What is oliguria. What is oliguria, and how to deal with it? Oliguria polyuria
Normally, an adult's kidneys produce 1.5 to 2 liters of urine per day. Oliguria is most often an acute pathological condition in which daily urine production does not exceed 400 ml. A sharp reduction in urination may indicate the development of a wide range of disorders, but in most cases, oliguria develops in the presence of acute renal failure.
What is oliguria
Oliguria is a pathological condition in which a person has low urine output. The volume of urine excreted per day with this pathology ranges from 80 to 400 ml/day in an adult; less than 1 ml/kg/h in infants; less than 0.5 ml/kg/h in children. Oliguria is often acute and is the earliest sign of renal dysfunction. This is one of the clinical signs of acute renal failure, which is used as a criterion.
Not all cases of acute kidney injury are characterized by oliguria. Renal failure resulting from nephrotoxic drugs, interstitial nephritis, or asphyxia of the newborn is often nonoliguric in nature, associated with less severe renal damage, and has a better prognosis.
Nephron is a structural unit of the kidney that produces urine
In most clinical situations, acute oliguria is reversible and does not lead to renal failure. However, identifying and promptly treating reversible causes is critical because the time frame for effective treatment may be short.
Forms of the disease
Based on its origin, oliguria is classified into three main forms:
- prerenal - caused by a long-term decrease in renal blood flow (including due to dehydration due to poor care, vomiting, diarrhea, severe blood loss, severe burns);
- renal - caused by a disease (acute glomerulonephritis, nephritis, chronic pyelonephritis in the last stage) or kidney injury, their toxic damage;
- postrenal - caused by disorders outside the kidney, including blockage of the urinary tract by a stone or tumor, narrowing of the lumen of the urethra; inflammation or proliferation of prostate tissue in older men; compression of the ureters by an enlarged uterus in pregnant women.
Oliguria - a critical decrease in daily urine output
Prerenal failure is a functional response of structurally normal kidneys to reduced blood supply, or poor microcirculation.
Intrinsic, or renal, kidney failure is associated with structural damage to the kidneys. This includes acute renal tubular necrosis (from prolonged ischemia, drugs or toxins), primary glomerular or renal vascular lesions.
Postrenal failure is a consequence of mechanical or functional obstruction of the urine flow. This form of oliguria and renal failure usually responds to removal of the obstruction.
Postoperative oliguria is separately distinguished. Surgical patients often experience a decrease in urine output after major surgery. A decrease in daily diuresis (urine volume per day) in these cases may be a normal physiological response to:
- blood loss (decrease in glomerular filtration rate secondary to a decrease in circulating blood volume);
- response of the adrenal cortex to stress.
A decrease in daily urine output can be temporarily observed in elderly patients due to operations in the perineum and rectum.
Causes and provoking factors
The etiology of oliguria varies depending on age and concomitant diseases. Decreased urine output in adults may be a sign of conditions such as:

There are many causes of oliguria due to acute kidney injury in newborns, including the following:
- oxygen deficiency in the fetus during childbirth;
- acute respiratory failure syndrome;
- hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells with the release of hemoglobin into the environment;
- sepsis or shock;
- Congenital heart defect;
- certain medications, for example, Indomethacin, as well as the pregnant woman taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or ACE inhibitors.
Intrarenal causes of oliguria in newborns include:

Postrenal causes include:
- narrowing of the urethra;
- neurogenic bladder;
- ureteral obstruction (bilateral).
Advances in the treatment of critically ill neonates, infants with congenital heart defects, and children undergoing bone marrow and solid organ transplantation have led to a significant expansion of the etiology of pediatric acute kidney injury. The most common causes of decreased urine output in newborns are congenital heart defects, acute tubular necrosis, sepsis and bone marrow transplantation.
The main causes of prerenal oliguria in acute kidney injury in children of young age and older:
- gastrointestinal problems such as vomiting and diarrhea;
- internal hemorrhage;
- impaired renal function due to certain diseases (diabetes insipidus, diabetes mellitus);
- nephropathy with loss of salts due to long-term use of diuretics;
- extensive skin damage - such as burns;
- surgery, trauma;
- shock - for example, septic, toxic and anaphylactic;
- autoregulation disorders due to the use of certain drugs, including Cyclosporine, immunosuppressants (Tacrolimus), ACE inhibitors and NSAIDs;
- disturbance of the volumetric velocity of cardiac blood flow due, for example, to congenital or acquired heart failure.
Intrinsic renal causes of oliguria in children may include the following:
- acute tubular necrosis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- interstitial nephritis;
- the action of an internal or external toxic factor;
- graft rejection.
Acute tubular necrosis and nephrotoxins are the most common causes of decreased urine output due to acute kidney injury in children. In most clinical situations, oliguria is reversible and is associated with the restoration and regeneration of tubular epithelial cells.
Symptoms of oliguria
The main symptom of oliguria is a small amount of urine excreted by the body. Associated symptoms depend on the underlying pathology that caused the disorder. These may include:
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- symptoms of intoxication: nausea, vomiting, loose stools;
- pain and/or spasms in the lower back, lower abdomen;
- low blood pressure;
- swelling (primarily of the legs);
It is important not to confuse true and false oliguria. The latter is a decrease in daily diuresis in response to insufficient water supply from the outside, heavy sweating and other factors that affect the body's urine output. False oliguria is accompanied by a feeling of dry mouth and thirst. There is general weakness and dizziness.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out in the nephrology or urology department of the hospital. Initially, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract must be prescribed to exclude obstructive processes (blockage of the urinary tract).
General clinical and biochemical urine and blood tests are required. If the kidneys are damaged, protein will be detected in the urine (normally no more than 0.033 g/l) and the epithelial tissue lining the kidneys from the inside, increased levels of leukocytes (normally no more than 3-5 in the field of view) and red blood cells (normally no more than 2 in line of sight).
Further examination methods will depend on the tests obtained and the results of the ultrasound. These may include:

