Is it possible to cure celiac disease in a child? What do parents need to know about childhood celiac disease? A pediatric gastroenterologist talks. Treatment of pathology with probiotics
Celiac disease is a condition in which there is an intolerance to gluten, or gluten. This substance is found in cereal plants. Gluten is found in barley, wheat, oats and rye. With this disease, it is strictly forbidden to eat these foods. Celiac disease is usually diagnosed in children, and symptoms can vary in intensity. Another name for this condition is celiac enteropathy.
Forms of the disease
Celiac disease in children occurs in different ways. Doctors distinguish three forms of this condition. Each of them is characterized by a certain degree of severity of the main features.
- Typical celiac disease. All symptoms of the condition are quite pronounced. With this form, diagnosing the disease is not difficult.
- Atypical celiac disease. Doctors call this form low-symptomatic. Signs of the disease are mild. In other words, this condition is characterized by erased symptoms. Diagnosing the disease in this case is more difficult. A number of additional examinations will be required.
- Hidden celiac disease. Diagnosis of this condition is extremely difficult. The disease does not manifest itself in any way for several years. Without additional tests and examinations, it is impossible to confirm the diagnosis.
Gluten intolerance is a chronic condition. It is impossible to completely cure the disease. If a doctor has diagnosed a child with such a diagnosis, then a special diet must be followed throughout his life.
Diagnosis of the disease
In some cases, characteristic symptoms indicate the presence of a pathology of the digestive system. However, with indolent forms, additional diagnostics are necessary.
A baby with suspected gluten intolerance should be shown to a pediatrician.  Doctors usually prescribe the following examinations:
Doctors usually prescribe the following examinations:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs;
- X-ray of the intestines;
- colonoscopy;
- laboratory diagnostics.
The disease is detected using laboratory tests. Specialists examine the child's stool, blood, and samples of intestinal mucus.
There is no specific diagnostic scheme for celiac disease in children. The doctor focuses on the external manifestations and complaints of the parents. After this, various examinations are prescribed.
Detection of disease in newborns
Celiac disease does not manifest itself in any way in a newborn child. This condition reveals itself only if an allergen enters the body. In celiac disease, this is gluten. If a woman feeds her baby exclusively with breast milk, then the likelihood of developing symptoms is low.
However, it should be remembered that all substances from a nursing woman’s food will be contained in small concentrations in her milk. Therefore, the first mild signs of the disease will appear in the newborn if the mother eats porridge made from wheat or oats. Bread and baked goods will have a similar effect.
Gluten intolerance is a hereditary disease. If it is diagnosed in parents, then the child is at risk. Complementary foods are administered to such a baby with caution.
In most children, celiac disease is diagnosed precisely when they begin to learn to eat adult foods. The baby reacts normally to the introduced vegetable purees, but after getting acquainted with the cereals, digestive problems begin. For this reason, pediatricians advise choosing gluten-free cereals to introduce your child to grains. Rice, buckwheat or corn are great.
Typical symptoms of the disease
Your pediatrician will tell you what celiac disease is. This condition is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, by which parents can suspect the disease.
- Frequent defecation. If stool is observed about 5 times a day, then this may be caused by gluten intolerance. Diarrhea is a common companion to celiac disease in children under one year of age and older.
- Liquefaction of feces. Watery stool consistency and the appearance of mucus, fat or foam are signs of celiac disease. An unpleasant odor also indicates a problem.
- Bloating. Another manifestation of pathology is bulging of the abdomen.
- Lack of weight. A child with gluten intolerance eats well, but gains little weight. This is especially obvious during the period of introducing complementary foods.
All of these signs indicate the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies. The child must be shown to the pediatrician. The doctor will order an examination.
Additional symptoms of the disease
 Indirect signs can also indicate gluten intolerance in a child. Thus, children with celiac disease are usually whiny and irritable. Opposite manifestations can also be observed - lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue.
Indirect signs can also indicate gluten intolerance in a child. Thus, children with celiac disease are usually whiny and irritable. Opposite manifestations can also be observed - lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue.
Other additional signs include:
- dry skin;
- dermatitis;
- low muscle tone;
- bone fragility;
- bleeding gums;
- poor posture;
- anemia;
- dental problems.
A child with this disease does not receive the necessary microelements, vitamins and other nutrients from food. Later, with the onset of adolescence, problems with the reproductive system are noted. Girls may not have menstrual flow.
Necessity of diet
If you suspect gluten intolerance, your doctor will recommend avoiding such foods. A child should not be given bread and cereals based on the following grains:

It is important to remember that there are products that contain a dangerous substance in hidden form. These are any canned food and semi-finished products. Do not eat sauces, seasonings, ice cream, or filled candies. Even baby purees may contain gluten. For this reason, it is important to especially carefully choose food for complementary feeding and further nutrition.
In the winter season, the child will receive the necessary carbohydrates from permitted grains: buckwheat, corn, rice. Potatoes are allowed. Summer and warm weather allow you to eat fresh vegetable purees prepared without preservatives.
A diet for possible celiac disease in children is prescribed for at least 6 months. Next, the doctor analyzes the results of therapy. If the intensity of the symptoms has decreased and the child begins to feel better, the diagnosis is confirmed. Such children must follow a special diet throughout their lives.
Complications of celiac disease
Treatment for celiac disease in children is necessary. The body's inability to digest gluten is due to a lack of necessary enzymes. There is no drug treatment for this condition. Therapy is associated with adherence to a gluten-free diet. This is a necessary measure, since lack of treatment can lead to complications.
 Celiac disease is almost always accompanied by pain. The child experiences discomfort during bowel movements. After eating, the discomfort intensifies.
Celiac disease is almost always accompanied by pain. The child experiences discomfort during bowel movements. After eating, the discomfort intensifies.
If measures are not taken and gluten is not excluded from the diet, the child will develop allergic reactions. Swelling is often observed. This is a consequence of impaired protein metabolism.
Another complication of enteropathy is rickets. The child's bones become brittle and often break. Posture becomes distorted and scoliosis appears. Problems begin with leather derivatives. Nails break and hair falls out. In children with celiac disease, tooth enamel is often destroyed and caries appears.
The most serious complications of celiac enteropathy are:
- malignant neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract;
- arthritis;
- diabetes;
- autoimmune disorders;
- pericarditis.
To avoid the development of dangerous conditions, it is important to start therapy in a timely manner. The child will be recommended special nutrition. Vitamins will strengthen the immune system. Enzymatic and probiotic preparations will regulate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
1628 views
Celiac disease is a serious disease in which the immune system attacks the small intestine in response to gluten consumption. The immune system accepts it as a protein foreign to the body and begins to actively produce antibodies, thereby damaging the small intestine. For this reason, the disease is considered to be autoimmune. Symptoms of celiac disease in children may include chronic diarrhea, weight loss and fatigue.
How to recognize the disease?
Each child with celiac disease may complain of different symptoms. While diarrhea and weight loss are classic signs of celiac disease in children, most cases are asymptomatic.
In addition to diarrhea and weight loss, the disease may include:
- pale skin (anemia);
- headaches;
- acid reflux;
- heartburn;
- constant fatigue and apathy;
- damage to tooth enamel;
- numbness in the limbs;
- abdominal pain;
- joint pain;
- bad breath.

Celiac disease in children under one year of age in 75% of all cases manifests itself as overweight or obesity. In the case of a child becoming ill at an older age, the signs may be as follows:
- chronic constipation;
- diarrhea that lasts several weeks;
- delayed puberty;
- growth retardation;
- bloating and abdominal pain;
- yellow teeth with an uneven surface.
How to determine celiac disease in an infant? In infants, the disease can be recognized by a swollen abdomen, chronic diarrhea, developmental delays, moodiness and crying due to abdominal pain. Some children may develop itchy, blistered skin. The rash appears on the buttocks, torso, head, knees and elbows.

