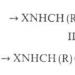Chloroform and its effect on humans. Test work chloroform Chloroform at home
(Chloroformium, trichloromethane) is a colorless transparent liquid with a peculiar sweetish odor and pungent taste.
Chloroform is miscible in all proportions with alcohol, ether, fatty and essential oils and is a good solvent for many organic (paraffin, resin, rubber, lecithin) and some inorganic substances (iodine, sulfur, phosphorus).
Chloroform is quite unstable. In the light it is oxidized by oxygen, forming chlorine, hydrochloric acid and especially poisonous phosgene, so it is important to avoid chloroformation in an open flame. To protect chloroform from decomposition, it should be stored in orange glass bottles. For the same purposes, alcohol and sometimes methenamine are added to it.
Chloroform belongs to the group of fatty drugs that cause reversible paralysis of all vital functions. This effect is found in all organisms - bacteria, protozoa, plants, animals.
The local effect of chloroform is expressed in irritation of both sensitive nerve endings and other tissue elements. On the skin, liquid chloroform first causes a feeling of cold associated with its evaporation, then burning and redness, and when protected from evaporation, inflammation with the formation of blisters.
On mucous membranes, the irritant effect is even more pronounced and ingestion of chloroform can lead to severe damage to the stomach, bloody vomiting and diarrhea.
Chloroform vapors are less irritating, but when inhaled they lead to a variety of reflexes that disrupt respiratory movements, cardiac activity and other functions.
The high toxicity of the substance can cause cardiac arrhythmias, dystrophic changes in the myocardium, cirrhosis and liver atrophy.
Chloroform was one of the first drugs proposed as an anesthetic (general anesthesia). Since the mid-19th century, it has been widely used in anesthesiological practice.
With an excessive dose of chloroform during anesthesia, primary respiratory arrest could occur due to paralysis of the respiratory center.
The most dangerous complications during anesthesia were observed in cardiac activity - up to and including sudden cardiac arrest.
Due to the introduction of new drugs and methods of general anesthesia into medicine, in 1985 the drug chloroform for anesthesia (Chloroformium pro narcosi) was excluded from the range of drugs. At the same time, the drug “Chloroform”, intended for external use, has been retained in the nomenclature. Due to its irritating effect on the skin, this drug (usually mixed with methyl salicylate, turpentine and other agents) is used for rubbing for neuralgia and myositis. In rare cases, chloroform is prescribed in the form of drops for vomiting, hiccups (mixed with valerian tincture), as well as in the form of a special “Anti-smoke mixture” for damage to the respiratory tract by irritating arsines (a poisonous colorless gas - a chemical compound of arsenic and hydrogen).
The discovery of many chemical substances was not intentional, but accidental, during the synthesis or study of the properties of a substance. However, many of the accidentally discovered substances became very important; they were used not only in chemistry, but also in medicine, industry and other fields. Chloroform, which will be discussed further, is one of these substances.
Name
The name of this substance has several varieties. After all, like all organic compounds, it obeys the laws of the general nomenclature of molecules, trivial names and a name based on the composition of the molecule.
Therefore, there are several possible names for chloroform:
- carbon trichloride;
- chloroform;
- trichloromethane.
Chloroform: what is it? You can understand it from the names of the compounds, or you can consider the geometric structure of the molecule.
Molecule structure
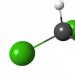
The chloroform molecule consists of three chlorine atoms and one hydrogen atom, each atom bonded to a central carbon. Essentially, the trichloromethane molecule is the product of hydrogen atoms on chlorine atoms in a methane molecule when exposed to certain conditions.
Moreover, all C-CL bonds are completely equivalent and highly polar. The C-H bond, against the background of other bonds that have appeared in the molecule, becomes even more polarized and becomes extremely vulnerable. Therefore, with further processing of the molecule, the C-H bond is easily broken and hydrogen is replaced by other atoms (for example, also chlorine with the formation of carbon tetrachloride).