Depending on the detected cause of decreased diuresis, one or another treatment plan is prescribed.
Treatment of oliguria
Therapy is primarily aimed at restoring water-salt balance, normalizing renal circulation and eliminating associated disorders. It includes droppers with the introduction of electrolyte solutions of a balanced composition. Impaired renal circulation is corrected by normalizing blood pressure with the help of vasodilators. In case of severe kidney damage, hemodialysis is necessary - cleansing the blood of toxins using an “artificial kidney” machine.
Hemodialysis is a method of extrarenal blood purification for acute and chronic renal failure
Adults with the prerenal form of the disease are prescribed diuretics. However, the use of diuretics is contraindicated until the underlying cause of oliguria is established. Further treatment is aimed at the underlying disease that caused the oliguria.
Oliguria of an infectious nature is treated with antibacterial agents. The selection of drugs is made based on the results of the antibiogram and depends on the type of bacterial pathogen.
In case of acute tubular necrosis, supportive therapy is provided, which includes:
- cessation of exposure to nephrotoxin, if possible;
- maintaining normal blood volume;
- providing parenteral nutrition (intravenous administration of nutrients);
- treatment of infections (preferably with drugs that are not nephrotoxic).
Self-medication of oliguria with medications or folk remedies is inappropriate and dangerous, which can distort the clinical picture and results of urine tests and can lead to an erroneous diagnosis.
In case of acute kidney inflammation, in addition to drug treatment, diet therapy is prescribed (table No. 7). It includes fractional five or six meals a day in small portions. The patient's diet excludes the use of:
- table salt in any form;
- compounds of extractive substances contained in broths containing meat, fish, poultry, vegetables and mushrooms;
- tea, coffee.
Table No. 7 limits the use of:
- animal protein (lean poultry and fish in limited quantities);
- liquids (no more than 800 ml per day).
The diet improves metabolic processes in the patient’s kidneys and urination, creates favorable conditions for reducing inflammation.
If the cause of oliguria is blockage of the ureters with stones or a tumor, or narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract, then surgical treatment is indicated to remove obstructions to the outflow of urine.
A decrease in diuresis that is not associated with pathologies of internal organs is physiological. To eliminate false oliguria, it is necessary to satisfy the body's need for fluid as quickly as possible. For this purpose, use pharmaceutical electrolyte solutions (Regidron, Disol, Sorbilact) or prepare a saline solution yourself by dissolving 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. salt and sugar. They are designed to quickly restore water-salt balance. Tonic caffeine-containing drinks are temporarily excluded due to their dehydrating effect.
Treatment prognosis
The prognosis for acute kidney injury caused by prerenal causes, as well as for acute tubular necrosis, is usually quite good if appropriate therapy is started in a timely manner. Urine formation in the body is restored after the underlying disease is cured.
Mortality rates for oliguria due to acute renal failure vary widely depending on the causes and associated health status. The mortality rate varies from 5% for patients with various kidney injuries to 80% among patients with multiorgan failure requiring treatment in the intensive care unit. The most common causes of death are sepsis and cardiovascular or pulmonary dysfunction.
Possible complications
Poisoning of the body with substances that are retained when water-salt metabolism is disrupted, and the inappropriate use of broad-spectrum antibiotics contribute to the development of infectious complications. Urinary tract and respiratory infections develop in 30–70% of patients. Cardiovascular complications develop as a result of excess fluid and sodium retention. These include: high blood pressure, congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema. Excess potassium causes arrhythmia - an abnormal heart rate.
Other complications include disorders:
- gastrointestinal - anorexia, nausea, vomiting, obstruction and bleeding;
- hematological - anemia and platelet dysfunction;
- neurological - confusion, inability to maintain a fixed posture, drowsiness and convulsions;
- other electrolyte/acid-base disorders are metabolic acidosis, hyponatremia, hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia.
If the condition is not treated, it worsens and threatens the onset of anuria - a complete cessation of urination, which leads to fatal poisoning of the body with toxic products of its own vital activity.
Prevention
To prevent diseases of internal organs associated with a sharp reduction in diuresis, it is important:
- promptly treat pathologies of the urinary system;
- immediately seek medical help at the first signs of a decrease in the volume of urine excreted;
- do not allow self-medication, including the use of folk diuretics.
The physiological norm of diuresis may vary depending on the amount of fluid drunk, the intensity of sweating, breathing rate, and other factors.
To prevent the development of false oliguria, it is enough to control the intake of the required amount of fluid into the body during intense physical activity, in hot weather, or in a stuffy room.
Physiological oliguria in late pregnancy does not require treatment. It is corrected using a fluid intake regimen selected by a specialist, monitoring salt intake, and stops after childbirth.
Norm and pathology of urine analysis: video
For the diagnosis of many diseases, a fairly important indicator is the amount of urine produced per day. Oliguria in medicine is usually called a decrease in the volume of daily urine. This disorder is not considered an independent disease, but only a symptom of acutely increasing kidney failure. The development of such a problem is caused not only by diseases of the urinary tract, but also by prolonged dehydration, the use of certain medications, and a state of shock. In the absence of timely and correct therapy, the patient’s urine production may stop completely, which will lead to serious and irreparable consequences.
General information about pathology
What is oliguria? This concept implies a sharp reduction in the volume of urine excreted. Such a violation often warns of a decrease in the performance of the urinary tract organs and the presence of certain health problems in a person.
The process of urine formation begins in the glomeruli. It is there that the fluid is filtered, then reabsorption (reabsorption) occurs in the tubules. When this mechanism is disrupted, the patient experiences either unregulated accumulation of water in the body (overhydration) or excessive loss of fluid (dehydration). All this affects the quality and quantity of urine. In the first situation, the patient experiences an increase in daily diuresis, and the density and concentration of discharge decreases. In the second case, a decrease in the volume of urine produced develops, and its specific gravity exceeds the permissible norm several times.
The definition of oliguria is applicable for those pathological conditions in which a decrease in the amount of fluid secreted is not associated with excessive intake or loss of water from the body. The emergence of problems with the functioning of the urinary organs must be promptly recognized and eliminated, otherwise disruption of the filtration and reabsorption processes can have an extremely negative impact on human health.
Many patients are interested in the question: “What is oliguria and why is it so dangerous?” With this pathology, the elimination of unnecessary metabolic products slows down - this leads to the development of intoxication of the entire body. A reduction in the volume of urine excreted negatively affects the patient’s well-being - he experiences discomfort when urinating, unpleasant and painful sensations in the lower abdomen, lethargy, and weakness. The reason for this condition is the accumulation in the body of toxic substances, urea, creatinine, nitrogenous bases and other metabolic products.
When daily diuresis decreases, a person notices a very rare urge to urinate. If this phenomenon does not disappear within 3-4 days, you should urgently visit a doctor.
The normal amount of urine excreted by the kidneys in one day (24 hours) is:
- in adult men – up to 1.8-2 l;
- for women - from 1.5 to 1.6 l;
- in a newborn child – 0.2 l;
- in infants under 1 year – 0.8 l.
At the same time, the minimum indicator of diuresis in adults is 0.5 liters. Such a small amount of discharge appears when the patient drinks no more than 800 ml of water per day. If the urine volume is less than 500 ml per day, oliguria develops. If there is no urine or its amount decreases to 50 ml, anuria is indicated.
Attention! When a person’s urinary organs function normally, and the volume of fluid drunk per day remains constant, the average daily urine output does not change. The above norms are calculated for healthy people whose drinking regime is from 1.5 to 2 liters. About 3/4 of the fluid entering the body is excreted through the urinary tract, and the remaining 1/4 through the digestive, respiratory system and skin.
Types and reasons
Oliguria is caused by various disorders. The cause of the development of this pathology is often diseases of the kidneys and urinary organs, but the problem does not always lie precisely in them. Other conditions also affect the amount of fluid excreted through the kidneys. Depending on the cause of oliguria, there are three main types of this disease, listed below.