Diagnostic measures
The disease can be diagnosed at a very early stage, because from about 5 months of age, parents begin to introduce small amounts into the baby's diet. The first symptoms appear immediately after eating in the form of vomiting and diarrhea. In older children, the list of side effects is significantly expanded. After consulting a doctor, celiac disease in children is diagnosed using several methods.
Health history
The doctor will take a medical history and interview the parents. Questions could be:
- what physical symptoms does the child have;
- how long do they take to appear;
- how often symptoms occur;
- are there any family members suffering from autoimmune diseases;
- child development according to average statistical data.
Physical examination
Depending on the symptoms of the little patient, the doctor will conduct a physical examination, the purpose of which will be:
- definition of anemia;
- palpation of the abdomen for pain;
- visual determination of abdominal enlargement;
- determination of loss of sensation in the limbs;
- examination of the skin for skin rashes.
If the doctor suspects a pathology, he will recommend a blood test.

Blood analysis
Blood tests can help detect:
- antigliadin antibodies;
- endomial antibodies;
- antibodies against transglutaminase.
Blood is screened for antibodies against deamidated gliadin peptide (TSG), and sometimes antigliadin (AGA) and andomysial antibodies (EMA).

Colonoscopy of the small intestine
Experienced doctors who have encountered this pathology more than once and know how to identify celiac disease in a child often prescribe a colonoscopy first. Intestinal colonoscopy is considered the most accurate test for intestinal diseases. The doctor uses a special camera to examine the inside walls of the intestines and take samples of the intestinal lining. Typically, multiple samples are obtained to improve diagnostic accuracy.
If the villi in the small intestine appear abnormal, the doctor concludes that the child has a suspected pathology. Violation of the structure of the villi does not allow the body to break down carbohydrates and dairy products. This explains why many children with celiac disease are also lactose intolerant.
DNA diagnostics
Celiac disease is a genetic disease, which means that the baby inherited it from one of the parents. To accurately confirm or rule out the disease, it is best to begin screening for celiac disease in a child with a DNA test. To carry out this diagnostic method, a smear is taken from the inner surface of the cheek and it is checked whether the gene responsible for celiac disease is in the DNA chain.
What is the essence of treatment?
Once the disease is diagnosed, the main goal of treatment for celiac disease in children will be a gluten-free diet, which will need to be followed throughout life. Yes, it will be difficult and will require parents to pay special attention to their baby’s food. You will also need to monitor food in the kindergarten and school canteen. The child will have to learn to live in a new way. The diet should be developed by a specialist. You should not do this on your own, since the baby’s diet should remain rich in nutrients.

In addition to dietary treatment, supplementation with iron, folic acid, calcium and, if indicated, vitamin B12 is often recommended.
Gluten-free diet
Parents of young patients should know which foods contain gluten and which do not. It is also worth understanding that some products contain hidden gluten. If a label says “gluten-free,” this usually indicates that there is a harmless level of gluten, not no gluten at all.
Important! With strict adherence to the diet, the intestines usually heal and symptoms disappear, but eating gluten again may cause a relapse.
Prohibited Products
The diet for celiac disease in children includes a complete avoidance of the following foods:
- pasta;
- semolina;
- margarine;
- canned food;
- products that contain yeast;
- seasonings;
- wheat;
- rye;
- barley;
- oats;
- sausages;
- crab sticks;
- ice cream;
- cakes, cookies and other sweets containing gluten.

Gluten-free alternatives to bread, flour, pasta and other foods are now widely available.
Authorized Products
It will be quite difficult to create a menu for your baby, because most of the child’s familiar and favorite foods will be excluded from the diet.
You can include in your diet:
- porridge (rice, corn, buckwheat);
- fish;
- all types of meat, including liver, kidneys, lungs;
- dairy products (milk, cheese, fermented baked milk, sour cream, butter);
- fruits vegetables;
- honey, sugar;
- spices (salt, pepper);
- coffee, tea, cocoa;
- gluten-free desserts.
It is important to carefully study the ingredients on the label when purchasing food. Most supermarkets have special sections where only gluten-free foods are displayed.