Let's look at what chloroform looks like. The formula looks like: CHCL 3. The structural formula will look like this:

Both structures reflect the chemical essence that chloroform carries. The formula shows that the molecule is quite stable and strict conditions must be applied to enter into reactions.
Physical properties
The physical properties of trichloromethane can be characterized as follows:
- Under normal conditions (room temperature, normal atmospheric pressure 100 kPa, humidity not higher than 80%), this substance is a strongly odorous, colorless liquid. The smell of chloroform is quite sharp, heavy, enveloping, reminiscent of the smell of ether. The substance tastes sweet, but you should not try it, as it is extremely toxic.
- It does not dissolve in water, it can dissolve only in different types. With water it can form low-concentration (0.23%) solutions.
- The boiling point of this compound is lower than that of water, approximately 62 0 C.
- The melting point is sharply negative, -63.5 0 C.
- The density of chloroform is greater than and is 1.483 g/cm3.
- The strong, pronounced toxic nature of the substance in its effect on the body belongs to the group of narcotic compounds.
When dissolved in water, carbon trichloride is capable of forming azeotropic mixtures. In this case, the chloroform in the solution will be 97.5%, and water only 2.5%. The boiling point of such a solution is lower compared to that of pure trichloromethane and is 52 0 C.

Chemical properties
Like all chlorinated derivatives of methane, chloroform does not exhibit chemical activity. Therefore, there are few reactions that are characteristic of it. For example, treatment with chlorine molecules in the process of technological production of all methane derivatives by chlorination. To do this, liquid chloroform is taken, the reactions proceed according to a radical mechanism, requiring the presence of ultraviolet radiation as a prerequisite and light quanta.
CHCL 3 + CL 2 = CCL 4 + HCL
According to the reaction equation, it is clear that the product is completely chlorine-substituted methane - carbon tetrachloride. Such reactions are one of the ways to produce carbon tetrachloride in industry.
Chemical properties also include an azeotropic mixture with water, which chloroform can produce. What it is? That is, one in which the components of the solution do not undergo any changes when boiling. It is impossible to separate such a mixture into fractions using the boiling method.
Another type of reaction that chloroform can undergo is the replacement of halogen atoms with other atoms or functional groups. For example, when reacting with an aqueous solution, it forms sodium acetate:
chloroform + NaOH(aqueous solution) = + sodium chloride + water
In addition, a practically significant reaction is the interaction of chloroform with ammonia and potassium hydroxide (concentrated solution), since as a result of such interaction,
Chloroform + ammonia + potassium hydroxide = KCN + + water
Chloroform storage
In the light, trichloromethane decomposes to form dangerous, toxic products:
Chloroform = phosgene + hydrochloric acid + molecular chlorine + carbonic anhydride
Therefore, the storage conditions for chloroform must be special - dark glass bottles with dense ground-in stoppers. The bottle itself should be stored away from sunlight.

Receipt
Chloroform is produced in several ways.
1. A multi-stage process of methane chlorination, which occurs by a radical mechanism under the influence of ultraviolet light and high temperature. The result is not only chloroform, but also three other products: chloromethane, dichloromethane and carbon tetrachloride. The reaction looks like this:
CH 4 + CL 2 = CH 3 CL + HCL - chloromethane and hydrogen chloride are formed
CH 3 CL + CL 2 = CH 2 CL 2 + HCL - dichloromethane and hydrogen chloride are formed
CH 2 CL 2 + CL 2 = CHCL 3 + HCL - trichloromethane (chloroform) and hydrogen chloride are formed
CHCL 3 + CL 2 = CCL 4 + HCL - carbon tetrachloride and hydrogen chloride are formed
In this way, trichloromethane is synthesized in industry.
