penicillins does not lead to the development of clostridia - the main culprits of pseudomembranous colitis.
Cephalosporins
Most cephalosporins promote the growth of enterobacteria and clostridia. Cefaclor and cefradine do not affect the intestinal biocenosis.
Erythromycin
M-cells of the epithelium of the small intestine produce the hormone motilin, which affects intestinal motility, promoting the movement of food through the digestive tract. Erythromycin stimulates the production of motilin, thereby accelerating the emptying of the stomach and intestines, which is manifested by diarrhea (diarrhea).
Clavulanic acid
Clavulanic acid, which is part of many antibiotics (amoxiclav, amoxicillin/clavulanate), also stimulates intestinal motility.
Tetracycline and neomycin negatively affect the intestinal epithelium, causing a direct toxic effect.
Fluoroquinolones
Antibiotics of this group suppress the growth of normal intestinal microflora, but do not promote the growth of clostridia.
Lincomycin
If a patient has loose stools for 2 days in a row, two days after starting antibiotics and up to 2 months after stopping them, antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) occurs. This condition means that the patient has experienced pathological changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora (intestinal dysbiosis). Its incidence ranges from 5 to 25% among patients treated with antibiotics.
If diarrhea occurs with symptoms of intoxication and high leukocytosis, then clostridia should be considered the cause.

Rice. 5. The bulk of the intestinal microflora is concentrated in the parietal zone of the intestine.
Those at risk for developing antibiotic-associated diarrhea are:
- children aged from 2 months. up to 2 years old and adults over 65 years old,
- patients with diseases of the stomach and intestines,
- patients who were treated with antibiotics for more than 3 days,
- use in the treatment of a large number of antibiotics,
- severe immunodeficiency.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics contributes to the development of dysbacteriosis and increases the allergenicity of the body. The risk of developing diarrhea after antibiotics is not affected by the method of administration of antibiotics or their dosage. Cases have been described where diarrhea developed even after a single dose.
Symptoms of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis
The clinical picture of dysbiosis after antibiotics has a wide range of manifestations - from minimal to life-threatening. In 70% of patients, symptoms of the disease appear during the treatment period. In 30% of patients - after completion of treatment.
- Initially, loose stools (diarrhea) without any impurities. It often goes away on its own within 3 to 4 days. Sometimes the patient is bothered by cramping pain in the abdomen. The general condition of the patient is quite satisfactory. Endoscopic picture of AAD without pathology. With the development of colitis, inflammation of the intestinal wall (swelling and hyperemia) is noted.
- With the negative development of the disease, the severity of the process increases, symptoms such as fever appear, stools become more frequent, the level of leukocytes in the blood increases, leukocytes appear in the stool, and pseudomembranous colitis gradually develops, caused by clostridia.
Asymptomatic dysbacteriosis → antibiotic-associated (diarrhea or diarrhea) → colitis → pseudomembranous colitis.
Pseudomembranous colitis is an extreme form of clostridium infection.
Pseudomembranous colitis after antibiotics
Pseudomembranous colitis often develops during treatment with antibiotics, less often - 7-10 days after their discontinuation. It is based on the activation of pathogenic flora and primarily clostridia ( Clostridium difficile). Cases of the development of colitis as a result of the proliferation of staphylococci, Klebsiella, Salmonella and Candida fungi have been described. Among all pseudomembranous colitis, colitis caused by antibiotic use ranges from 60 to 85% in adults.
Clostridia produce toxins that lead to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. Contacts between cells (enterocytes) are disrupted, which leads to increased permeability of the intestinal wall with the subsequent development of symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, and cramps. The inflammatory process is localized more often in the large intestine, less often in the small intestine.

Rice. 6. The photo shows a classic “volcano” lesion in pseudomembranous colitis (histological picture). The process of exudation has gone beyond the mucous membrane of the ulcer, and the process of formation of fibrous films begins. Symptoms of the disease increase rapidly during this period.
Signs and symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis
The disease is characterized by loose, scanty, watery stools with a frequency of 10 to 30 times a day, abdominal pain and fever. Diarrhea persists for 8 to 10 weeks. Persistent diarrhea leads to loss of electrolytes and water. The volume of circulating blood decreases, blood pressure decreases. Severe dehydration develops. A decrease in the level of albumin in the blood leads to the development of peripheral edema.
Leukocytosis in the blood reaches 15 10 9 /l. In some cases, higher rates are observed. A decrease in the number of leukocytes is recorded in patients who received chemotherapy for cancer. The colon becomes damaged, dilates (toxic dilatation), and perforates. If timely and adequate assistance is not provided, the disease often ends in the death of the patient.
Endoscopic picture
For diarrhea caused by taking antibiotics, endoscopy does not reveal any changes. With the development of colitis, catarrhal inflammation first appears. Further, against the background of hyperemia and edema of the intestinal wall, erosions appear.
During endoscopy for pseudomembranous colitis, fibrinous films (pseuvomembranes) are observed on the intestinal mucosa, which form in areas of necrosis of the mucous membrane. Fibrinous films have a pale yellowish color, often ribbon-shaped. Their size ranges from 0.5 to 2 cm in diameter. The intestinal epithelium is absent in places. As the disease progresses, bare areas and areas covered with films expand and occupy a larger area of the intestine.