Prerenal form
In this case, the decrease in diuresis is caused by a decrease in the amount of fluid located in the extracellular space. Such a violation provokes the release of sodium chloride from the bloodstream. This type of oliguria occurs in the following pathological conditions:
- water-salt imbalance;
- severe vomiting;
- gastric drainage;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- heart and vascular diseases (arrhythmias, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, severe heart failure);
- use of diuretics (overdose);
- obstruction of the small and large intestines;
- quite severe burns of the skin;
- massive blood loss.
Renal form
This form of oliguria develops due to the occurrence of various diseases of the filtering organs - the kidneys. Symptoms of this disorder appear in the following pathologies:
- autoimmune diseases (Huspacher syndrome, vasculitis, glomerulonephritis);
- kidney infection;
- ingestion of various toxins into the patient’s body (snake or spider venom, acetone, vinegar, heavy metals, gasoline, alcohol, mushrooms);
- vascular diseases.
Postrenal form
In such a situation, the cause of oliguria is a violation of the passage of urine through the urethral canal. The decrease in the volume of urine excreted here is due to the following factors:
- the presence of neoplasms in the urinary organs;
- the appearance of stones in the lumen of the ureters and renal pelvis;
- in men - prostate pathologies (adenoma and malignant tumors of the prostate gland);
- obstruction of the urinary tract by blood clots;
- reduction of the ducts of the urethra;
- compression of the retroperitoneal space by large neoplasms (mostly malignant).
The concept of false oliguria
All of the above forms of this pathology are considered true. They appear when there are any serious problems with human health. But false oliguria - what is it? This type of disorder occurs when there is a physiological decrease in the amount of urine, which is caused by the special needs of the body, and not by the disease. This decrease in urine volume appears briefly and disappears on its own.
The cause of false oliguria is too much fluid loss. This condition often develops in patients with simultaneous vomiting and diarrhea. A very hot climate also affects diuresis, since in this case the amount of moisture evaporated from the surface of the skin increases significantly.
A false form of pathology can be found in women in the first trimester of pregnancy. Oliguria in this case is often provoked by insufficient drinking regimen, compression of the urethra by an enlarged uterus, and swollen tissues. Unlike a true decrease in the amount of urine, a false one occurs without disrupting the functionality of the urinary tract.
How does this pathology manifest itself?
The main sign of this phenomenon is a decrease in the volume of urine excreted by the patient per day. A condition in which a person notices a slight decrease in urine output is not considered oliguria if the person being studied does not have a feeling of discomfort or any other health changes. In this case, a man or woman can even independently determine the possible causes of the disorder - excessive sweating, insufficient drinking regimen. The appearance of a small amount of discharge in such a situation becomes a normal, physiological phenomenon.
A downward change in diuresis causes the patient to develop corresponding clinical signs. The following symptoms of oliguria are distinguished:

- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- feeling unwell, lethargy, drowsiness;
- the appearance of bloody impurities and large clots in the urine;
- elevated temperature;
- stool disorders (diarrhea);
- chills and fever;
- pain in the lower abdomen (radiates to the back, lower back);
- Blood pressure levels drop sharply.
Such symptoms are characteristic of oliguria, which itself often becomes a manifestation of some illness. A decrease in the amount of fluid secreted in this case is usually accompanied by signs of pathology corresponding to this disease.
Good to know! The symptoms of oliguria should not be confused with dysuria, a condition in which the patient feels the bladder is full and cannot empty it. When the daily volume of urine decreases, it does not accumulate in this organ, and therefore the person does not feel the desire to go to the toilet.
Diagnostic measures
A specialist determines the presence or absence of such a violation. For this purpose, the amount of urine excreted is calculated hourly and throughout the day. Every hour, a person's kidneys must filter about 40-50 ml of fluid. As a result, daily diuresis is at least 1200-1300 ml. This average figure in healthy women and men almost never drops below 1500 ml. The amount of urine excreted by the patient per day is calculated using a special container with divisions.
If the presence of oliguria is established as a result of the examination, the search begins for the cause of this problem. The following diagnostic methods help the doctor with this:

- general clinical analysis of urine;
- measuring blood pressure;
- biochemical blood test;
- examination of the patient to identify hidden edema;
- laboratory urine tests (Kakovsky-Addis, Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky);
- Sometimes kidney tissue is taken for a biopsy.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of this condition includes eliminating the cause or disease that triggered the development of oliguria in this case. It is also important to restore normal blood circulation in the urinary organs, eliminate water-salt and acid-base imbalances, and promptly prevent the occurrence of complications.
Medications in such a situation are selected by a specialist depending on the main reason that caused the decrease in diuresis. If this is an ailment such as pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, the patient undertakes to adhere to the principles of dietary nutrition. Sometimes, during the diagnostic process, a person is found to have stones or tumors, which is considered an indication for immediate surgical treatment.

Therapy of oliguria in various cases requires the use of the following medications:
- Antibacterial agents - help eliminate infectious pathogens (Oxacillin, Cefuroxin, Azithromycin).
- Anticoagulants - used when there is an increased likelihood of blood clots (thrombosis of the kidney arteries): Warfarin, Heparin.
- Diuretics – eliminate swelling (Furosemide, Lasix).
- Cytostatics – stop the progression of tumor processes.
- Specific antidotes – used in case of poisoning with toxic substances or toxins.
- Antihypertensive medications – they are used to correct high blood pressure (Amlopril, Captopres, Dinoric).
- Isotonic solutions - for the treatment of severe intoxication and shock (Reopoliglyukin, Hemodez).
If the urinary tract has lost its patency as a result of mechanical obstruction, it is necessary to remove the foreign body from the lumen of the urethral canal. For this purpose, emergency surgery is performed to remove the tumor and stones.
This pathology should be treated only after a correct diagnosis has been made. Self-therapy with diuretics is unacceptable and dangerous. It is not always possible to get rid of such a disorder with the help of diuretic medications. In the treatment of this pathology, they have pronounced effectiveness in the prerenal form of oliguria. In other cases, diuretics can only harm the patient, since these drugs change the concentration of urine and its properties. Therefore, if there is a long-term decrease in the amount of urine excreted, do not hesitate and immediately consult a urologist.
Important! After the baby is born, a decrease in urine output is noted for several days. This physiological phenomenon is due to the formation of the lactation process in the mother. In the future, oliguria in children manifests itself for the same reasons as in adults.
A qualified specialist should select the appropriate treatment for such a disorder based on laboratory test data. Getting rid of oliguria is quite simple - usually it is enough to eliminate the main cause of the pathology.
Have you noticed that the urge to urinate has become less frequent? It is quite possible that a condition of the body such as oliguria has arisen. The deviation represents a sharp slowdown in the process of urine formation in the body. Oliguria is not an independent disease; it is only evidence of malfunctions and problems in the functioning of the entire urinary system. Which ones? Let's look further.
Oliguria is...
The body of a healthy person secretes a certain volume of urine, which can change not only throughout the day, but throughout the year. Diuresis changes are influenced by many factors: a person’s age and gender, physical activity, volume of fluid consumed, type of work, climatic conditions, etc.If there is a pathological decrease in the amount of urine excreted, which significantly deviates from the norm, then a body condition such as oliguria occurs. .
The normal urine output for a healthy person is from 1.2 to one and a half liters per day.
With oliguria, urine production processes slow down while fluid consumption remains unchanged. A person drinks the same volumes of various liquids, but the urge to urinate occurs very rarely. The decrease in diuresis volumes per day can reach 400 ml. In this condition, urine stops flowing into the bladder. Doctors note that oliguria should not be considered as an isolated deviation, but one should look for deeper causes of its occurrence and disturbances in the functioning of the entire urinary system.
Why does oliguria occur?
There are many reasons for the occurrence of such a condition as oliguria. Doctors distinguish three main groups of such reasons:Prerenal(functional). In turn, they are divided into two subspecies:
- shock with a decrease in blood pressure (can occur against the background of heavy sudden bleeding during injury, surgery, myocardial infarction, peritonitis, sepsis, and other cardiogenic types of shock);
- hypovolemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in blood volume in the circulatory system, which can be observed with severe burns, prolonged diarrhea, intestinal obstruction, acute eczema and other renal or extrarenal Na+ losses.
Renal. Associated with all kinds of kidney damage, the most common of which are:
- renal failure in the acute stage;
- uremia;
- glomerular inflammation of the kidneys;
- nephritis (chronic or acute form);
- systemic vasculitis.