2. Interaction between bleaching lime and ethyl alcohol. This is a laboratory method.
3. Preparation of chloroform by electrolysis (action of electric current) on alkali metal chlorides in an atmosphere of acetone or ethyl alcohol. Also a laboratory method for producing trichloromethane.

Cleaning
Once chloroform is obtained, it needs to be purified. After all, if it is used for medical purposes, then the content of impurities in it is simply unacceptable. If the purpose of use is technical, then the content of foreign substances should be limited.
There may be various impurities that chloroform contains. What it is? What are they?
- Ethanol.
- Hydrogen chloride.
- Phosgene.
- Chlorine.
There are two main ways to purify chloroform from these impurities:
- abundant rinsing with water followed by drying (allows you to completely get rid of ethanol);
- trichloromethane is washed with a strong acid, then with a strong alkali, then with water. Subsequent processing consists of drying using a water-removing agent - calcium chloride. The substance is then distilled in a fractional column.

History of discovery
Since when has chloroform been known? What is it and what was it used for before? Let's try to figure it out.
The first mention of this substance dates back to 1831. It was then that trichloromethane was obtained by chemist Guthrie from Harbor. However, his goal was not this substance at all; it was a successful by-product. The chemist was looking for solvents for rubber, experimented and accidentally obtained chloroform.
In the same year and a year later, two more scientists independently obtained this substance as a result of experiments. These are Eustace Liebig (who made a huge contribution to the development of chemistry) and Eugen Suberein. Their task was to find an anesthetic, and they found it. True, they learned about this effect of chloroform and began to use it a little later, only in the 1840s.
The structural formula and interaction of atoms inside the molecule was studied and constructed by the chemist Dumas in 1834. He proposed and assigned the name to chloroform, which he gave in honor of ants. In Latin, ant is pronounced formiata, and the contents of these insects are capable of being formed from chloroform. Based on this, its name was determined.
Biological effect on humans
Chloroform fully justifies its use as an anesthetic. The effect on humans is very specific, covering several major organ systems.
The degree of impact depends on factors such as:
- concentration of inhaled substance;
- duration of use;
- way to get inside.
If we are talking about pure, medical chloroform, then its use is strictly dosed, precise and local. Therefore, of the possible contraindications, only some are implemented. If we are talking about evaporated chloroform in the air and inhalation by a person, then the effect here is much more serious and destructive.
So, when inhaling trichloromethane for 10 minutes, swelling of the respiratory tract, pulmonary spasms, cough, and sore throat may occur. If exposure is not stopped, poisoning will occur immediately. The nervous system (both the brain and the spinal cord) will be affected, resulting in death.
Chloroform also has a detrimental effect on the liver, digestive organs and kidneys. Its effect is especially destructive if the solution is taken orally. The following reactions of the body to taking chloroform are observed:
- dizziness;
- vomiting and nausea;
- persistent headaches;
- depression of the nervous system and, as a result, fatigue;
- elevated temperature;
- allergic rashes, redness of the skin.

Studies and experiments on different animals showed the following results:
- Long-term ingestion of chloroform orally in the form of liquid causes abortion, multiple pathologies and mutagenesis of future generations.
- When living in an atmosphere of chloroform, animals were depressed, lethargic, and their life expectancy was significantly reduced.
- Based on experiments on mice, it was concluded that trichloromethane is carcinogenic.
Such results were obtained by chemist and medical scientists when studying the effects of chloroform on living organisms.
Application in medicine
The first mention of the use of this substance for medical purposes dates back to 1847. It was then that the scientist, doctor, and chemist Holmes Coote first proposed the use of chloroform as an anesthesia. This had a positive effect on the person during the operation - complete loss of consciousness, absence of any sensations.
However, later, when the patient regained consciousness, it turned out that his nausea and vomiting did not stop. Later, more precise standards for the use of this substance were established to avoid such consequences.
The English obstetrician James Simpson played a very important role in the introduction of chloroform into medicine. It was he who proved the positive significance and effect of the compound during the birth process.