Is disability granted?
Currently, all children with ceakilia are given disability for a period of 5 years. After time has passed, parents, after re-examination, extend the terms and so on until the child is 16 years old.
Results
A diagnosis of celiac disease means that a child will have to avoid gluten for the rest of their life. Learning a new way of eating is one of the hardest things about this disease. Especially at the beginning, following a gluten-free diet can be a difficult stage in the life of parents, since it will require adaptation to changes in the dietary habits of the little patient.
The comforting news may be that there are now many products available for people with celiac disease. Gluten-free products will help prevent the development of serious complications in adult life, such as severe infections, pregnancy problems, osteoporosis, depression, epilepsy, and cancer. The most important thing is to quickly diagnose the pathology and begin treatment.
Celiac disease in children is a hereditary pathology. Another name is Guy-Herter-Heubner disease. The mechanism of its development is explained by gluten intolerance. The substance is a protein, an excess of which is observed in wheat, barley, rye and food products containing it. Gluten irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and activates the immune system, prompting it to respond by producing antibodies to its own cells. As a result, autoimmune inflammation develops and intestinal tissue is destroyed.
Factors predisposing to celiac disease

The main cause of Guy-Herter-Heubner disease is genetic predisposition. But various pathologies and conditions can also provoke its development, for example:
- defects of the small intestine;
- weak immunity;
- abdominal surgery;
- infection of the body, affecting the villous structure of the intestine;
- diseases of an autoimmune nature - dermatitis, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis.
Dr. Komarovsky, together with other specialists, puts forward a viral theory of the origin of the disease. The diagnosis of “viral celiac disease” is confirmed by the detection of specific antibodies to the adenovirus in the blood.
Clinical features of celiac disease

The primary symptoms of celiac disease in children do not appear immediately. In infants, they are observed during the period of introducing complementary foods, when gluten-containing products are introduced into the diet. More clear deviations characteristic of the disease are established before the year, at approximately 7–8 months. For some children, the picture of pathology appears closer to their 3rd birthday.
All parents should know the typical symptoms of celiac disease. These include:
- vomit;
- swelling;
- refusal to eat;
- bloating;
- signs of rickets;
- growth retardation;
- body weight deficiency;
- lack of teeth;
- early caries;
- mood swings;
- secretion of fetid, foamy, etc.
Atypical symptoms of celiac disease are a number of disorders that are not directly related to the digestive system. These are:
- arthritis;
- anemia;
- dermatosis;
- hair loss;
- dental problems;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- symptoms inherent in endocrine diseases.

Untimely treatment of celiac disease causes exhaustion of the body and inhibits the development of the child. As you get older, the clinical picture of the disease changes. In children of kindergarten age, celiac disease is accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and problems with bowel movements. The physical development of a sick child differs from that of his peers.
In adolescence and young adulthood, celiac disease in children develops against the background of a deficiency of vitamins, minerals and various nutrients that the body does not receive. Help to recognize an anomaly:
- anemia;
- osteoporosis;
- short stature;
- itching and rash on the body;
- delayed puberty;
- underdevelopment of tooth enamel.
How is celiac disease diagnosed?

The pediatrician makes the primary diagnosis based on a general examination of the child and refers the patient to a gastroenterologist. Suspicions are confirmed after receiving laboratory and instrumental diagnostic answers. Laboratory research methods include genetic tests, biochemical and general blood tests, bacteriological, microscopic and biochemical examination of stool.
Among the instrumental ways to diagnose celiac disease are:
- colonoscopy;
- X-ray of the intestine;
- histological analysis of a biopsy taken from the mucous membrane of the tract.
Principles of celiac disease therapy