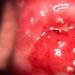
Rice. 7. The photo shows pseudomembranous colitis. Yellowish fibrous films (pseudomembranes) are visible.
CT scan
A computed tomography scan reveals a thickened wall of the large intestine.
Complications
Infectious-toxic shock, perforation of the large intestine and peritonitis are serious complications of pseudomembranous colitis in adults. When they develop, conventional therapy is powerless. Removing part of the intestine is the only treatment.
The fulminant form of the disease is fatal in half of the cases.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the determination of enterotoxins A and B of Clostridium difficile in the stool.
The latex agglutination test is a qualitative method for diagnosing pseudomembranous colitis. It allows you to detect the presence of enterotoxin A in stool within one hour. Its sensitivity and specificity are high and amount to more than 80%.

Rice. 8. The photo shows a view of the intestine with pseudomembranous colitis. Ribbon-shaped pseudomembranes are visible, covering a large area of the intestine (macropreparation).
Treatment of pseudomembranous colitis
The drugs of choice for the treatment of pseudomembranous colitis in adults are the antimicrobial drugs vancomycin and metronidazole.
conclusions
Intestinal dysbiosis is an underlying condition that occurs for a variety of reasons. Almost every person experiences dysbiosis during their life. In most cases, this condition occurs without visible symptoms and goes away without leaving a trace without treatment, without affecting general well-being. If the situation develops negatively, symptoms appear, the main of which are diarrhea (diarrhea). One of the reasons for the development of dysbiosis is the use of antibiotics.
Antibiotics are prescribed only by a doctor; it is he who will select the correct single daily and course doses of the drug. Read the instructions carefully before taking the medicine.
How often have you taken antibiotics without a doctor's prescription? Have you ever had problems with bowel movements (diarrhea) after taking antibiotics?
Articles in the section "Dysbacteriosis"Most popularIf diarrhea occurs after antibiotics, how to treat this manifestation? People often ask doctors this question. Diarrhea, otherwise called diarrhea, can appear after taking antibiotics, which are most often prescribed by doctors for a quick effect. Therefore, it is necessary to be yourself aware of the treatment of a particular disease in order to help your body.
Diarrhea is the constant release of liquid stool for 1-2 days. Due to the reduced content of plant fibers in stool, stool becomes liquid. If there is a feeling of pain, sharpness, then this is called irritable bowel syndrome.
Mostly, diarrhea can appear after using antibiotics or with frequent use of laxatives.
The reason for its appearance may be associated with the use of antibacterial therapy for diseases of the stomach and intestines.
 The use of antibiotic therapy is sometimes simply unavoidable, but it can have side effects. Of the unfavorable symptoms that may appear after taking antibiotics, diarrhea is not in last place. He is the one who most often appears first. Poor functioning of the digestive system may include the following symptoms:
The use of antibiotic therapy is sometimes simply unavoidable, but it can have side effects. Of the unfavorable symptoms that may appear after taking antibiotics, diarrhea is not in last place. He is the one who most often appears first. Poor functioning of the digestive system may include the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- constipation;
- vomit.
When using antibiotics, loose stools may appear immediately after the first use, and after complete absorption into the intestines, everything may stop. The symptom can be caused by both herbal preparations and drug treatment.
It can be called:
- ergot alkaloids;
- digitalis preparations;
- various laxatives.
Why does diarrhea occur after antibiotics? The peculiarities of such drugs are that bacteria do not need air, and if favorable conditions are created, they create spores. With small doses of antibacterial drugs, the patient may not feel any changes in the body. But after treatment it is necessary to undergo a recovery course, since the body has suffered greatly.
If symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist. This indicates an incorrectly prescribed dosage or inappropriate medication.
What does antibiotics mean?
 Antibacterial agents include: sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones, drugs of the nitrofuran series and with cytostatic effects.
Antibacterial agents include: sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones, drugs of the nitrofuran series and with cytostatic effects.
Antibiotics are divided into several groups: penicillin (penicillin), macrolides (macropen, erythromycin), beta-lactam with a small addition of clavulanic acid, cephalosporin antibiotics. The last group belongs to the most fast-acting and powerful means.
Loose stools may occur after using antifungal medications. These include: ketoconazole, terbinafine, fluconazole.
All antibiotics kill absolutely everything that might get in their way. When they are taken, both beneficial and completely harmless microorganisms suffer. Therefore, after the use of antibiotics, dysbiosis appears, which leads to a disruption in the maintenance of a normal environment in the intestines. The action of the drugs affects the change in the balance between bad and beneficial microorganisms. This may cause bloating or diarrhea.
What you need to take to avoid consequences