However, over time, newer, safer and more modern methods of anesthesia than chloroform have emerged. Its use in medicine has practically disappeared. Today it is used in the form:
- ointment component for external use;
- as an additional anesthetic in combination with other substances and only in very small concentrations;
- as drops to relieve nausea and vomiting.
Industrial Applications
Chloroform is also used in industry. Its use relates to various chemical syntheses, where it plays the role of a solvent, degreaser, main or additional component for the production of important substances used in all spheres of human activity.
Chloroform is an organic chemical compound whose formula is shown below. Under normal conditions, it is a colorless liquid with a sweet taste and ethereal odor. It is almost insoluble in water and does not burn.

This is a chlorinated derivative of methane, which is obtained by heating bleach with ethyl alcohol. This reaction consists of 3 parts:

You will need to assemble the device as shown in the figure below. The thermometer must be inserted into the test tube of the Wurtz flask; it must reach the bottom of the flask. Pour bleach (63.5 g) into a 0.5 liter Wurtz flask and fill it with water (250 ml). You will receive a semi-liquid mixture, to which you should add ethyl alcohol (14.5 ml). After that, close the flask with a stopper with a thermometer, and heat it on the grid, after connecting it to the refrigerator. An exothermic reaction must begin, although at first the reaction occurs without external energy supply, the temperature is constant, and the chloroform in the form of a liquid is distilled with water into the cylinder. The layer of chloroform will be under the layer of water in the cylinder. Using a separating funnel, you can separate the chloroform from the water. You should get about 20 ml of the substance.

How to obtain chloroform from ethyl alcohol
Take 430 g of bleach (with a CaO2Cl2 content of about 23.4%), mix with one and a half liters of water, adding 100 g of caustic lime and 100 ml. 88.5% alcohol. The resulting mixture is distilled. Milk of lime and calcium chloride are added to the distillate, then the separated chloroform is separated. Mix chloroform with sulfuric acid and carry out restification.
How to make chloroform from acetone
You should take 275 g of bleach and dilute it with 800 ml. water, slowly adding a mixture of 70 ml. water and 22 g of acetone.
Making chloroform from sodium and potassium hypochlorites
In this method, you electrolyze an aqueous solution of potassium chloride and alcohol (you can use acetone or aldehyde instead of alcohol). This method gives pretty good results in terms of the amount of substance released.
Electrochemical method
Platinum plates are used for the cathode and anode (the cathode should be in porous clay).
Composition of the cathode liquid: hydrochloric acid (1.19) – 30 ml.
Composition of the anode liquid: 80 g of crystalline Ba(OH)2∙8H2O, which dissolves in 300 ml. water at 50 C; 1 g. BaСl2∙2H2O.
30 ml is added to the anode liquid. alcohol A current of 2 A and a voltage of 8 V are required, with a consumed current of 6.3 Ah. The temperature is raised from 50 to 70 degrees, gradually adding alcohol. The required current density is 4 A per 100 cm2 and 10 A per 100 cm2 at the anode and cathode, respectively. The cathode liquid should also be changed. The resulting chloroform is isolated along with excess alcohol.
Chloroform on prescription. In the 19th century, the substance, along with cocaine and heroin, was considered a medicine. Chloroform solution Kimball White Pine was sold in pharmacies as a cough and bronchitis mixture. Doctors prescribed the compound for asthmatics.
Chloroform was also recommended as an anesthetic. In the 21st century, the substance is prohibited for internal use. What changed? Apparently properties of chloroform and its effect on humans has been clarified and these clarifications are clearly not in favor of the famous mixture.
Properties of chloroform
Trichloromethane - scientific name chloroform. Formula substances – CHCL 3. It's liquid. It has no color, but it tastes sweet. The sweetness is accompanied by a burning sensation, and the smell of the composition is pungent. Chloroform pharmacy 19th century offered in combination with organic solvents. The substance does not mix with water.