Treatment for a child with symptoms of celiac disease is varied. The patient is put on a diet, vitamins, enzymes and probiotics are prescribed. Diet therapy involves eliminating foods containing gluten from the diet. In addition to cereals and baked goods, dangerous protein is found in sauces, sausages and dairy products. Children are not allowed to eat ice cream.
Infants are transferred to artificial adapted formulas with hydrolyzed cow's milk protein or soy:
- Nutri-soy;
- Frisosoy;
- Pregestimil.
In case of exacerbation of celiac disease, medicinal mixtures become the basis of children's nutrition. As the condition stabilizes, the diet is gradually enriched with dairy-free, gluten-free cereals, vegetable puree and cottage cheese.
To improve the activity of the digestive glands, enzymes are included in the treatment - Pangrol, Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin. The ratio of harmful and beneficial intestinal flora is corrected with probiotics - Bifiform, Acipol, Laktofiltrum.
Vitamin therapy is aimed at replenishing missing vitamins and microelements. Treatment with multivitamins is developed individually. The child must take the course in spring and autumn. Additional indications for taking vitamins are infectious diseases and vitamin deficiency.
Celiac disease in children is a hereditary pathology in which the intestinal mucosa is affected and its function is impaired due to gluten (gluten) intolerance. It is found in large quantities in cereals. When symptoms of the disease appear, the child is prescribed a special diet, which, if followed, will normalize his condition within a year, otherwise the pathology can cause disability and death.
The main cause of gluten intolerance syndrome is considered to be genetic disorders that lead to damage to the intestinal mucosa when consuming foods containing gluten.
The following diseases are considered provoking factors of celiac enteropathy:
- autoimmune pathologies of the thyroid gland and pancreas;
- colitis;
- chronic inflammation of the liver;
Stress or surgery, for example, removal of appendicitis, can give impetus to the onset of the disease. But the exact causes of celiac disease are unknown.
Symptoms of celiac disease in children

Often the onset of celiac disease coincides with the introduction of complementary foods that contain flour products into the baby’s diet. Therefore, parents can see the first signs of celiac disease when the child reaches the age of 6-12 months. Symptoms of celiac disease in a child under 2 years of age may include the following:
- frequent, foamy, greasy stools with a strong odor;
- stool is light or has a grayish tint;
- weight loss;
- growth retardation compared to peers;
- constant tearfulness;
- lethargy or excessive agitation;
- pale skin;
- lack of appetite;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- nausea that ends with vomiting;
- lactase deficiency, which is manifested by rumbling in the stomach, bloating after drinking milk.
Pathogenic intestinal bacteria are usually not detected in stool, and stool cannot be normalized by antibiotic therapy and taking enzyme medications.
Children with celiac disease experience delayed psychomotor development; they begin to hold their heads up, crawl, and walk later than their peers. They show less interest in new toys and people.
Signs of celiac disease in children over 2 years of age and adolescents may include:
- loose stools alternating with constipation;
- pallor;
- fast fatiguability;
- short stature (girls do not grow more than 155 cm, boys - 165 cm);
- delayed sexual development;
- underdevelopment of the mammary glands;
- swelling of the legs;
- characteristic skin rash of allergic origin;
- bright mucous membranes;
- frequent infections.
Girls begin their periods at 15 years of age or later.
Half of children with celiac disease develop osteoporosis, a decrease in bone density. This leads to spontaneous fractures. By eliminating grains, bone density will be restored.
Due to celiac disease, the absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, iron, calcium, and vitamins is impaired, and hypovitaminosis develops, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dry skin;
- dental dystrophy;
- hair loss;
- problems with nail plates;
- stomatitis;
- decrease in hemoglobin level.
Diagnostics and tests
In making a diagnosis, the doctor is helped by examining the child, taking an anamnesis, and instrumental research methods. The doctor assesses the patient's height and weight and palpates the abdomen. The following laboratory tests and instrumental methods help in making a diagnosis:
- clinical blood test;
- bacteriological examination of feces, studying it under a microscope, determining the amount of soap and fatty acids in feces;
- blood biochemistry, which will show a reduced content of proteins, calcium, phosphorus, cholesterol, lipids, non-heme iron;
- genetic tests;
- intestinal biopsy, during the procedure the doctor takes a small section of the mucous membrane for further examination;
- FGDS allows the doctor to examine and assess the condition of the digestive tract;
- An abdominal ultrasound can help see damage to the intestines and determine the cause of digestive problems;
- X-ray, which allows you to detect osteoporosis and intestinal dyskinesia, to see horizontal levels in the intestinal loops.
- Densitometry helps measure bone density.
If celiac disease is suspected, the child is referred for consultation to an allergist-immunologist. Your doctor may prescribe a gluten-free diet for a while and then repeat the tests. If the results of the repeated examination are better, the doctor will diagnose celiac disease.