All of the above diseases lead to disruption of the outflow of urine.
Renal oliguria can also occur due to poisoning of the body with nephrotoxic substances (drugs) or severe kidney injury.
Postrenal. Observed when all kinds of obstacles occur directly in the urinary tract with:
- urolithiasis or blockage of the ureters with blood clots after kidney bleeding;
- the presence of tumors in the organs of the genitourinary system or organs located nearby;
- obstruction of the urinary canal - stenosis, neoplasms, etc.
An infrequent root cause of postrenal oliguria is injuries received during childbirth due to breech presentation of the fetus.
In men, this type of oliguria can be observed with prostatitis or prostate adenoma.
A fairly common cause of oliguria is all kinds of bacterial infections. So, for example, such a serious disease as cholera provokes severe dehydration of the body and, if treatment is not timely, can lead not only to serious consequences and the development of oliguria, but also to death.
Why kidneys don't work well (video)
What interferes with kidney function? Elena Malysheva and her colleagues talk about the consequences of a serious illness.Symptoms
The main symptom of a condition such as oliguria is a decrease in the volume of urine excreted. Oliguria is not a condition when a person notices changes in the volume of urine excreted, but does not feel any discomfort and can name the probable reasons for the decrease in diuresis: a decrease in the amount of fluid consumed, excessive sweating, etc. In such a situation, a decrease in urine volume during the day is the norm.Against the background of a decrease in diuresis volumes, other symptoms:
- clots or blood streaks in the urine;
- , radiating to the lumbar area;
- general malaise, weakness;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- feverish condition;
- diarrhea, nausea, vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
It is important not to confuse oliguria with a condition where a person feels that the bladder is full, but cannot empty it. With oliguria, the bladder is almost always empty and the person does not feel the urge to empty it.
Since oliguria is a symptom of some diseases, the main manifestation of this condition will be not only a decrease in the volume of urine excreted, but also typical symptoms characteristic of a particular disease.
If you have problems with urination (video)
Do you have problems urinating? Elena Malysheva and her colleagues talk about the most common problems with urination.False oliguria
A condition in which there is a physical decrease in the volume of urine excreted, but no renal diseases or abnormalities are identified in the patient.Most often, false oliguria occurs with a sharp decrease in the volume of fluid consumed while simultaneously increasing the loss of the same fluid for a variety of reasons. At the same time, renal function remains at the same level. Changes in the kidneys can be diagnosed in cases of severe dehydration. In such a situation, false oliguria can develop into a more severe condition called renal failure.
Why false oliguria may occur
Oliguria does not occur on its own. Certain reasons lead to the appearance of this condition. Frequent “culprits” of false oliguria are psychogenic and iatrogenic factors.
Psychogenic. In the vast majority of cases, they are observed in girls and women who deliberately limit themselves in fluid intake, most often to combat extra pounds or eliminate such a phenomenon as facial swelling. Such causes of false oliguria are quite problematic to determine, since representatives of the fairer sex often hide their restrictions on fluid intake.

Iatrogenic. Observed in cases where a reduction in the patient’s fluid intake is recommended by the doctor. For example, with late gestosis in pregnant women, acute pancreatitis during an exacerbation, etc.
The main signs of false oliguria:
- excessive dryness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dehydration of the body;
- weight loss;
- stool disorders (mainly constipation);
- prolonged low-grade fever for a long period of time (slight increase in body temperature ranging from 37 to 37.50C).
The presence or absence of changes in renal function is of primary importance in the process of diagnosing false oliguria.
Oliguria in children
In the first few days of life, newborns experience so-called physical oliguria. The condition does not pose a threat to the child’s life and goes away as the lactation process normalizes. In other cases, the reasons for decreased diuresis in children are similar to adults.In addition to the daily volume of urine output in the child, parents should note:
- shade of urine (bright yellow, pale yellow, reddish, etc. - an atypical color can be an alarm);
- the presence of foreign impurities in the urine (blood clots or streaks, white “flakes”, etc.);
- transparency of urine (cloudy urine is another sign of abnormalities);
- activity and general well-being of the baby.
If you detect the slightest changes or deviations from the norm, it is recommended to immediately visit a doctor.
Parents should closely monitor not only the child’s diuresis and well-being, but also pay due attention to their child’s drinking regime. Especially when it comes to very young children who are not yet able to independently express their thirst and desire to drink. Insufficient water consumption, frequent diarrhea, deficiency of breast milk are possible causes of oliguria in children, which can be dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the child.
Sometimes a pathological condition such as oliguria can occur during pregnancy (see also -). The most common reasons for changes in diuresis in pregnant women are as follows:
- compression of the ureters by the enlarged uterus;
- excessive absorption of fluid by tissues.