By the beginning of the 20th century, doctors recorded hundreds of cases of cardiac and respiratory arrest. All the deceased took medications that contained chloroform. Where Doctors immediately assumed a connection between the substance and the deaths of patients. But the harmful effects of the drug were proven only in the 1960s. Trichloromethane was banned in 1967.
Chloroform vapor causes sleep, loss of motor activity and sensitivity. Life processes slow down. There is a loss of strength. Therefore, trichloromethane has long been a pain reliever during operations and a popular anesthesia.
After undergoing surgery, patients sometimes developed cirrhosis of the liver and heart rhythm disturbances. They were a consequence of the toxicity of the drug. For weakened organisms it was often disastrous. So anesthesia was removed from the list of medications.
Chloroform effect on humans has a three-stage effect. After inhalation, a stage of incomplete consciousness begins. Then, there is excitement. Anesthesia is only the 3rd stage. It paralyzes connections in the spinal cord and brain.
That is, complete anesthesia occurs. The strength of the drug depends on its storage. The substance must be isolated from oxygen. Trichloromethane interacts with it and slowly decomposes.
A 1% addition of ethyl alcohol can slow down the decomposition process of chloroform. Without “protection,” trichloromethane decomposes into hydrogen chloride, formic acid and phosgene. Chloroform - soporific means.

But, if a reaction occurs with potassium hydroxide, the mixture will put you to sleep forever. The result of the interaction is the well-known potassium cyanide. A more harmless compound is trichloromethane with concentrated alkalis. Carbon monoxide is formed.
Some reactions require elevated temperatures. For chloroform, this is considered to be 50-60 degrees. At 62 Celsius, the substance boils, giving water almost 40 degrees. The density of trichloromethane, on the contrary, is greater than that of water - 1,483 grams per cubic centimeter. The viscous liquid looks like ether.
Preparation of chloroform
Buy chloroform problematic. But, the substance can be obtained in the laboratory. There are 3 ways. The first is multi-stage. The basis is methane. It needs to be chlorinated. The reaction is only possible under ultraviolet light and at high temperatures.
But it’s possible to get not only chloroform. Action the reaction is also aimed at the formation of carbon tetrachloride, dichloromethane and chloromethane. The first is used as a solvent in the production of freons, that is, refrigerants. Dichloromethane dissolves paints and is used to remove them. Chloride is needed to synthesize silicones.
The first method of producing chloroform has 4 stages. First, hydrogen chloride is released paired with chloromethane. The second stage is the formation of the same hydrogen chloride and dichloromethane. Chloroform is extracted at the 3rd stage. The second product of the reaction is hydrogen chloride. It is also released at the last stage, when tetrachloromethane is synthesized.
Chloroform - anesthesia, which was previously obtained by combining ethyl alcohol and bleaching lime. The reaction is one-step and most suitable for laboratory implementation. Under simplified conditions, the electrolysis method can also be used. An atmosphere of ethyl alcohol is required.

Sometimes it is replaced with acetone. The main characters of the reaction are alkali metal chlorides. It is through them that electric current is passed, decomposing into components, among which there are chloroform.
Put to sleep human, even in the old days, was allowed only with pure chloroform. But, after all 3 methods of obtaining it, the substance remains contaminated. Among the impurities: - phosgene, hydrogen chloride, ethyl alcohol and chlorine. Ethanol is removed by repeatedly washing the trichloromethane with water. Then comes the treatment with calcium chloride. It draws out the remaining water.
If the impurities include not only ethyl alcohol, it is necessary to wash the chloroform first with a strong acid, then with the same alkali, and only then with water. Calcium chloride appears again in the finale. When its mission is completed, trichloromethane is sent for distillation. It is carried out in a fractional column.
Uses of chloroform
While chloroform is no longer relevant in medicine, it continues to be used in industry. The substance is necessary for dozens of chemical syntheses. In them, trichloromethane plays the role of a solvent. Chloroform can also degrease. In reactions it acts as a main or auxiliary component.