Treatment
Treatment of celiac disease in children is aimed at restoring intestinal function, normalizing weight and eliminating the lack of essential substances: vitamins, calcium, iron.
The main thing in the treatment of pathology is adherence to a gluten-free diet, that is, the elimination of the provoking factor of the disease. In most children, diet therapy leads to a weakening of the signs of celiac disease and normalization of intestinal function. Typically, for the organ to fully recover, at least 3 months must pass after giving up gluten-containing foods. During this entire time, it is necessary to adjust the content of substances important for the body, for which the doctor may prescribe the following medications in injections:
- iron-containing products;
- vitamins;
- calcium-containing products;
- saline solutions for intravenous administration.
If a child with celiac disease requires parenteral nutrition, parenteral nutrition is prescribed.
When the diet does not bring results, glucocorticoids (prednisolone) are prescribed to relieve inflammation. Treatment with them can last 1.5-2 months.
To improve digestion in celiac disease, children are prescribed enzyme preparations: Creon, Micrasim. To normalize the intestinal microflora, the child is given probiotics and prebiotics: Hilak forte, Acipol, Bifidumbacterin.
Gluten-free diet for celiac disease

Foods containing gluten should be excluded from the diet of a child with celiac disease, such as:
- pasta;
- semolina;
- wheat, oats, barley, rye.
The following foods may contain small amounts of gluten:
- canned fish and meat;
- sausages;
- cocoa powder;
- soy products;
- ice cream;
- chocolate;
- sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise;
- products containing malt.
A sick child should avoid bouillon cubes, instant soups, instant coffee and kvass.
Children with celiac disease usually cannot have whole milk, as many of them are lactose intolerant.
The following products are allowed:
- corn, rice, buckwheat, millet cereals;
- hard-boiled eggs, steam omelet;
- boiled, stewed or baked meat;
- butter and vegetable oil;
- berries, fruits and vegetables;
- legumes;
- fish.
There are gluten-free products in stores, they are marked with a crossed out ear.
Komarovsky about gluten and the gluten-free diet
Complications
The disease has a wave-like course, it can cause disability, mental and mental retardation, and the death of a child.
Children with celiac disease may develop ulcers in the small intestine and are more likely to develop digestive tract cancer. The disease may cause infertility in the future.
To stop the progression of pathology and the onset of complications, you must follow a gluten-free diet throughout your life. Therefore, if a child shows signs of celiac disease, you should immediately show him to the doctor so that the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and select treatment.