With oliguria in pregnant women, edema can be not only external, but also internal.
Treatment of oliguria in pregnant women is selected individually by the doctor and may include:
- limiting the amount of salt consumed;
- reducing fluid consumption;
- gentle diet.
Diagnostics
The main goal of diagnosis is to determine the causes of oliguria. To determine the root causes, a history is taken, and a comprehensive examination of the whole body is prescribed.The attending physician may suspect changes or disturbances in urine output in the following cases:
- the patient has neoplasms in the urinary tract;
- Ultrasound determined the presence of stones in the bladder;
- signs of abdominal disorders are noted.
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- various types of urinary system infections;
- presence of anemia;
- renal failure.
- additional urine tests;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, including the kidneys and bladder, to determine the presence of cysts;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity with the introduction of a contrast agent to identify stones or other tumors in the kidneys;
- CT scan and kidney scan;
- blood serum analysis;
- cytoscopy (examination of the urethra using a mini-telescope).

If necessary, the patient may be advised to consult with specialists (upon the recommendation and discretion of the attending physician).
Treatment of oliguria
After determining the causes of oliguria, the attending physician prescribes complex treatment, which is carried out simultaneously in several areas:- Elimination of the causes of oliguria or diseases that led to its appearance and development.
- Correction of water and acid-base balance in the body.
- Normalization of blood circulation processes.
- Treatment of complications arising from the underlying disease.
Surgery. If stones or other formations are found in the kidneys, surgery may be recommended. When identifying tumors of an oncological nature, surgery is performed as soon as possible.
Treatment with diuretics. Doctors note that uncontrolled use of drugs with a diuretic effect for oliguria can lead to very disastrous consequences. Such medications are indicated only in the case of prerenal oliguria (a condition in which the blood supply to the kidneys is impaired). In addition, taking diuretics leads to a significant change in the main clinical parameters of blood and urine.
During human life, the kidneys filter and remove part of the decay products from the body along with excess fluid - urine. The rate of urine excretion in healthy people may vary; it depends on many factors, from the ambient temperature and the amount of fluid consumed, to the level of physical activity and the individual characteristics of the body. But if, during a normal, measured way of life, the amount of urine decreases sharply (for example, from 500 ml to 300), this indicates problems with the kidneys, and the condition itself is called oliguria.
Oliguria is a decrease in diuresis (the amount of urine excreted by a person per day). This condition occurs in acute renal failure or advanced chronic renal failure. Even if there are no symptoms of the disease and you feel good, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
The waste products of the body, which must be excreted along with urine, are very toxic; their accumulation in the body can cause severe intoxication, including complete organ failure or coma.
Insufficient urine excretion by the kidneys is a symptom in itself, but diagnosing the disease that provoked it is the task of doctors. It is important to distinguish oliguria from urinary retention; in the second case, it is produced in sufficient quantities, but is not excreted from the body, accumulating in the bladder.
The main task in diagnosis is to find out the cause of oliguria. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder, a urine test, and a general blood test are prescribed. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Timely detection of urinary retention in infants is very important, since, unlike adults, they cannot complain of malaise, and unpleasant consequences can occur much faster.
Causes of insufficient urine production
Very often, oliguria is identified with acute or chronic renal failure. Indeed, this syndrome is one of its symptoms, but it can also indicate other pathological processes. Therefore, before starting treatment, it is important to determine the root cause. There may be several of them:
- When the nephron is not yet damaged and is able to effectively perform its functions, but due to weakened blood supply it does not function effectively. This condition can occur due to blood loss, after operations, when receiving injuries in the kidney area, as a result of thrombosis, and so on. This condition does not pose any significant danger, but if the nephron is left without blood flow for an extended period of time, it degrades or dies and cannot be restored.
- If the tissue that makes up the kidneys dies or changes so much that it is no longer able to perform its functions, this can lead not only to oliguria, but also to a complete lack of diuresis. The cause may be acute or chronic renal failure, oncology, injury to the kidneys or their vessels. For example, with extensive hematomas in the kidney area, when the blood does not saturate their tissues, they begin to gradually die. Such changes can also occur with extensive burns, when, as a result of significant overheating, the kidneys seem to be “cooked” and no longer function. These injuries are the most serious and usually cannot be treated.
- The cause of oliguria can also be a mechanical effect on the ureters when they are blocked. This phenomenon occurs with urolithiasis, certain types of hematomas, tumors or cystic formations. In this case, surgery may be the most effective.
Symptoms of oliguria
Excretion of urine from the body in insufficient volume is the main symptom of oliguria. If your health does not worsen, you should pay attention to the amount of fluid consumed, the intensity of physical activity and the ambient temperature. In the summer, when intense sweating occurs, if a person drinks little fluid, the feeling of a full bladder occurs infrequently, literally several times a day, and the volume of urine is reduced. This is not a sign of illness.
If, with regular fluid intake, normal temperature and a sedentary lifestyle, urine output is significantly reduced or absent, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. In cases where oliguria is caused by a change in the morphological structure of the kidneys, this may also be accompanied by symptoms of general malaise, for example:
- Blood in urine. This does not mean single red blood cells visible in the urine under a microscope during analysis, but visually detectable bleeding or the characteristic pinkish color of urine.
- Cloudy urine with purulent discharge.
- Paroxysmal or aching pain in the kidney area or during urination, and sometimes after, which indicates the presence of fine sand.
- Increase in temperature or change in blood pressure.
- Weakness, dizziness, nausea. These symptoms are characteristic of intoxication; if they appear, it means that urinary retention lasts more than a few days.
- Swelling, both local and throughout the body.
Treatment of oliguria
The initial stages of oliguria do not require hospitalization. Treatment can be carried out at home, and only in special cases are IVs, day hospital treatment or inpatient treatment under the supervision of a doctor prescribed. Depending on the cause of urine retention, drug treatment may be prescribed. It is usually combined with a diet, and in addition to excluding certain foods, the doctor can regulate the amount of fluid consumed by the patient, which is also of no small importance.
It is difficult to predict a specific treatment regimen in advance; it will depend on the pathology that caused urinary retention. In addition to eliminating the root cause, symptomatic treatment and therapy aimed at improving the general condition of the patient are also carried out.
After the end of treatment, even when diuresis is returned to normal, the doctor may recommend continuing the diet; this recommendation must be followed, otherwise the disease may return.
Treatment with folk remedies is strictly contraindicated, since at best it will not help, and at worst it can cause significant harm. Usually, when self-medicating for problems with urinary retention, people try to stimulate diuresis with the help of diuretics, which is strictly prohibited in this case, because it can lead to serious problems with the kidneys and more.
Consequences of oliguria
The prognosis for this disease is favorable, oliguria is mostly reversible, and with timely treatment, health is restored without any consequences for the patient. It is especially important to monitor the amount of daily urine in pregnant women or small children, since all processes occur much faster in them; treatment and assistance must be started as early as possible.
If you neglect to contact a specialist, the consequences can be serious, including anuria (complete cessation of urine excretion from the body), which will lead to severe intoxication with failure of internal organs and possible death. If oliguria is caused by acute renal failure, then if not treated in a timely manner or incorrectly diagnosed, it can become chronic, which entails serious health problems, including failure of one or both kidneys.
Prevention of oliguria
To prevent oliguria from leading to serious consequences, it is necessary to diagnose it in time. To do this, you need to pay attention to the ratio of fluid consumed to fluid that is excreted from the body. You also need to pay attention to indicators such as the color, consistency and smell of urine. Any deviation from the norm, if it is repeated several times in a row, serves as a signal that a visit to the doctor is necessary.
To ensure that your kidneys serve you for a long time and are healthy, you should avoid drinking large amounts of alcohol and not using diuretics or other medications without a doctor’s prescription. It is also worth remembering the dangers of self-medication and the benefits of a healthy lifestyle. If you have already encountered a similar disease, then to prevent relapses you should adhere to the diet recommended by your doctor and undergo an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and bladder every six months.
Oliguria is a condition in which urine production in the body is reduced. There are certain factors in the development of this phenomenon, including kidney inflammation, infections, medications, insufficient fluid intake, the adrenal glands' reaction to stress, and others. This article discusses issues such as the causes of the disease "oliguria", symptoms, treatment of the disease, and diagnostic methods. Some folk remedies for the treatment of this disease have also been proposed.
What is oliguria
The disorder occurs when the amount of urine produced in the body sharply decreases. The norm for kidney function is considered to be a urine volume of 1.5 liters per day. In case of illness, this figure decreases to 300-500 ml or less. Doctors do not consider oliguria as an independent disease; it acts as a side condition as a reaction to other health problems. What can lead to the development of the disease? Read about it further.
Oliguria: reasons
Let's consider the main factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease. Oliguria is a condition in which the body produces too little urine. This may be the result of insufficient fluid intake, damage to the kidneys, which become unable to function normally and produce urine. There are quite a variety of factors that provoke the development of the disease “oliguria”. The reasons may be dehydration, heart disease (heart failure, collapse of the cardiovascular system, also known as Low fluid volume leads to a malfunction of the kidneys, the amount of urine excreted decreases.
Infections, glomerulonephritis
Oliguria is a pathology that can also be caused by certain infectious bacterial infections, in particular cholera, leading to dehydration due to loss of fluid and electrolytes, the development of weakness, hypotension, extreme thirst, muscle cramps, acute watery diarrhea, tachycardia and vomiting. If cholera is not treated, a person can die within hours.
Acute glomerulonephritis is another factor that can provoke the occurrence of the disease “oliguria”. Symptoms in this case include fatigue, mild fever, high blood pressure and swelling, nausea, vomiting, headache, as well as pulmonary congestion and abdominal pain.
Heart failure
In heart failure, oliguria can also develop simultaneously, which is a consequence of a decrease in blood output from the heart and an increase in renal perfusion. In such cases, a person may experience fatigue and weakness, swelling of the neck veins, tachycardia, shortness of breath, as well as a dry cough.
Hypovolemia
Hypovolemia is another cause of the development of the disease "oliguria". Symptoms and treatment of the disease are based on overcoming the signs of the primary disease, including fatigue and lethargy, muscle weakness, anorexia, and hypotension. A distinctive feature of the signs of oliguria caused by hypovolemia is dry mucous membranes and sunken eyeballs.