Chloroform price also interested in those who want to purchase a solution for household purposes. The substance can replace turpentine. It is kept at home and in garages as a solvent. Using trichloromethane, you get rid of stains from drying oil, fats, adhesives and resins.
Chloroform continues to be used in morgues. Here the substance slows down the decomposition processes of bodies. Living creatures receive trichloromethane only in some veterinary clinics. The purpose is the same as that previously applied to people - anesthesia. In rare cases, it is administered to pigs and dogs.

Rumors about the role of chloroform in criminal cases do not stop. Remember scenes from films, fragments from detective stories, where criminals put victims to sleep by holding a handkerchief soaked in trichloromethane to their nose?
While the person is unconscious, the attackers rob, look for secret documents, and kill. In the 20th century, such cases appeared not only in films and literature.
But after the ban on chloroform, getting it became problematic. Now crimes committed with a toxic substance are rare. However, investigators say that this also happens.
As a rule, chloroform is used by those who have official access to it, the same mortuary workers, or students of medical institutes undergoing internship there.
Under normal conditions, this substance is a colorless volatile liquid with a pronounced ethereal odor and sweet taste. Chloroform in pharmaceuticals is an emulsion that is intended for topical use and is available in a dark glass bottle.
The use of Chloroform is now not as widespread as before, when the drug was widely used in medical practice for general anesthesia. Due to its harmful effects on the human body, Chloroform was abandoned in favor of other, safer drugs.
It is worth noting that a way to use Chloroform safely has yet been found. To do this, the drug is supplied with a large amount of oxygen, and, at the same time, the exact dosage is maintained. But, nevertheless, it is used extremely rarely for pain relief during surgical interventions.
pharmachologic effect
- The action of Chloroform as an anesthetic is associated with a decrease in the phase transition temperature of membrane lipids, which, in turn, increases the fluidity of nerve cell membranes.
- The soporific effect of Chloroform on humans is based on the ability of the substance to strongly depress the central nervous system, as a result of which the ability to act volitionally is lost, consciousness is depressed, and there is no reaction to external stimuli
- Chloroform anesthesia is characterized by illusions, delusions, anxiety, unmotivated, uncoordinated movements. In some people, the reaction is clinical-tonic seizures
- The substance is very toxic, it depresses the cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory systems, and destroys the liver. According to statistics, every tenth inhabitant of the planet is allergic to this drug
- If the drug is applied locally, its mechanism of action is based on irritation of receptor nerve endings and other elements of the tissue system
- Once on the skin, Chloroform begins to evaporate, causing a person to feel cold. Following this, the patient will feel a burning sensation and note redness of the skin. If there is protection from evaporation, severe inflammation will occur on the skin with the formation of blisters
- In case of contact with mucous membranes, the effect of Chloroform will be more pronounced and the irritation will be much stronger.
- If Chloroform enters the human body orally, the result will be bloody vomiting, diarrhea, and severe damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
- The vapors of the substance do not have such a pronounced irritating effect, but, one way or another, they are toxic and can disrupt the functioning of some organs and systems in the human body (myocardial dystrophy, severe cardiac dysfunction, cirrhosis and liver atrophy)
- Chloroform anesthesia has four stages - analgesia, excitement, surgical stage, awakening.
- At the first stage, when the patient is in a state of lethargy or drowsiness, but at the same time conscious, diagnostic tests or simple surgical operations are performed. At the stage of analgesia, superficial sensitivity to pain is lost, but, at the same time, susceptibility to thermal effects remains, the person feels touch
- At the second stage, medical manipulations cannot be carried out, since the patient is no longer conscious, but motor and speech activity is still preserved (the person may try to get up from the table, tear off his mask, scream). At this stage, the anesthesiologist continues to saturate the body with Chloroform to achieve a deeper state.