In order to avoid dysbiosis and diarrhea, it is necessary to maintain the body's microflora in the required quantity. For this purpose, drugs have been created that are recommended by doctors. They contain special bifidobacteria, for example, linex, lactovit, bifiform, yogurt, hilak-forte. They are simply necessary to prevent the occurrence of discomfort and symptoms. But before using them, it is recommended to consult with your doctor and study the attached instructions.
Any antibiotics are considered the strongest remedy in the fight against a particular disease. And they are the ones who have a detrimental effect on the state of the intestinal microflora. Unfortunately, we also cannot do without them, since bacteria and viruses mutate and change every day, so we have to create a stronger means to combat them. The stronger the medicine, the worse it will affect the intestines and, accordingly, the entire human body.
Loose stools are dangerous because water, all nutrients, vitamins and minerals are quickly removed from the body. This is especially dangerous for children, since everything happens much faster for them than for an adult, and there can be serious consequences.
How to treat diarrhea after antibiotics? It is best to try to avoid this condition and use medications with special care. The simplest and most acceptable way to protect against the consequences is the use of kefir. It is this product that contains a huge amount of bifidobacteria. The microorganisms it contains help restore the intestinal microflora to its previous state.

Any diarrhea that occurs will go away quickly or not appear at all. If this method does not help, you can use special products that contain beneficial bacteria. Also, do not forget about the restorative diet and proper regimen. You should not overeat during this period; you must give up all bad habits.
In the fight against such a disease, you can also use a folk recipe based on beneficial herbs: St. John's wort, mint, immortelle, thyme and fennel. All herbs must be mixed in equal quantities, pour boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. This is a very healthy and tasty remedy.
It is necessary to remove heavy and fatty foods that are harmful to the stomach from the diet as quickly as possible. You need to try to cleanse the body of remaining antibiotics. It is recommended to eat bran and drink kefir, but it is undesirable to consume rice, as it tends to complicate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the best way to treat diarrhea after taking medications:
- First of all, do not panic, as everything can be cured.
- Hygiene must be maintained.
- You should avoid any stress.
- Tell your doctor.
With proper and timely treatment, the body will quickly return to normal and all unpleasant symptoms will disappear. It is worth remembering that stomach upset can be caused even by unwashed fruit that was eaten before taking the antibiotic. In this case, after taking medications, diarrhea can be eliminated with the help of auxiliary medications, after which intestinal functionality will be restored.
If you doubt that the appearance of diarrhea was associated with antibiotics, then by looking at the stool you can determine which part of the intestine is affected and what exactly needs to be treated. It is very important to determine in what period of time loose stools most often occur. All this will help to accurately determine the causes of diarrhea. And, of course, you should not neglect going to the doctor, as self-medication can further harm your health.
- Folk remedies for fractures: helping clinical treatment
- Nettle decoction Nettle decoction indications for use and contraindications
- Celandine: medicinal properties, contraindications, photo Celandine where it grows
- What disease does a yellow tongue indicate?
- Treatment of prostate adenoma at home Methods of treatment of prostate adenoma
- Definition of qibla - direction to the Kaaba
- Treatment with verses of the Koran Treatment with the Koran for all diseases
- Day of lifting the blockade of Leningrad (1944)
- Retri Pala 3.3 macros 5. Caps and characteristics for Rpal
- What is chifir (chifir) in the zone?
- What to do in stalker clear sky
- How to remove phlegm from the bronchi at home
- Cancer neck plant. Snake mountaineer. Cancer neck root
- What are the benefits of kombucha?
- What is dropsy: types and treatment
- Flax seeds for kidney treatment
- Can you drink flax if you have kidney disease?
- How to cure a dry cough quickly To prepare it we will need
- Kombucha and its treatment of the digestive system
- Sore throat - treatment at home