Other factors
Other causes include pathologies such as chronic renal failure, especially in its final stage, acute pyelonephritis, renal vein occlusion, and gestosis during pregnancy. There are also patients who develop oliguria after surgery, in which case the disease is a reaction of the body to a number of factors - dehydration, loss of large amounts of blood, severe infections leading to toxic shock, urinary obstruction caused by an enlarged prostate gland. It is also possible to react to postoperative medications, for example, diuretics, Methotrexate, and anticholinergic medications.
Diagnostics
For the disease "oliguria", treatment is prescribed after diagnosis and identification of the exact causes of the pathology. The doctor examines the patient, studies his medical history, and conducts a conversation in which important information is the volume of fluid consumed per day, the amount and color of urine excreted. Particular attention is paid to the presence of any aggravating factors and accompanying symptoms - fever, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, increased thirst, recent injuries, medications, allergies.
Diagnostic tests are also needed to confirm the causes of oliguria. The doctor orders a urine test to check for inflammation or infection in the kidneys. X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent helps to identify kidney stones and tumors, and ultrasound diagnostics are necessary to check for cysts.

Other diagnostic procedures include a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis, and a cytoscopy, in which a flexible telescope is inserted into the blood. Blood tests indicate the presence of anemia, kidney failure and possible urinary tract infections.
Signs and symptoms
Oliguria is classified based on the factors that cause the disease. For example, prerenal oliguria results from renal hypoperfusion and decreased fluid intake, resulting in dehydration, diarrhea, bleeding, and sepsis. Renal occurs due to impaired renal function caused by taking medications, hypoperfusion, that is, a decrease in their filtering ability. Postrenal oliguria develops when the outflow of urine is obstructed due to an enlarged prostate, tumor, or hematoma.
The disease is determined based on the amount of urine excreted. For example, in infants it is diagnosed when the volume of urine is less than 1 ml per kilogram of weight per hour, in older children - less than 0.5 ml per kilogram of weight per hour, in adults - less than 400 ml per day. If a person notices a steady decrease in the amount of urine produced, then this is a cause for concern and may indicate the presence of the disease “oliguria”. In children, during the first 3 days of life, an insufficient amount of urine produced is considered normal. This is a feature of the functioning of the kidneys during this period. It is called "transient oliguria".

In adults, the disease often manifests itself with general symptoms such as dizziness, rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, often high fever and vomiting. If a gradual decrease in diuresis is observed over two weeks, then the culprit of the disorder may be acute necrosis of the renal tubules. Symptoms of oliguria may also include arrhythmia, muscle weakness, lethargy, confusion, itching, cramps, and heart failure. The formation of stones in the ureters, urethra and kidneys also often leads to oliguria. The symptoms are as follows: severe pain in the groin, pubic area and external genital area, nausea, bloating, vomiting, fever and chills.
Oliguria and nephrotic syndrome in children
Since the kidneys are responsible for the production of urine in the body, the characteristics of diuresis can be considered as a reflection of the condition of these organs. Nephrotic syndrome is a common kidney problem in children and often leads to kidney failure. In a healthy kidney, blood flows through it and releases excess fluid, waste, and creatinine to form urine. For children with nephrotic syndrome, decreased urine output means the kidneys are unable to filter blood properly. The less urine produced per day, the more severe the kidney condition. Oliguria in children with nephrotic syndrome is a dangerous sign, as it indicates that damaged kidney tissue cannot be repaired. In such circumstances, immediate medical attention and treatment is the only option to avoid dialysis and the need for a kidney transplant.

Nephrotic syndrome can be managed with drug therapy, but damaged kidney tissue is more difficult to restore.
Treatment of the disease
Oliguria is a disease whose effective treatment involves three successive stages:
- elimination of the pathological cause, the underlying disease;
- restoration of homeostasis of the body;
- treatment of complications.
Therapy for a disease always depends on the cause that caused it, and in most cases, diuresis can be restored and the body’s condition normalized. One of the treatment methods today is to insert a catheter into the urethra in order to eliminate its obstruction and remove the accumulation of urine. If there is a risk of kidney failure, then an artificial filter is used instead of a kidney, which allows the normal removal of waste products from the blood to be restored.

In some cases, hospitalization is necessary; in the hospital, the patient is given intravenous fluid if dehydration is observed. It is also recommended to stop taking any medications that may be toxic to the kidneys. It is important to restore normal renal perfusion; this requires correction of arterial hypotension and vasodilatory drug therapy.
Polyuria, anuria, oliguria
Problems with the production and excretion of urine can be of various types. There are other forms of diuresis disturbance, in addition to such a malfunction as oliguria. Anuria is a pathology in which the flow of urine into the bladder is stopped. It is important not to confuse anuria with acute urine retention, when it enters the bladder but is not removed from there. Another disorder is polyuria, in which, on the contrary, a lot of urine is produced. An increase in urine formation may be associated with diseases of the kidneys themselves, with hormonal and other disorders of the body. Polyuria, oliguria, and anuria require treatment, which is based, first of all, on eliminating the root cause.
Home remedies for treatment
There are several natural and safe remedies for the treatment of oliguria, the risk of side effects from their use is minimal. Some of the folk recipes are very popular and have long been used to normalize diuresis. For example, they are very useful, helping to remove toxins from the body, and also stimulate the functioning of the kidneys and pancreas.

A mixture of chopped cilantro and buttermilk (a low-fat byproduct of butter making) is very effective. Drink this drink with every meal. Anemarrhena leaves and roots are very useful in the treatment of oliguria. All you need to do is pour 300 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the dried mixture of this plant and let it brew for a couple of hours. To improve your condition, drink two glasses of this infusion daily until diuresis returns to normal.
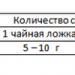
Plantain seeds and gentian root are considered very effective in treating the disease. Taking a decoction of these herbal remedies promotes urine formation and also reduces swelling of the prostate gland. Many healers advise drinking so-called copper water. Pour clean water into a copper container overnight, and the next day drink this water with copper ions. You can increase urine flow by using cardamom powder diluted in warm milk. You should drink this drink every day until you get results.
So, we have considered such issues as oliguria, symptoms, treatment of the disease. If any manifestations of the disease occur, consult a doctor immediately. In addition, it is recommended to avoid fatty and salty foods, eat a balanced diet, including as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible in your diet. Urinate as soon as you feel the urge to urinate. Drink more water to protect your body from dehydration.
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?