- The third stage is characterized by immersion in deep anesthesia; it is at this stage that the main surgical operations are performed. The third stage is reached due to the influence of the substance on the reflex centers that are located in the medulla oblongata. Due to this, the patient loses muscle tone, his reflex function decreases and there is no sensitivity to external stimuli
- The use of the drug at present (we have already mentioned this) is quite safe. Precise dosing of the substance, combined with a large amount of oxygen, allows you to immediately move on to the third stage, bypassing the excitation stage. In addition, this makes the substance less toxic
Indications
- The main indication for the use of the drug is situations when the patient needs to be put under general anesthesia (for surgical interventions)
- In combination with methyl alcohol of salicylic acid and turpentine, it is used as a local remedy with an irritating effect. Used for neuralgia and myositis (inflammation of skeletal muscles)
- Chloroform water in combination with valerian root tincture is used to treat abdominal pain, flatulence, hiccups, and as an antiemetic
Contraindications
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Kidney and liver failure
- Asthenic syndrome
- Skin purulent-inflammatory diseases - for external use
Side effects
- If the drug is used to induce anesthesia by inhalation, a weakening of cardiac activity (up to cardiac arrest), a drop in blood pressure, and collapse are possible.
- If vapors get on the mucous membrane, severe irritation may begin, which is characterized by redness, burning, strong mucus discharge, lacrimation and salivation, severe coughing attacks, nausea, vomiting
- When used externally, there is a risk of serious irritation or even inflammation of the skin.
Important! If you frequently inhale vapors of a substance, addiction may develop - substance abuse.
Instructions for use
- To induce anesthesia, a mixture of oxygen and chloroform is supplied at a concentration of 3-4 vol.%. To maintain the surgical stage, 1-1.5 vol.% is required
- Only chloroform water is used orally, where the substance content is 0.5%. It is recommended to take a tablespoon 3-4 times a day
- When used for external use, the medicine is applied to the desired area and rubbed very gently
Overdose
Even a low concentration of the substance can cause severe poisoning with liver damage. At the same time, all side effects worsen. Particularly dangerous is depression of the respiratory center and serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart (disturbances in rhythm, frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, up to cardiac arrest).
In case of overdose, the patient is first connected to a ventilator and hyperventilated.
To cleanse the blood, hemodialysis is performed.
For chloroform poisoning, hydrocortisone injections are indicated at a concentration of 1 ml per kg of body weight.
Symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Important! During the recovery period after chloroform poisoning, drinking alcohol and fatty foods is contraindicated.
I created this project to tell you in simple language about anesthesia and anesthesia. If you received an answer to your question and the site was useful to you, I will be glad to receive support; it will help further develop the project and compensate for the costs of its maintenance.
- Isolating the contour of a liquid drop in the problem of determining surface tension Isolating the contour of a drop
- Method for producing calcium peroxide
- Feo color. Chemical properties. Refractory black pyrophoric powder, insoluble in water. Methods for obtaining iron
- Sodium thiosulfate Natrii thiosulfas (ln) Thiosulfate chemical formula
- Rhodanide method for determining iron
- Baking soda: formula, application
- Carbonates. Baking soda formula. Baking soda: formula, application Safety of baking soda for humans
- Description of the disease, signs, treatment
- Liver diseases: causes, types, symptoms and prevention What is a virus in the liver
- Helminthic infestation: causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
- Folk remedies
- Food fermentation and its importance
- Study of pharmacokinetics and bioavailability - journal of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics High performance liquid chromatography
- Test work chloroform Chloroform at home
- Noble gases and their properties Noble gases what causes the inertness of these gases
- Raman and NIR spectroscopy Problems of NIR spectrometry and how to solve them
- Side specialties of tantalum
- What is tantalum and where is it used?
- Molecular effects of enzyme action
- Cervical dysplasia: first signs, symptoms and treatment