A child with celiac disease should have a separate table and utensils. When preparing food for him, you must follow the following recommendations:
- If in a house where there is a child with celiac disease, other family members do not follow a gluten-free diet, then you need to separate the kitchen equipment.
- Food for a child should not be mixed with the same spoon as dishes for a regular table.
- You cannot cook food with and without gluten in the same pan. It is advisable to have separate utensils for preparing gluten-free food. When this is not possible, it is recommended to thoroughly wash all pots.
- It is advisable to prepare gluten-free food for your child before preparing meals for the rest of the household. If food is being prepared at the same time, you should wash your hands thoroughly after touching foods containing gluten.
- Sharing cutting boards and knives for slicing regular and gluten-free bread is prohibited.
- If gluten gets into your child's food during cooking, it will have to be cooked again.
Disability due to celiac disease
Whether a child with celiac disease will be given a disability depends on the severity of the disease. It is intended for patients who, due to the disease, have a severe metabolic disorder, which has led to a significant delay in physical (body weight deficiency) and psychomotor development, which cannot be eliminated within six months of therapy. The presence of complications and the involvement of not only the digestive tract, but also other organs in the pathological process are also taken into account.
When celiac disease is diagnosed at an early stage and the child follows a gluten-free diet, the prognosis is favorable and disability is not given.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for celiac disease. If a child has a hereditary predisposition to celiac disease, then it is recommended to show him to the doctor once every six months in order to promptly identify the pathology.
Relatively recently, a number of studies have been conducted on the atypical form of celiac disease in children.
Research results:
- It has been noted that the atypical form of celiac disease is more common in older children. Less common in children starting from 5 years of age.
- It has been observed that girls suffer from celiac disease more often than boys.
- A close relationship between atypical celiac disease and damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which is responsible for the proper joint functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, has been proven. Disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus lead to damage to the adrenal glands, lack of body weight, and diseases of the thyroid gland.
- There has been a proven connection between celiac disease and diseases such as type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroiditis. If a child is diagnosed with one of the above diseases, the likelihood of having the other two is extremely high.
- There is a proven connection between celiac disease and various diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Many children whose examination consisted of identifying exclusively diseases of the gastrointestinal tract were later diagnosed with an atypical form of celiac disease.
- The research results also revealed three groups of symptoms of atypical celiac disease in children.
Symptoms of an atypical form of celiac disease in children
The most common symptoms of atypical celiac disease in children are:
- growth retardation;
- low weight;
- neurological disorders;
- delayed sexual development;
- atopic dermatitis;
- anemia;
- alopecia;
- thinned small intestinal mucosa.
In atypical celiac disease, children may sometimes exhibit intestinal and extraintestinal symptoms of typical celiac disease. However, in the atypical form of celiac disease they are less pronounced.
This group of symptoms includes:
- intermittent diarrhea (periodic);
- periodic abdominal pain;
- weakness and fatigue;
- osteoporosis;
- aphthous stomatitis.
The third group of symptoms of atypical celiac disease includes symptoms that are more often observed in the latent (hidden) form of celiac disease:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, gastroduodenitis, etc.);
- bronchial asthma;
- hives;
- psoriasis;
- Vetiligo;
- obesity;
- chronic viral infections.
Diagnosis of atypical celiac disease in children
The main part of the diet in a gluten-free diet should be vegetables, fruits, cereals and cereals (derived from grains that do not contain gluten), meat, eggs, vegetable fats and finished products that do not contain gluten (gluten-free baked goods, baked goods without gluten-free, gluten-free pasta, gluten-free sausages and sausages, gluten-free sauces and seasonings, gluten-free pates, etc.)
In most cases, children with atypical celiac disease need to avoid eating dairy products in addition to foods containing gluten. The reason is lactose or casein intolerance, developing due to celiac disease or as an independent disease. Symptoms of dairy intolerance include flatulence, severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rash.
With strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, the health of children suffering from an atypical form of celiac disease begins to recover after 2-3 weeks.
When treating an advanced form of celiac disease, the body's recovery process may take longer.
In addition, the duration of recovery depends on whether the child has diseases and complications caused by celiac disease. Eliminating them usually takes much longer than eliminating the symptoms of atypical celiac disease.
When treating atypical celiac disease, along with a gluten-free diet, rehabilitation therapy is mandatory - vitamin therapy, courses of enzyme preparations, courses of probiotics and other restorative measures.
Prognosis of the course of an atypical form of celiac disease in children
A severe and very severe prognosis is possible when diagnosing a very advanced stage of celiac disease.
Therefore, early diagnosis of celiac disease is important to avoid the development of complications.
If celiac disease is diagnosed in a timely manner and appropriate treatment is prescribed, the prognosis is good.
In most cases, following a gluten-free diet eliminates the symptoms of celiac disease and restores the intestinal mucosa and absorption function.
The main condition for a favorable prognosis is lifelong adherence to a gluten-free diet (foods gluten free).
IMPORTANT. Violation of the diet leads to resumption and progression of the disease and increases the risk of complications.
Gluten free desserts. Puffed rice with powdered sugar, roasted nuts or seeds, orange jelly, grapefruit jelly and persimmon jelly
- Why persimmons are mouth-watering and how to make them sweeter
- Exercises for pregnant women
- So that the persimmon becomes soft and does not knit
- What to do if the persimmon knits hard
- What to do if you burn your hands with hot pepper
- How to remove the film from pork liver
- Liquid smoke how to use in the oven
- Atherosclerotic heart disease Disease as a cause of death
- Captopril - indications and instructions for use (how to take tablets), analogues and reviews
- Coding of chronic colitis in ICD 10 ulcerative colitis
- Streptocide (tablets): instructions for use
- What is considered a violation of regularity?
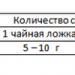
- How much soda is contained in different containers?
- How to prepare herbal antibiotics at home
- Solotvyno salt lamp
- How does muscle pain from stress manifest itself?
- Activated carbon (manufacturing)
- What is activated carbon made from?
- Reduces blood pressure
- Why do persimmons make your mouth stick? Why does persimmon knit?